The Adaptronic engine management system offers significant tuning capabilities but can sometimes trigger Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) in vehicles equipped with OBDII systems. This article addresses common DTCs encountered when using an Adaptronic ECU, specifically focusing on USDM RX-8s with Select ECUs manufactured before April 2012. While future Adaptronic iterations may resolve some of these issues, understanding these codes and their solutions remains crucial for achieving optimal performance and passing OBDII readiness tests.
Understanding Adaptronic’s Default DTC Reset Behavior
By default, the Adaptronic is programmed to reset DTCs immediately upon activation. This feature is beneficial for vehicles without stringent emissions requirements. However, it can pose challenges for vehicles subject to OBDII readiness tests, especially in regions with mandatory emissions inspections. These tests often rely on accumulated diagnostic data, and immediate DTC resets can hinder accurate assessment. To circumvent this, configuring the Secondary Serial “In” Port to a setting other than “ELM327” prevents automatic DTC resets, allowing for proper diagnosis.
Common Adaptronic OBDII DTCs and Solutions
Several DTCs are commonly associated with Adaptronic ECUs in RX-8s:
P0661 (SSV Solenoid Valve Control Circuit Low ON 2): This code arises from wiring discrepancies between the Adaptronic Select and the factory ECU regarding the SSV and VDI systems. Although functionality remains unaffected, the code persists. Solutions include masking the code with an AccessPORT (AP) or bypassing the Adaptronic for SSV and VDI control by directly connecting the 1L and 1W leads to the factory ECU.
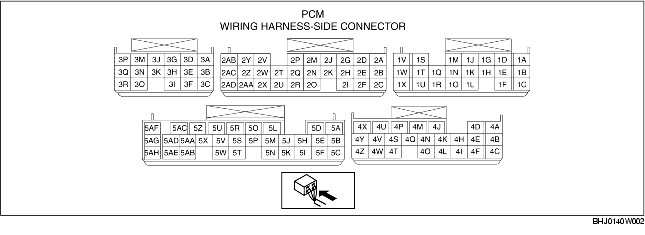 RX-8 Wiring Diagram
RX-8 Wiring Diagram
P2401 (EVAP System Leak Detection Pump Control Circuit Low): This code results from an omission in the 2004 Mazda workshop manual regarding EVAP pump to ECU pinouts (positions 4D and 4H). Adaptronic, adhering to the incomplete diagram, doesn’t facilitate communication between these components, leading to the DTC. Bridging 4D and 4H across the Adaptronic and factory ECUs effectively resolves this issue. Future Adaptronic production runs are expected to address this problem. Masking the code with an AP will not enable passing the EVAP Readiness test.
Boost-Related DTCs:
- P0172 (System Too Rich (Bank 1)): Common in forced induction setups, especially when air-fuel ratios (AFRs) enter the 11s. Masking with an AP or avoiding boost conditions are typical solutions.
- P2097 (Post Catalyst Fuel Trim System Too Rich bank1): Often indicates a missing or malfunctioning catalytic converter. An AP can mask the code, or a catalytic converter can be installed.
- P0410 (Secondary Air Injection System): Triggered by a disconnected air pump. Even when masked, the Secondary Air Pump Readiness test will fail until the air pump is reconnected.
Conclusion
Addressing these common Adaptronic Obdii DTCs is crucial for ensuring proper vehicle operation and passing emissions tests. While some solutions involve masking codes with an AccessPORT, it’s important to understand the underlying causes and implement corrective measures whenever possible. By understanding these common issues, users can optimize their Adaptronic-equipped vehicles for both performance and compliance.
