Obdii Serial communication is the backbone of modern vehicle diagnostics, allowing technicians and enthusiasts to access valuable data. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides the tools and expertise you need to master this essential technology. Exploring the intricacies of On-Board Diagnostics, Second Generation (OBD-II) unlocks a wealth of possibilities for vehicle maintenance and performance optimization. Discover the power of automotive diagnostics, diagnostic scan tools, and vehicle communication protocols.
1. What is OBDII Serial Communication?
OBDII, or On-Board Diagnostics II, is a standardized system used in vehicles to monitor and control various engine and emissions-related parameters. OBDII serial communication refers to the method by which diagnostic tools communicate with the vehicle’s computer (ECU – Engine Control Unit) to retrieve data and diagnose issues. This communication happens through a standardized port, usually located under the dashboard.
1.1 The Importance of OBDII
- Emissions Control: OBDII was initially mandated to ensure vehicles meet emission standards.
- Diagnostic Capabilities: It provides a standardized way to access vehicle health information.
- Repair Efficiency: Technicians can quickly identify problems, reducing repair time and costs.
1.2 Key Components of OBDII Communication
- OBDII Port: The physical connector in the vehicle.
- Diagnostic Tool: A device used to read and interpret data from the ECU.
- Communication Protocol: The language used for data exchange between the tool and ECU.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The vehicle’s computer that manages engine and emission systems.
Alt: OBDII connector highlighting its role in vehicle self-diagnostics.
2. Understanding OBDII Protocols
Several communication protocols are used in OBDII systems. Each protocol has its own set of rules and specifications for data transmission. Here are the primary protocols:
2.1 SAE J1850 PWM and VPW
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Used primarily by Ford.
- Data Rate: 41.6 kbps.
- Voltage: Variable.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Used by GM.
- Data Rate: 10.4 kbps.
- Voltage: Variable.
2.2 ISO 9141-2
- Description: An older protocol used by Chrysler, European, and Asian vehicles.
- Data Rate: 10.4 kbps.
- Voltage: 12V.
- Key Feature: Uses a K-line for communication.
2.3 ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000)
- Description: An improved version of ISO 9141-2.
- Data Rate: Variable, but generally faster than ISO 9141-2.
- Voltage: 12V.
- Key Feature: Uses a K-line and can use a L-line for initialization.
2.4 CAN (Controller Area Network)
- Description: The most modern and widely used protocol. Mandated in the US for all vehicles manufactured after 2008.
- Data Rate: Up to 1 Mbps.
- Voltage: 2.5V nominal.
- Key Feature: High-speed, robust, and allows multiple ECUs to communicate.
- Standards:
- ISO 15765-4 (CAN): Standard for emissions-related data.
- SAE J2284 (CAN): Standard defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers.
2.5 Protocol Comparison Table
| Protocol | Primary Use | Data Rate | Voltage | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAE J1850 PWM | Ford | 41.6 kbps | Variable | Pulse Width Modulation |
| SAE J1850 VPW | GM | 10.4 kbps | Variable | Variable Pulse Width |
| ISO 9141-2 | Chrysler, Euro, Asia | 10.4 kbps | 12V | K-line communication |
| ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000) | Chrysler, Euro, Asia | Variable (Faster) | 12V | K-line, optional L-line |
| CAN (ISO 15765-4) | Modern Vehicles | Up to 1 Mbps | 2.5V | High-speed, robust, multi-ECU communication |

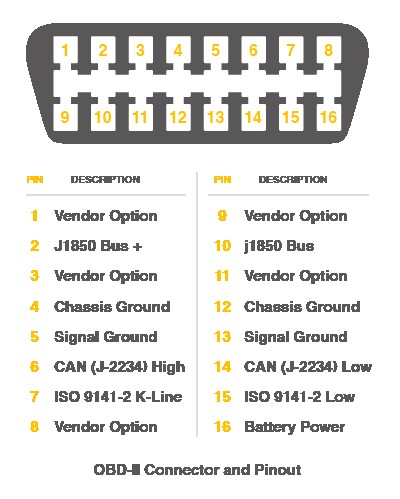
3. The OBDII Connector: Pinout and Functionality
The OBDII connector is a 16-pin diagnostic link connector (DLC). Each pin has a specific function, allowing the diagnostic tool to interface with the vehicle’s systems.
3.1 Standard OBDII Pinout
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 2 | SAE J1850 Bus+ |
| 3 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 4 | Chassis Ground |
| 5 | Signal Ground |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) |
| 7 | ISO 9141-2 K Line |
| 8 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 9 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 10 | SAE J1850 Bus- |
| 11 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 12 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 13 | Manufacturer Discretionary |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) |
| 15 | ISO 9141-2 L Line |
| 16 | Battery Voltage (12V or 24V depending on the vehicle) |
3.2 Understanding Pin Functions
- Pin 2 & 10 (SAE J1850): Used for J1850 PWM and VPW protocols.
- Pin 4 & 5 (Ground): Provide ground connections for the diagnostic tool.
- Pin 6 & 14 (CAN High & Low): Used for CAN communication.
- Pin 7 & 15 (ISO 9141-2 K & L Line): Used for ISO 9141-2 communication.
- Pin 16 (Battery Voltage): Provides power to the diagnostic tool.
Alt: Detailed OBD-II CAN Bus Pinout diagram showing each pin’s function.
4. OBDII Serial Data Parameters (PIDs)
OBDII systems use Parameter IDs (PIDs) to identify specific data points. These PIDs allow diagnostic tools to request and receive real-time data from the vehicle’s ECU.
4.1 Standard OBDII PIDs
Here are some common OBDII PIDs:
| PID | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | Supported PIDs [01-20] | – |
| 03 | Fuel System Status | – |
| 04 | Calculated Engine Load Value | % |
| 05 | Engine Coolant Temperature | °C |
| 06 | Short Term Fuel Trim – Bank 1 | % |
| 07 | Long Term Fuel Trim – Bank 1 | % |
| 08 | Short Term Fuel Trim – Bank 2 | % |
| 09 | Long Term Fuel Trim – Bank 2 | % |
| 0A | Fuel Rail Pressure | kPa |
| 0B | Intake Manifold Absolute Pressure | kPa |
| 0C | Engine RPM | rpm |
| 0D | Vehicle Speed | km/h |
| 0E | Timing Advance | degrees |
| 0F | Intake Air Temperature | °C |
| 10 | Mass Air Flow Rate | g/s |
| 11 | Throttle Position | % |
| 12 | Commanded Secondary Air Status | – |
| 13 | Oxygen Sensors Present (in 2 Banks) | – |
| 14 | Oxygen Sensor 1 Voltage | V |
| 15 | Oxygen Sensor 2 Voltage | V |
| 16 | Oxygen Sensor 3 Voltage | V |
| 17 | Oxygen Sensor 4 Voltage | V |
| 18 | Oxygen Sensor 5 Voltage | V |
| 19 | Oxygen Sensor 6 Voltage | V |
| 1A | Oxygen Sensor 7 Voltage | V |
| 1B | Oxygen Sensor 8 Voltage | V |
| 1C | Commanded EGR Duty Cycle | % |
| 1D | EGR Error | % |
| 1E | Commanded Evaporative Purge | % |
| 1F | Fuel Level Input | % |
| 20 | Supported PIDs [21-40] | – |
4.2 Interpreting PID Data
- Engine Load: Indicates the percentage of maximum available engine power being used.
- Fuel Trim: Shows how much the ECU is adjusting fuel delivery to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio.
- Engine RPM: The rotational speed of the engine’s crankshaft.
- Vehicle Speed: The current speed of the vehicle.
- Oxygen Sensor Voltage: Indicates the oxygen content in the exhaust gases.
4.3 Enhanced PIDs
Beyond the standard PIDs, manufacturers often include enhanced PIDs that provide more specific data. These PIDs are not standardized and vary between vehicle makes and models.
5. Reading and Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in the ECU that indicate a specific problem or malfunction. Reading and clearing these codes is a crucial part of OBDII diagnostics.
5.1 Types of DTCs
- P Codes (Powertrain): Related to the engine, transmission, and fuel system.
- B Codes (Body): Related to body systems like airbags, power windows, and central locking.
- C Codes (Chassis): Related to chassis systems like ABS, traction control, and suspension.
- U Codes (Network): Related to network communication between different ECUs.
5.2 DTC Structure
A DTC typically consists of five characters:
- First Character: Indicates the system (P, B, C, or U).
- Second Character: Indicates the code type (0 for standard, 1 for manufacturer-specific).
- Third Character: Indicates the subsystem (e.g., fuel system, ignition system).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific code number.
Example: P0300 – Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
5.3 Reading DTCs
Diagnostic tools can read stored DTCs from the ECU. The tool will display the code and often provide a brief description of the problem.
5.4 Clearing DTCs
After addressing the issue, DTCs can be cleared using a diagnostic tool. Clearing the codes erases the fault memory in the ECU.
Warning: Clearing DTCs without fixing the underlying problem will only temporarily remove the code. The code will reappear if the issue persists.
6. Selecting the Right OBDII Diagnostic Tool
Choosing the right OBDII diagnostic tool is essential for effective vehicle diagnostics. The market offers a wide range of tools, from basic code readers to advanced scan tools.
6.1 Types of OBDII Tools
- Basic Code Readers:
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs.
- Pros: Affordable, easy to use.
- Cons: Limited functionality, may not provide detailed data.
- Ideal For: DIY enthusiasts and basic troubleshooting.
- Mid-Range Scan Tools:
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs, view live data, perform basic tests.
- Pros: More features than basic code readers, wider vehicle coverage.
- Cons: More expensive than basic code readers.
- Ideal For: Intermediate DIYers and small repair shops.
- Advanced Scan Tools:
- Functionality: Read and clear DTCs, view live data, perform advanced tests (e.g., actuation tests, module programming), access manufacturer-specific data.
- Pros: Comprehensive functionality, wide vehicle coverage, access to advanced features.
- Cons: Expensive, requires training to use effectively.
- Ideal For: Professional technicians and large repair shops.
6.2 Key Features to Consider
- Vehicle Coverage: Ensure the tool supports the makes and models you work on.
- Protocol Support: Verify the tool supports the necessary OBDII protocols.
- Live Data: Ability to view real-time data from the ECU.
- Bi-Directional Control: Ability to send commands to the ECU to perform tests.
- Update Capability: Ability to update the tool with the latest software and vehicle coverage.
- User Interface: Intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface.
- Display: Clear and easy-to-read display.
- Durability: Rugged construction to withstand use in a shop environment.
6.3 Recommended OBDII Tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of OBDII diagnostic tools to meet your needs. Here are some recommended options:
- Entry-Level OBDII Reader:
- Features: Reads and clears DTCs, displays basic live data.
- Ideal For: Home mechanics and quick diagnostics.
- Mid-Range Professional Scan Tool:
- Features: Reads and clears DTCs, displays live data, performs actuation tests, supports multiple protocols.
- Ideal For: Professional technicians and small repair shops.
- Advanced Diagnostic Platform:
- Features: Full system diagnostics, module programming, advanced actuation tests, access to manufacturer-specific data.
- Ideal For: Experienced technicians and specialized repair facilities.
7. Practical Applications of OBDII Serial Communication
OBDII serial communication has numerous practical applications in vehicle diagnostics and repair.
7.1 Diagnosing Engine Problems
- Misfires: Identify which cylinder is misfiring using DTCs and live data (e.g., RPM fluctuations).
- Fuel System Issues: Diagnose fuel trim problems, oxygen sensor failures, and fuel injector issues using live data and DTCs.
- Emissions Problems: Identify issues with the catalytic converter, EGR system, and other emissions-related components.
7.2 Monitoring Vehicle Performance
- Real-Time Data: Monitor engine parameters like RPM, speed, and temperature to assess performance.
- Data Logging: Record data over time to analyze trends and identify intermittent problems.
- Performance Tuning: Use OBDII data to optimize engine performance and fuel efficiency.
7.3 Performing Routine Maintenance
- Service Resets: Reset service reminders and maintenance indicators.
- System Checks: Perform routine system checks to ensure proper operation.
- Component Testing: Test individual components (e.g., sensors, actuators) to verify functionality.
7.4 Enhancing Vehicle Security
- Theft Detection: Use OBDII data to detect unauthorized access to the vehicle.
- Remote Monitoring: Monitor vehicle location and usage remotely.
- Immobilization: Remotely disable the vehicle in case of theft.
8. Advanced Techniques in OBDII Serial Communication
For experienced technicians and advanced DIYers, there are several advanced techniques to explore in OBDII serial communication.
8.1 Custom PID Development
- Description: Creating custom PIDs to access data that is not available through standard PIDs.
- Application: Allows access to manufacturer-specific data and specialized parameters.
8.2 ECU Programming and Flashing
- Description: Reprogramming the ECU with updated software or custom tunes.
- Application: Improving engine performance, fixing software bugs, and enabling new features.
8.3 CAN Bus Analysis
- Description: Analyzing CAN bus traffic to diagnose network communication problems.
- Application: Identifying issues with ECU communication, sensor failures, and wiring problems.
8.4 Reverse Engineering
- Description: Disassembling and analyzing ECU software to understand its inner workings.
- Application: Developing custom PIDs, creating tuning software, and enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
9. OBDII Serial Communication and the Future of Automotive Diagnostics
OBDII serial communication is evolving with advancements in automotive technology.
9.1 OBDIII and Beyond
- OBDIII: A proposed future standard that would require vehicles to report emissions problems directly to regulatory agencies.
- Remote Diagnostics: The ability to diagnose and repair vehicles remotely using telematics data.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using OBDII data to predict when maintenance will be needed, reducing downtime and repair costs.
9.2 The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to staying at the forefront of automotive diagnostics. We offer:
- Cutting-Edge Tools: The latest OBDII diagnostic tools and equipment.
- Expert Training: Comprehensive training programs to help technicians master OBDII technology.
- Technical Support: Expert technical support to assist with diagnostic challenges.
By partnering with CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can ensure you have the tools and knowledge to succeed in the rapidly evolving world of automotive diagnostics.
10. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your OBDII Needs?
When it comes to OBDII diagnostic tools and solutions, CARDIAGTECH.NET stands out as a premier provider. Here’s why you should consider us for your automotive diagnostic needs:
10.1 Wide Range of Products
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers an extensive selection of OBDII tools, from basic code readers to advanced diagnostic platforms. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, we have the right tool for your needs.
10.2 High-Quality Products
We partner with leading manufacturers to offer high-quality, reliable OBDII tools. Our products are rigorously tested to ensure they meet the highest standards of performance and durability.
10.3 Competitive Prices
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers competitive prices on all our OBDII tools and solutions. We strive to provide the best value for your investment, without compromising on quality.
10.4 Expert Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert support and guidance. Whether you need help selecting the right tool or troubleshooting a diagnostic problem, we’re here to assist you.
10.5 Training and Resources
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers comprehensive training programs and resources to help you master OBDII technology. From online tutorials to in-person workshops, we provide the knowledge and skills you need to succeed.
10.6 Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is our top priority. We are committed to providing exceptional service and support to ensure you are completely satisfied with your purchase.
10.7 Convenient Shopping Experience
Our website, CARDIAGTECH.NET, offers a convenient and secure shopping experience. You can easily browse our products, compare features, and place your order online.
10.8 Fast Shipping
We offer fast and reliable shipping to ensure you receive your OBDII tools and equipment as quickly as possible.
10.9 Return Policy
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a hassle-free return policy. If you’re not completely satisfied with your purchase, you can return it for a full refund or exchange.
10.10 Commitment to Innovation
We are committed to staying at the forefront of automotive diagnostics. We continuously update our product offerings and training programs to reflect the latest advancements in OBDII technology.
By choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can be confident that you are getting the best OBDII tools, solutions, and support available.
Call to Action
Don’t let vehicle diagnostic challenges slow you down. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today to discover the perfect OBDII tools for your needs! Our expert team is ready to provide personalized recommendations and support. Whether you’re tackling engine issues, optimizing performance, or performing routine maintenance, we have the solutions to help you succeed.
Contact us now:
- Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (641) 206-8880
- Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET
FAQ Section
1. What is OBDII serial communication?
OBDII serial communication is the process by which diagnostic tools communicate with a vehicle’s computer (ECU) to retrieve data and diagnose issues.
2. What are the main OBDII protocols?
The main OBDII protocols are SAE J1850 PWM, SAE J1850 VPW, ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000), and CAN (ISO 15765-4).
3. Where is the OBDII port located in a vehicle?
The OBDII port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
4. What are DTCs?
DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) are codes stored in the ECU that indicate a specific problem or malfunction.
5. Can I clear DTCs myself?
Yes, you can clear DTCs using a diagnostic tool, but it’s important to address the underlying issue first.
6. What is live data in OBDII diagnostics?
Live data refers to real-time data from the ECU, allowing you to monitor engine parameters and sensor readings.
7. What is the CAN bus?
The CAN (Controller Area Network) bus is a high-speed communication network that allows multiple ECUs to communicate with each other.
8. What are PIDs?
PIDs (Parameter IDs) are codes used to identify specific data points in the OBDII system.
9. How do I choose the right OBDII diagnostic tool?
Consider factors like vehicle coverage, protocol support, live data capabilities, and budget when selecting an OBDII tool.
10. What are enhanced PIDs?
Enhanced PIDs are manufacturer-specific PIDs that provide more detailed data than standard PIDs.
Unlock the full potential of your vehicle’s diagnostics with CARDIAGTECH.NET today.
