Experiencing OBDII trouble codes with your vehicle can be frustrating. If you’ve recently encountered the P054 code, you’re likely looking for answers. This code, often related to oxygen sensors, can seem confusing, especially when you encounter terms like “catalyst monitor sensors.” Let’s break down the P054 code, understand its meaning, and explore how it relates to your vehicle’s oxygen sensor system.
The OBDII code P054 generally indicates a problem with the Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1, Sensor 1). While the original poster in our forum mentioned codes P0054 and P2270, it’s important to note a slight discrepancy. The code mentioned, P0054, is actually related to Heated Oxygen Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2), while P2270 is indeed O2 Sensor Signal Stuck Lean Bank 1 Sensor 2. Both codes point towards issues with the oxygen sensors on Bank 1, Sensor 2, typically located downstream of the catalytic converter on many vehicles.
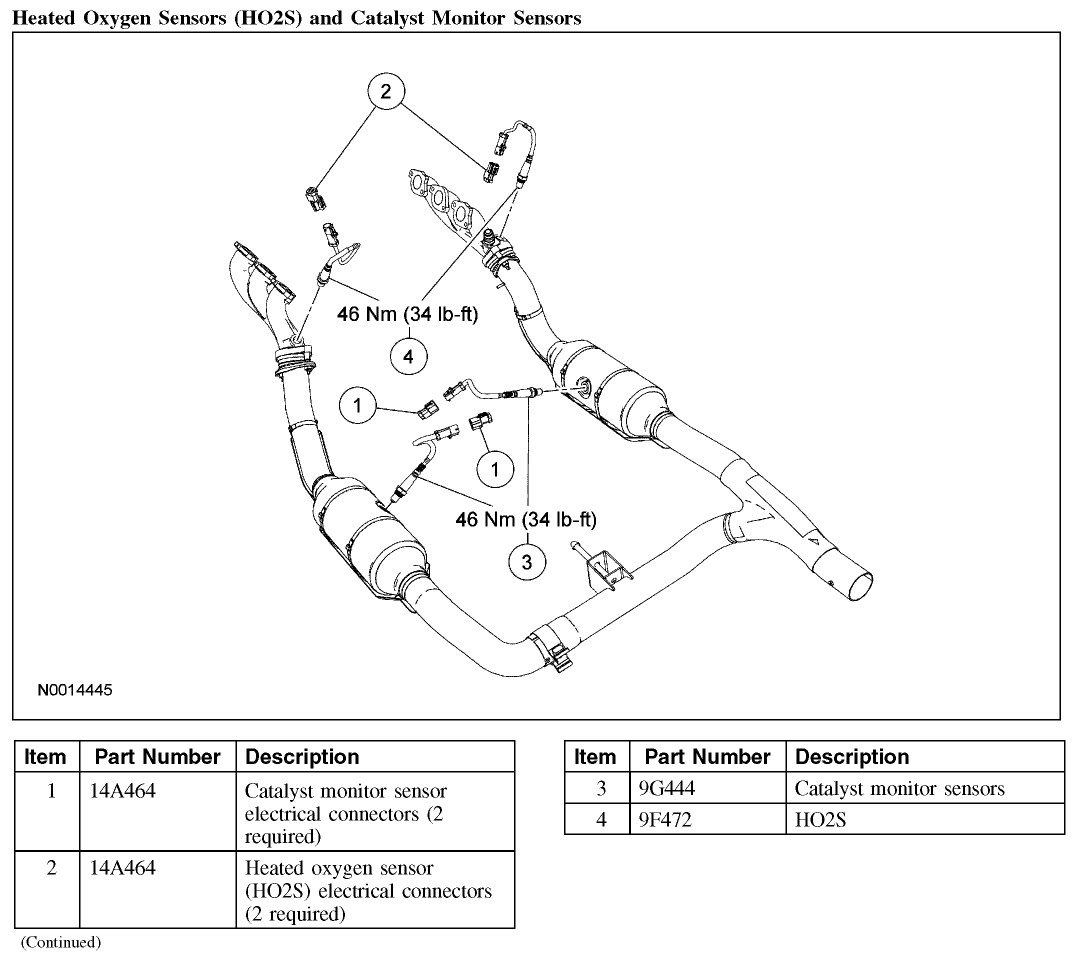
To clarify, let’s address the terminology confusion raised in the original post regarding “Catalyst monitor sensors.” In many vehicle repair manuals and diagrams, especially like those from ALLDATA, downstream oxygen sensors are sometimes referred to as “catalyst monitor sensors.” These sensors are indeed Heated Oxygen Sensors (HO2S) and their primary function is to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. They are located after the catalytic converter to measure the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases after they have passed through the converter.
In the context of a 2008 Ford F-150 XL 4.2L V6, as mentioned in the original post, Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine where cylinder number 1 is located (typically the passenger side in Ford vehicles). Sensor 2 is the downstream sensor, positioned after the catalytic converter. The confusion arises because these downstream sensors, while monitoring the catalyst, are still fundamentally Heated Oxygen Sensors.
The original poster correctly identified the potential part for their “Catalyst monitor sensor” as Motorcraft part # 4L3Z9G444AA, DY992. This part is indeed a compatible downstream oxygen sensor for many Ford vehicles, including the F-150. These sensors are designed to withstand the harsh environment of the exhaust system and provide crucial data to the engine control module (ECM) for optimal engine performance and emissions control.
Potential Causes of P054 and P2270 (Bank 1 Sensor 2):
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself may have failed due to age, contamination, or damage.
- Heater Circuit Issue: The P054 code specifically points to the heater circuit within the oxygen sensor. This circuit is essential for bringing the sensor to operating temperature quickly for accurate readings.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring to the oxygen sensor can disrupt the signal and heater circuit.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system near the oxygen sensor can affect readings and trigger codes.
- ECM/PCM Issues (Rare): In rare cases, a faulty engine control module (ECM) or powertrain control module (PCM) could be the cause.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Check the wiring and connectors to the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor for any obvious damage or corrosion.
- Sensor Testing: Use a multimeter to test the heater circuit resistance and sensor voltage. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific testing procedures and values.
- Scan Tool Data: Utilize a scan tool to monitor live oxygen sensor data. This can help identify if the sensor is responding correctly or is stuck lean (as indicated by P2270).
- Exhaust Leak Check: Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks, especially around the sensor location.
Conclusion:
OBDII codes P054 and P2270 on Bank 1 Sensor 2 of your Ford F-150, or similar vehicles, strongly suggest an issue with the downstream oxygen sensor. Understanding that “catalyst monitor sensors” are indeed downstream HO2 sensors clarifies the terminology. By systematically checking the sensor, wiring, and exhaust system, you can effectively diagnose and address the root cause of these codes, ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently and minimizes emissions. Replacing the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor is often the necessary repair to resolve these issues.