SavvyCAN, a powerful tool for analyzing CAN bus data, can be used to decode and troubleshoot OBDII codes like 271. However, users may encounter challenges when interpreting OBDII log files, particularly with multiplexed data frames. This article explores these challenges and potential solutions using a specific example of decoding Engine Speed from a standard OBDII data frame (CAN ID 0x7e8).
Understanding the OBDII Data and DBC File
Analyzing OBDII data in SavvyCAN requires a log file containing raw CAN data and a corresponding OBDII Database (DBC) file. The DBC file defines the structure of the CAN messages, including signal names, scaling factors, and multiplexing rules. In this example, we’re using a standard OBDII DBC file that utilizes extended multiplexing, a common practice for efficiently transmitting numerous parameters over the CAN bus. The sample log file contains typical OBDII responses from a vehicle.
Expected vs. Observed Behavior in SavvyCAN
Ideally, SavvyCAN should seamlessly interpret OBDII data when provided with a valid DBC file. This would allow for accurate signal decoding in both the trace view (individual message display) and the graph data view (plotting signals over time).
However, several discrepancies arise when using the provided OBDII DBC and log file:
Trace View Issues
While the DBC file validates correctly in other CAN analysis tools, SavvyCAN displays an error indicating invalid signals. Furthermore, the trace view doesn’t properly apply the multiplexing rules. Instead of displaying only the relevant signal based on the multiplexer byte, it shows all signals defined in the DBC for the given CAN ID. For instance, a frame with payload 04 41 0C 16 6C FF FF FF should be interpreted as Engine Speed (based on the 3rd byte, 0C), but SavvyCAN doesn’t isolate this signal.
Graph Data View Issues
Plotting Engine Speed in the graph data view reveals further issues. The graph incorrectly decodes all OBDII responses as Engine Speed, ignoring the multiplexing logic. This results in a nonsensical plot, as seen below. Only frames with the multiplexer byte 0C should trigger the Engine Speed decoding and plotting logic.
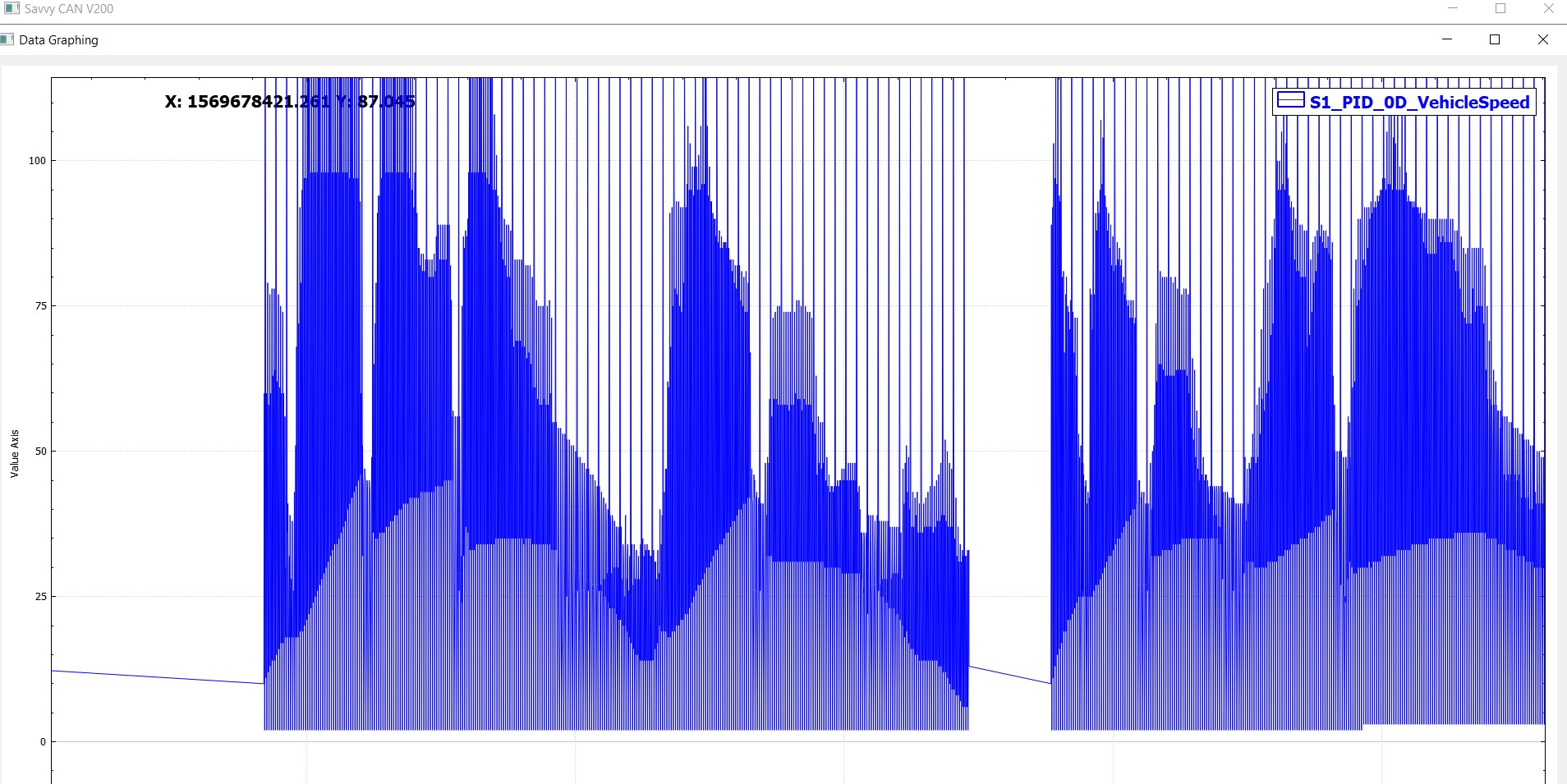 Incorrect Engine Speed Plot Due to Multiplexing Issues
Incorrect Engine Speed Plot Due to Multiplexing Issues
Addressing the Multiplexing Challenge
The core issue lies in SavvyCAN’s handling of extended multiplexing within OBDII DBC files. Resolving this would significantly enhance SavvyCAN’s utility for OBDII analysis. A potential solution involves improving SavvyCAN’s DBC parsing and signal decoding logic to correctly apply the multiplexing rules defined in the DBC. This would ensure that only the relevant signal is decoded and displayed for each OBDII response frame.
Conclusion
Accurately decoding OBDII data, particularly with complex multiplexing schemes, is crucial for vehicle diagnostics and analysis. While SavvyCAN offers a promising platform for CAN analysis, enhancing its support for OBDII extended multiplexing would significantly improve its effectiveness in this domain. This improvement would benefit a wide range of users working with OBDII data, facilitating more accurate troubleshooting and analysis of vehicle systems.
