The Obdii Port 2007 Hhr is your car’s diagnostic gateway, understanding its function, security risks, and potential modifications are essential. CARDIAGTECH.NET equips you with the knowledge and tools to protect your vehicle and enhance its performance, offering solutions like relocation kits, bypass switches, and protective covers, explore our offerings and fortify your ride today. Secure your vehicle’s data, optimize its performance, and maintain its longevity with enhanced security measures.
1. Understanding the 2007 HHR OBDII Port
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) port is a standardized interface found in virtually all cars manufactured after 1996, including the 2007 Chevrolet HHR. It provides access to a wealth of data related to your vehicle’s engine, emissions, and overall performance. Think of it as your car’s personal health monitor, constantly tracking various parameters and reporting any abnormalities.
1.1. What is the OBDII Port?
The OBDII port, short for On-Board Diagnostics II, acts as a communication hub, allowing technicians and vehicle owners to access the data stored within the vehicle’s computer system. This data is crucial for diagnosing issues, monitoring performance, and ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently. It’s like a universal translator for your car, making it easier to understand what’s going on under the hood.
1.2. Location in the 2007 HHR
In the 2007 HHR, the OBDII port is typically located beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. Its exact position might vary slightly, but it is generally found within easy reach, often near the steering column or the center console. Being easily accessible makes it convenient for diagnostic checks and accessing vital vehicle data.
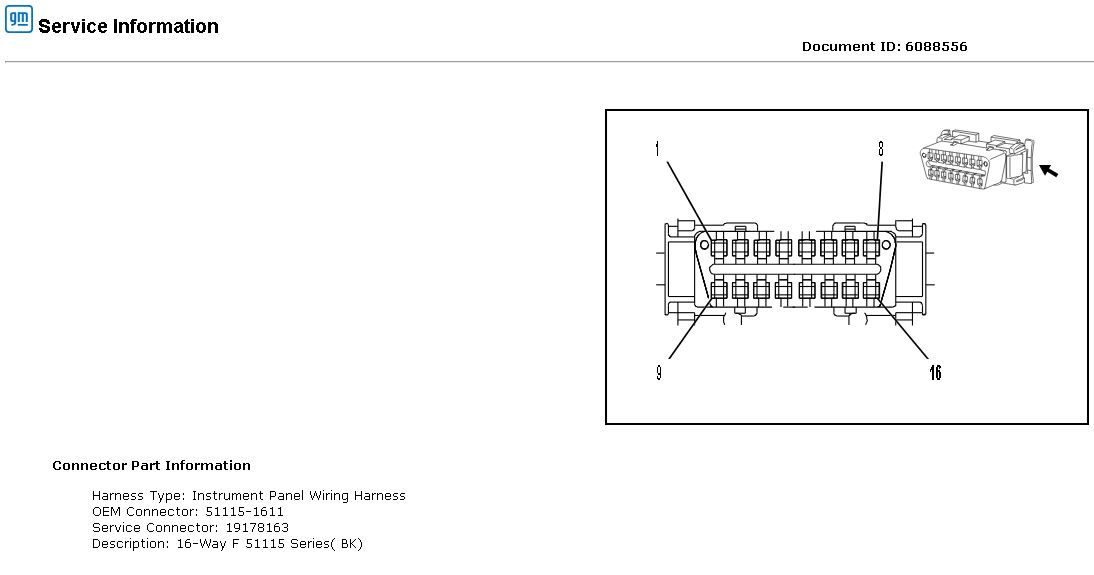
1.3. Standard Pinout and Function
The OBDII port has a standardized 16-pin layout, each pin assigned a specific function. This standardization ensures that diagnostic tools can communicate with any vehicle regardless of the manufacturer. Key pins include power, ground, CAN bus lines (for data communication), and manufacturer-specific pins. Below is a general overview, but always refer to your vehicle’s specific manual for accurate details:
| Pin Number | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | J1850 Bus Positive | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols. |
| 4 | Chassis Ground | Provides a ground connection to the vehicle’s chassis. |
| 5 | Signal Ground | Provides a signal ground for the OBDII system. |
| 6 | CAN High (J-2284) | Carries the high signal for the Controller Area Network (CAN) communication. |
| 7 | K-Line ISO 9141-2 | Used for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol, which is common in European vehicles. |
| 10 | J1850 Bus Negative | Used for SAE J1850 VPW and PWM communication protocols, providing the negative signal. |
| 14 | CAN Low (J-2284) | Carries the low signal for the Controller Area Network (CAN) communication. |
| 15 | L-Line ISO 9141-2 | Used for ISO 9141-2 communication protocol, providing the second wire for communication. |
| 16 | Battery Power | Provides direct power from the vehicle’s battery to the OBDII port, used by diagnostic tools. |
| 1, 3, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13 | Manufacturer Discretion | These pins are typically reserved for manufacturer-specific functions and can vary between vehicle makes and models. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for details on these pins. |
1.4. Common Uses
- Diagnostics: Identifying the cause of the check engine light or other warning indicators.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking parameters like engine speed, fuel consumption, and sensor readings.
- Reprogramming: Reflashing the ECU (Engine Control Unit) to improve performance or address software glitches.
- Security: Unfortunately, thieves can exploit the OBDII port to bypass security systems and steal vehicles.
2. Security Risks Associated with the OBDII Port
While the OBDII port provides valuable access for diagnostics and maintenance, it also presents a potential security vulnerability. Understanding these risks is crucial for protecting your 2007 HHR from theft and unauthorized access.
2.1. Vulnerability to Theft
Modern car thieves are increasingly sophisticated, using technology to their advantage. The OBDII port offers a convenient entry point for stealing vehicles, as it allows them to:
- Bypass the Immobilizer: Disabling the car’s immobilizer system, which prevents the engine from starting without the correct key.
- Program a New Key: Programming a blank key to start the car, even without the original key.
- Gain Unauthorized Access: Accessing and manipulating other vehicle systems, potentially disabling alarms or tracking devices.
2.2. Data Theft and Privacy Concerns
Beyond vehicle theft, the OBDII port can also be used to steal sensitive data about your driving habits and vehicle usage. This information can be used for:
- Tracking Your Location: Monitoring your movements and whereabouts.
- Aggressive Marketing: Targeting you with personalized advertisements based on your driving behavior.
- Insurance Fraud: Using your driving data to deny claims or increase premiums.
2.3. Examples of OBDII Port Exploits
Several real-world examples highlight the potential for OBDII port exploits:
- Key Programming Theft: Thieves use readily available devices to program new keys via the OBDII port, bypassing the car’s security system.
- ECU Cloning: Criminals clone the ECU, allowing them to start the car without the original key or immobilizer.
- Remote Access: Hackers can gain remote access to vehicle systems through the OBDII port, potentially controlling various functions.
3. Securing Your 2007 HHR OBDII Port: Practical Strategies
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to protect your 2007 HHR’s OBDII port and mitigate the associated security risks.
3.1. Physical Protection Methods
- OBDII Port Lock: A physical lock that covers the port, preventing unauthorized access. These locks typically require a key or combination to remove.
- OBDII Port Relocation: Moving the OBDII port to a hidden location, making it difficult for thieves to find and access.
- OBDII Port Shield: A metal shield that surrounds the port, preventing access with tools.
- Dummy Port: Replacing the original port with a non-functional dummy port can deter thieves.
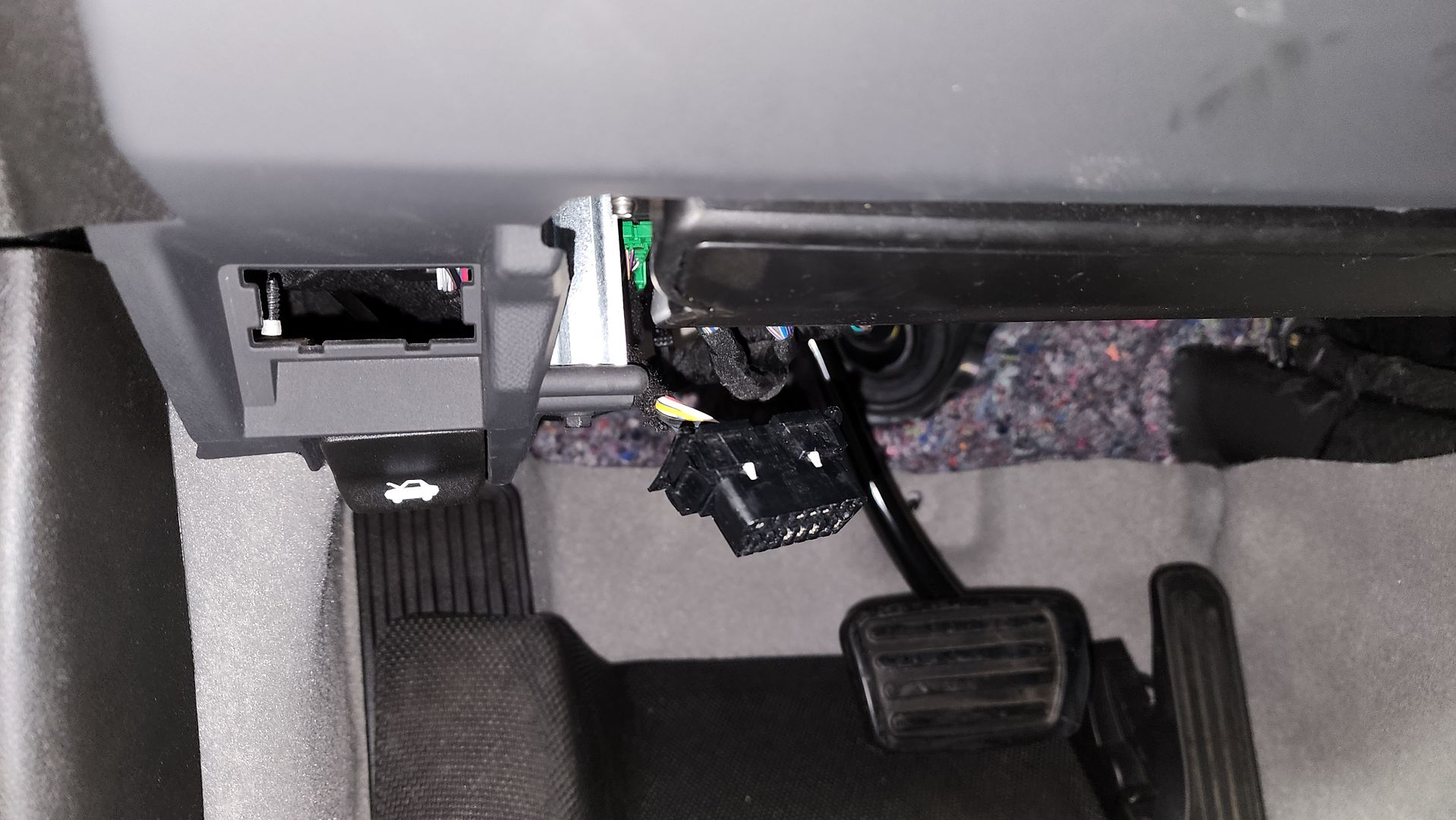 OBDII Port Relocation for Enhanced Security
OBDII Port Relocation for Enhanced Security
3.2. Electronic Security Measures
- OBDII Port Immobilizer: A device that disables the OBDII port unless a specific code or key is presented.
- OBDII Port Blocker: A device that prevents unauthorized communication with the vehicle’s computer via the OBDII port.
- Alarm System Integration: Integrating your car’s alarm system with the OBDII port, triggering the alarm if unauthorized access is detected.
3.3. Software and Programming Solutions
- ECU Reflashing: Reflashing the ECU with updated software that includes enhanced security features.
- Immobilizer Upgrades: Upgrading the car’s immobilizer system to a more secure version.
- Custom Security Protocols: Implementing custom security protocols that require specific authentication before allowing access to the OBDII port.
3.4. Best Practices for Owners
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Pay attention to suspicious activity near your car, especially in parking lots or unfamiliar areas.
- Park in Well-Lit Areas: Parking in well-lit areas can deter thieves.
- Consider a GPS Tracker: A GPS tracker can help you locate your vehicle if it is stolen.
- Regular Security Audits: Periodically check your car for any signs of tampering with the OBDII port or other security systems.
4. Modifying the OBDII Port: What You Need to Know
While modifying the OBDII port can enhance security or add functionality, it’s crucial to understand the potential implications and proceed with caution.
4.1. Hiding the OBDII Port
Hiding the OBDII port involves relocating it to a less accessible location. This can be done by:
- Extending the Wiring: Extending the OBDII port’s wiring harness and mounting the port in a hidden location, such as behind the glove box or under the seat.
- Using a Relocation Kit: Purchasing a pre-made relocation kit that includes the necessary wiring and mounting hardware.
Relocating the OBDII port makes it more difficult for thieves to access, but it’s essential to ensure the new location is still accessible for legitimate diagnostic purposes.
4.2. Installing a Bypass Switch
A bypass switch allows you to quickly disconnect the OBDII port, preventing unauthorized access. This can be achieved by:
- Interrupting the Power or Ground Wire: Installing a switch that interrupts the power or ground wire to the OBDII port.
- Using a Multi-Pole Switch: Using a multi-pole switch to disconnect multiple pins simultaneously.
When the switch is in the “off” position, the OBDII port is disabled, preventing thieves from using it to steal your car. When you need to use the port for diagnostics or other legitimate purposes, simply flip the switch to the “on” position.
4.3. Creating a Fake OBDII Port
Creating a fake OBDII port can deter thieves by giving them a false target. This involves:
- Purchasing a Dummy Port: Purchasing a non-functional OBDII port that looks identical to the real one.
- Wiring it with Basic Connections: Wiring the dummy port with basic connections like power and ground, so it appears functional to a thief’s scan tool.
The thief will waste time trying to access the fake port, potentially giving you time to react or deterring them from further attempts.
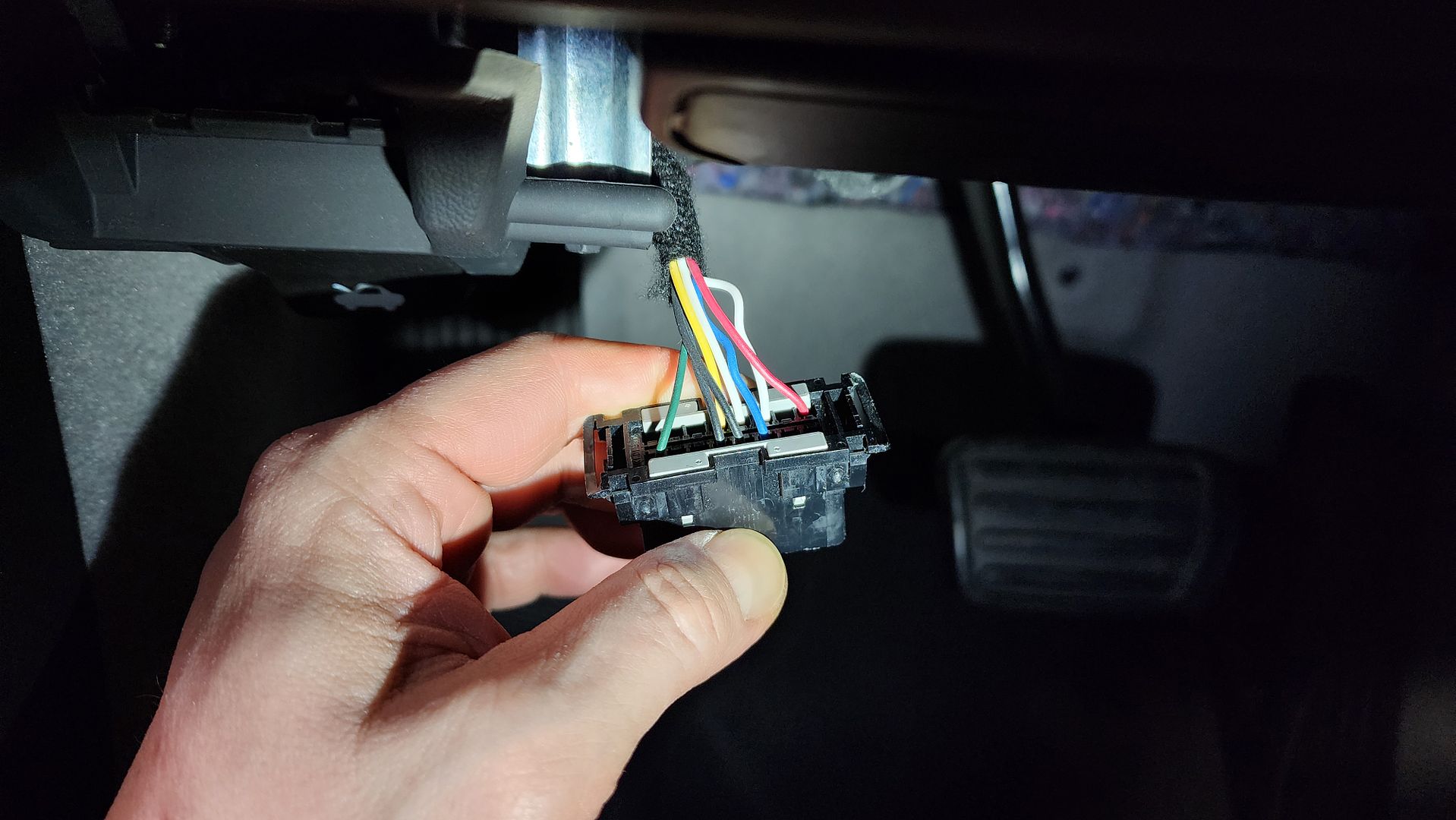 Disconnected OBDII Port Wires for Security
Disconnected OBDII Port Wires for Security
4.4. Potential Risks and Considerations
Modifying the OBDII port can introduce several risks:
- Warranty Issues: Modifying the OBDII port may void your car’s warranty.
- Electrical Problems: Improper wiring can lead to electrical problems or damage to the vehicle’s computer system.
- Diagnostic Difficulties: Hiding or disabling the OBDII port can make it difficult for technicians to diagnose and repair your car.
- Liability: If a thief is injured while attempting to access a modified OBDII port, you may be held liable.
Before modifying the OBDII port, carefully weigh the potential benefits against the risks and consult with a qualified mechanic or electrician.
5. Choosing the Right OBDII Tool for Your 2007 HHR
Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, having the right OBDII tool is essential for diagnosing and maintaining your 2007 HHR.
5.1. Basic OBDII Scanners
Basic OBDII scanners are affordable and easy to use, making them ideal for basic diagnostics. These scanners can:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Display the codes that indicate specific problems with the car’s systems.
- Clear DTCs: Erase the codes and turn off the check engine light.
- View Freeze Frame Data: Display the data that was recorded when the DTC was triggered.
Basic OBDII scanners are a great starting point for diagnosing common issues like a faulty oxygen sensor or a loose gas cap.
5.2. Advanced Scanners
Advanced scanners offer more features and capabilities than basic scanners, making them suitable for more complex diagnostics and repairs. These scanners can:
- Perform Live Data Streaming: View real-time data from various sensors and systems.
- Perform Bi-Directional Controls: Send commands to the car’s computer to test specific components.
- Perform System Tests: Run automated tests on various systems, such as the ABS or SRS.
- Access Manufacturer-Specific Codes: Read codes that are specific to your 2007 HHR.
Advanced scanners are essential for diagnosing more complex issues and performing advanced repairs.
5.3. Software and Apps
Several software and app-based OBDII solutions are available, offering a convenient and affordable way to access vehicle data. These solutions typically require a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBDII adapter that plugs into the OBDII port and communicates with your smartphone or tablet.
Software and app-based solutions can:
- Read and Clear DTCs: Similar to basic scanners, these solutions can read and clear diagnostic trouble codes.
- View Live Data: Display real-time data from various sensors.
- Perform Basic Diagnostics: Offer basic diagnostic capabilities.
- Provide Fuel Efficiency Information: Track your fuel consumption and provide tips for improving fuel economy.
Software and app-based solutions are a great option for DIY enthusiasts and car owners who want to monitor their vehicle’s performance.
5.4. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Tool
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool is compatible with your 2007 HHR.
- Features: Choose a tool that offers the features you need for your diagnostic and repair needs.
- Ease of Use: Select a tool that is easy to use and understand.
- Price: Consider your budget and choose a tool that offers the best value for your money.
- Updates: Check if the tool receives regular software updates to ensure compatibility with the latest vehicles and systems.
6. DIY Diagnostics and Repairs Using the OBDII Port
With the right tools and knowledge, you can perform many diagnostic and repair tasks on your 2007 HHR using the OBDII port.
6.1. Reading and Interpreting DTCs
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes that indicate specific problems with your car’s systems. When the check engine light comes on, it means the car’s computer has detected a problem and stored a DTC.
To read DTCs, you’ll need an OBDII scanner or a software/app-based solution. Once you’ve connected the tool to the OBDII port, follow the instructions to read the DTCs.
DTCs are typically five-character codes, with each character representing a specific piece of information:
- First Character: Indicates the system the code relates to (e.g., P for Powertrain, B for Body, C for Chassis, U for Network).
- Second Character: Indicates whether the code is generic (0) or manufacturer-specific (1).
- Third Character: Indicates the specific subsystem the code relates to (e.g., Fuel System, Ignition System, Emissions System).
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Indicate the specific fault within the subsystem.
Once you’ve read the DTC, you can use online resources or a repair manual to interpret the code and identify the problem.
6.2. Clearing DTCs
Once you’ve repaired the problem that triggered the DTC, you’ll need to clear the code to turn off the check engine light. To clear DTCs, use your OBDII scanner or software/app-based solution and follow the instructions to clear the codes.
Keep in mind that clearing DTCs will not fix the underlying problem. If the problem persists, the check engine light will come back on and the DTC will reappear.
6.3. Monitoring Live Data
Monitoring live data allows you to see real-time information from various sensors and systems. This can be helpful for diagnosing intermittent problems or monitoring the performance of specific components.
To monitor live data, use your advanced OBDII scanner or software/app-based solution and select the parameters you want to monitor. You can then view the data in real-time, either in a graphical or numerical format.
6.4. Common DIY Repairs
Many common repairs can be performed using the OBDII port and basic tools:
- Replacing a Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause poor fuel economy and emissions problems.
- Replacing a Loose Gas Cap: A loose gas cap can trigger the check engine light.
- Replacing a Faulty Mass Airflow Sensor: A faulty mass airflow sensor can cause poor engine performance.
- Resetting the Check Engine Light After a Repair: After performing a repair, you may need to reset the check engine light using an OBDII scanner.
7. Advanced OBDII Functions and Customization
Beyond basic diagnostics and repairs, the OBDII port can be used for more advanced functions and customization.
7.1. ECU Tuning and Reflashing
ECU tuning and reflashing involve modifying the software that controls your car’s engine. This can be done to:
- Improve Performance: Increase horsepower and torque.
- Improve Fuel Economy: Optimize fuel consumption.
- Adjust Shift Points: Modify the automatic transmission’s shift points.
- Disable Specific Features: Disable features like the EGR or catalytic converter.
ECU tuning and reflashing should only be performed by experienced professionals, as improper modifications can damage the engine or other vehicle systems.
7.2. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording data from various sensors and systems over time. This data can then be analyzed to:
- Identify Performance Issues: Detect subtle performance problems that may not trigger a DTC.
- Optimize Engine Performance: Fine-tune engine parameters for optimal performance.
- Track Vehicle Usage: Monitor vehicle usage and identify potential problems.
Data logging requires an advanced OBDII scanner or software/app-based solution with data logging capabilities.
7.3. Custom Gauges and Displays
The OBDII port can be used to display real-time vehicle data on custom gauges and displays. This can be done by:
- Using an OBDII Gauge: Purchasing a dedicated OBDII gauge that plugs into the OBDII port and displays selected parameters.
- Using a Smartphone or Tablet: Using a software/app-based solution and a smartphone or tablet to display custom gauges.
Custom gauges and displays can provide valuable information about your vehicle’s performance and can be customized to display the parameters that are most important to you.
8. OBDII Port and Emissions Testing
The OBDII port plays a crucial role in emissions testing, as it allows technicians to quickly and easily check the car’s emissions systems.
8.1. How OBDII is Used in Emissions Testing
During an emissions test, a technician will connect an OBDII scanner to the OBDII port and check for DTCs related to emissions systems. If any DTCs are present, the car will fail the emissions test.
The technician will also check the car’s “readiness monitors.” Readiness monitors are internal tests that the car’s computer performs to verify that the emissions systems are functioning properly. If the readiness monitors are not complete, the car may fail the emissions test, even if no DTCs are present.
8.2. Common Emissions-Related DTCs
Several DTCs are commonly associated with emissions problems:
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction
- P0401: Insufficient EGR Flow
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 2)
If your car has any of these DTCs, you’ll need to repair the problem before it can pass the emissions test.
8.3. Tips for Passing Emissions Tests
- Maintain Your Car: Regularly maintain your car to prevent emissions problems.
- Address DTCs Promptly: Address any DTCs related to emissions systems promptly.
- Ensure Readiness Monitors are Complete: Make sure the readiness monitors are complete before taking your car for an emissions test.
- Use a Fuel Additive: Consider using a fuel additive designed to clean fuel injectors and improve emissions.
9. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Modifying the OBDII port or accessing vehicle data raises several legal and ethical considerations.
9.1. Laws Regarding OBDII Port Access
Several laws regulate access to vehicle data and the OBDII port:
- The Driver Privacy Act of 2015: This law protects the privacy of vehicle owners by limiting the collection and use of their driving data.
- State Laws: Many states have laws that regulate access to vehicle data and the OBDII port.
It’s essential to be aware of these laws and regulations before modifying the OBDII port or accessing vehicle data.
9.2. Ethical Hacking and Security Research
Ethical hacking and security research play a crucial role in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in vehicle systems. However, it’s essential to conduct such research responsibly and ethically.
- Obtain Permission: Always obtain permission from the vehicle owner before accessing or modifying their vehicle’s systems.
- Disclose Vulnerabilities: Disclose any vulnerabilities you find to the manufacturer so they can be addressed.
- Avoid Causing Harm: Avoid causing harm to the vehicle or its occupants.
9.3. Privacy and Data Security
Protecting the privacy and security of vehicle data is paramount. When accessing or modifying vehicle data, be sure to:
- Use Secure Tools: Use secure OBDII scanners and software to prevent unauthorized access.
- Protect Your Data: Protect your data from unauthorized access by using strong passwords and encryption.
- Be Transparent: Be transparent with vehicle owners about how you are using their data.
10. Future Trends in OBDII Technology
OBDII technology is constantly evolving, with new features and capabilities being introduced regularly.
10.1. OBDIII and Beyond
OBDIII is a proposed standard that would require vehicles to automatically report emissions problems to regulatory agencies. This would allow for more efficient enforcement of emissions regulations and could potentially lead to remote diagnostics and repairs.
Beyond OBDIII, future OBD systems are likely to incorporate more advanced features, such as:
- Over-the-Air Updates: The ability to update vehicle software and firmware over the air.
- Predictive Maintenance: The ability to predict potential maintenance issues before they occur.
- Enhanced Security: More robust security features to protect against unauthorized access.
10.2. Integration with Smart Devices
OBDII technology is increasingly being integrated with smart devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. This allows for:
- Remote Monitoring: The ability to remotely monitor vehicle performance and diagnostics.
- Customizable Dashboards: The ability to create custom dashboards that display real-time vehicle data.
- Connected Car Services: Access to connected car services, such as remote start, door lock control, and vehicle location tracking.
10.3. Cybersecurity Advancements
As vehicles become more connected, cybersecurity becomes increasingly important. Future OBD systems are likely to incorporate more advanced security features, such as:
- Intrusion Detection Systems: Systems that can detect and prevent unauthorized access to vehicle systems.
- Firewalls: Firewalls that protect the vehicle’s network from external threats.
- Encryption: Encryption to protect sensitive data from being intercepted.
Is your 2007 HHR showing a check engine light? Worried about vehicle theft? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET or stop by our location at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States for expert advice and the best OBDII security solutions. Let us help you protect your investment and ensure peak performance!
FAQ: OBDII Port 2007 HHR
- Where is the OBDII port located in my 2007 HHR?
- The OBDII port is generally located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column.
- Can someone steal my car through the OBDII port?
- Yes, thieves can exploit the OBDII port to bypass security systems, program new keys, or disable the immobilizer.
- What is an OBDII port lock, and how does it work?
- An OBDII port lock is a physical barrier that covers the port, preventing unauthorized access. It usually requires a key or combination to remove.
- What is the purpose of relocating the OBDII port?
- Relocating the OBDII port to a hidden location makes it harder for thieves to find and access, adding an extra layer of security.
- How can a bypass switch protect my OBDII port?
- A bypass switch allows you to quickly disconnect the OBDII port, preventing unauthorized access while still allowing you to enable it for diagnostics.
- What is ECU tuning, and what are its benefits?
- ECU tuning involves modifying the software that controls your car’s engine to improve performance, fuel economy, or adjust shift points.
- What is data logging, and why is it useful?
- Data logging records data from various sensors over time, helping identify performance issues, optimize engine performance, and track vehicle usage.
- How is the OBDII port used in emissions testing?
- During emissions tests, technicians use the OBDII port to check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to emissions systems and to verify the readiness monitors.
- What are readiness monitors, and why are they important?
- Readiness monitors are internal tests that the car’s computer performs to verify that emissions systems function properly. They must be complete for the car to pass emissions tests.
- Are there any laws regarding OBDII port access?
- Yes, laws like the Driver Privacy Act of 2015 and various state laws regulate access to vehicle data and the OBDII port, ensuring privacy and security.

