Experiencing issues with your OBDII port and unable to connect your scan tool? Many DIY mechanics and car owners face this frustrating problem. If you’re struggling to get your OBDII scanner to communicate with your vehicle, especially for essential tasks like smog checks or diagnostics, you might be overlooking a simple yet crucial component: the OBDII fuse. This article dives into a real-world experience of troubleshooting a non-functional OBDII port and highlights the importance of checking what we’ll call the “super duty fuse” for your OBDII system.
Troubleshooting Steps for a Dead OBDII Port
When your OBDII port suddenly stops working, it can feel like a major car problem. However, often the fix is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide, starting with the easiest checks:
-
Verify Your Scan Tool: Before diving deep into your vehicle’s electrical system, ensure your scan tool is functioning correctly. Test it on another vehicle if possible, or try a different scan tool on your car. Smog shops, auto parts stores, or dealerships often have scanners you can use for testing. A faulty cable, as mentioned in the original story with a Scangauge cable, can also be the culprit.
-
Locate and Inspect the OBD Fuse (Super Duty Fuse): The most common cause for a dead OBDII port is a blown fuse. This “super duty fuse” is designed to protect the OBDII system from power surges. For many vehicles, especially Toyotas like the Tacoma mentioned in the original story, this fuse is located in the engine bay fuse box. Check your vehicle’s owner manual for the exact location and fuse number. In the case of the 2012 Toyota Tacoma, it’s fuse #7, a 7.5 amp fuse. While some online discussions mention fuse #19 (20A EFI fuse), focus primarily on the dedicated OBD or diagnostic fuse first. Visually inspect the fuse for a broken filament. Even if it looks okay, it’s a good practice to test it with a fuse tester or replace it with a new fuse of the correct amperage to rule it out.
-
Examine the Wiring: If the fuse is not the issue, the next step is to check the wiring between the OBDII port, the fuse box, and the Engine Control Unit (ECU). Look for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Perform a System Reset: Sometimes, a simple system reset can resolve communication glitches. Disconnect the negative battery terminal for about 30 seconds, then reconnect it. This can reset the vehicle’s computer systems and potentially restore OBDII port functionality.
-
Try a Powered OBDII Scanner: This is the key fix highlighted in the original story and can be a game-changer. Standard OBDII scanners rely on power from the vehicle’s OBDII port. If there’s a power delivery issue, they won’t work. However, powered OBD scanners have their own internal battery and supply their own power to communicate with the vehicle’s computer. If a powered scanner works, but a non-powered one doesn’t, it strongly indicates a power supply problem within your vehicle’s OBDII system – likely related back to that “super duty fuse” or associated wiring.
-
Consider ECU Issues (Less Likely): In rare cases, a faulty ECU could be the reason for OBDII port failure. However, this is less common, and you should exhaust all other troubleshooting steps before suspecting ECU problems.
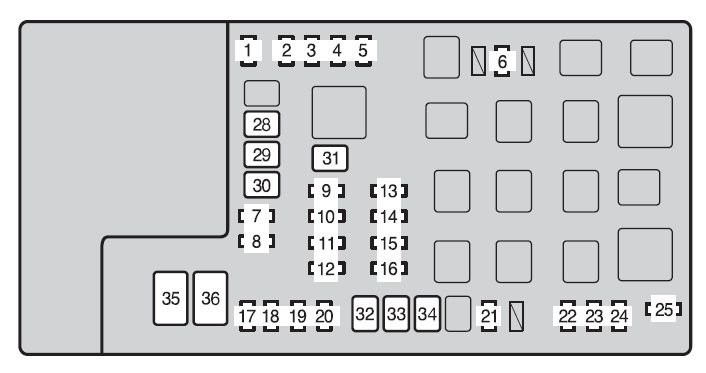 Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Toyota-tacoma-mk2-fuse-box-engine-compartment-type-a-2012.jpg
Engine bay fuse box location in a 2012 Toyota Tacoma, highlighting a typical area where the OBDII “super duty fuse” might be found. Consult your vehicle’s manual for the precise location and fuse designation.
Real-World OBDII Port Fix: The Powered Scanner Solution
The original author’s experience perfectly illustrates the powered scanner fix. After facing OBDII port issues on his 2012 Toyota Tacoma TRD Sport, and going through checks like fuses and wiring, he discovered that a standard Bluetooth OBDII dongle and even the smog check station’s equipment failed to connect.
However, at the Toyota dealership, their handheld scan tool, which was battery-powered, connected without any problems. The dealership’s technician explained that their scan tool provided its own power, bypassing any potential power issue with the truck’s OBDII port. Interestingly, even the smog check machine worked when equipped with an optional battery power port.
This story underscores a critical point: if you’ve checked the obvious – fuses and basic wiring – and your non-powered scanner still fails, a powered OBDII scanner could be the quick solution. It effectively isolates whether the issue is with your car’s power supply to the OBDII port or something else.
Conclusion: Don’t Underestimate the OBDII Fuse
While the exact reason for the initial OBDII port power failure in the original story remains somewhat unclear, the fix was definitively found with a powered scan tool. For anyone facing a non-functional OBDII port, especially when preparing for a smog test or diagnosing engine issues, remember to:
- Start with the “super duty fuse” check. It’s simple, quick, and often the solution.
- If fuses are good, consider a powered OBDII scanner. It can be an invaluable tool for diagnosing power-related OBDII port problems and potentially getting you back on the road or through your smog check without further complications.
While further investigation into the specific power pins of the OBDII port could be beneficial for a more permanent solution, utilizing a powered scanner offers an immediate and effective workaround for many OBDII communication issues.
