The Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) is a critical safety feature in modern vehicles, alerting drivers to low tire pressure. When TPMS sensors are replaced or tires are rotated, an Obdii Relearn procedure is often required to reset the system. This article explores the importance of OBDII relearn, comparing it to other TPMS relearn methods and outlining its benefits.
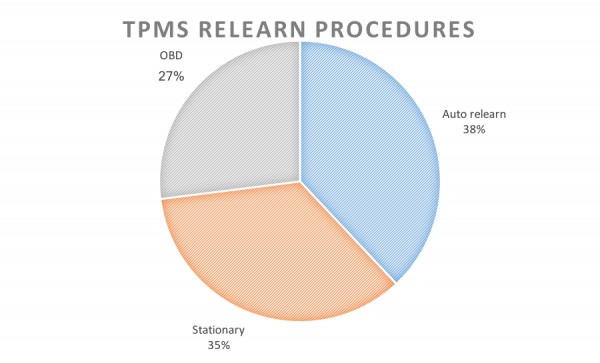
Chart showing different TPMS relearn procedures for various vehicle makes.
Understanding TPMS and the Need for Relearn
TPMS uses sensors to monitor tire pressure and transmit data to the vehicle’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU). This data triggers a warning light if pressure drops below a safe threshold. When TPMS components are serviced, the system needs to relearn the sensor IDs to function correctly. This process is called TPMS relearn. There are three primary types of relearn procedures: auto relearn, stationary relearn, and OBDII relearn.
Types of TPMS Relearn Procedures
- Auto Relearn: The vehicle automatically learns new sensor IDs after a certain period of driving. This method requires no tools but can be time-consuming.
- Stationary Relearn: This method requires a TPMS activation tool to trigger each sensor while the vehicle is in a specific learn mode. It’s faster than auto relearn but requires specialized equipment.
- OBDII Relearn: An OBDII relearn uses a TPMS scan tool connected to the vehicle’s OBDII port to directly transfer new sensor IDs to the ECU.
The Advantages of OBDII Relearn
OBDII relearn offers several advantages over other methods:
- Simplicity: The procedure is consistent across different vehicle makes and models, simplifying the process for technicians. It involves reading sensor IDs with a scan tool and then using the tool to transfer this information to the vehicle’s ECU via the OBDII port.
- Efficiency: OBDII relearn is generally faster than manual or stationary relearn procedures, saving valuable time in a shop environment.
- Accuracy: Directly transferring sensor IDs to the ECU minimizes the risk of errors and ensures accurate TPMS functionality.
Example of a TPMS scan tool connected to a vehicle’s OBDII port for an OBDII relearn procedure.
OBDII Relearn: The Industry Standard
OBDII relearn is rapidly becoming the preferred method for TPMS reset in professional automotive settings. Its efficiency, ease of use, and accuracy make it a valuable tool for technicians. Many TPMS tools, such as the VT56, offer built-in OBDII relearn procedures with step-by-step instructions.
TPMS tool displaying vehicle information after a VIN scan.
Conclusion
OBDII relearn provides a streamlined and reliable solution for resetting TPMS after service. While other relearn methods exist, OBDII relearn stands out due to its simplicity, speed, and accuracy. As vehicle technology advances, OBDII relearn is likely to become even more prevalent in the automotive industry. Investing in a quality TPMS scan tool with OBDII relearn capabilities is a wise decision for any automotive professional seeking to provide efficient and accurate TPMS service.