OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system that allows external devices to access diagnostic information from a vehicle’s computer. This information is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining vehicles. A key component of this system is the use of Parameter IDs (PIDs), which specify the type of data requested. This article focuses on OBDII PID 00, a fundamental PID that unlocks a wealth of information about a vehicle’s diagnostic capabilities.
OBDII diagnostic service/mode 01, defined in SAE J1979 / ISO 15031-5 standards, enables access to current emission-related data from a vehicle’s engine. This data includes analog and digital inputs/outputs, and system status information. The request for this data utilizes a PID, which tells the vehicle’s system what specific information is needed.
Decoding OBDII PID 00
PID 00 is a bit-encoded PID that acts as a gateway to understanding which other PIDs are supported by each Electronic Control Unit (ECU) in the vehicle. Essentially, it provides a roadmap of the available diagnostic data. This PID is essential because it allows diagnostic tools conforming to ISO 15031-4 to determine which communication protocol the vehicle uses and which specific data points can be accessed.
All emissions-related ECUs must support both service 01 and PID 00. This combination acts as a universal initialization or “ping” message for these ECUs, confirming communication and readiness.
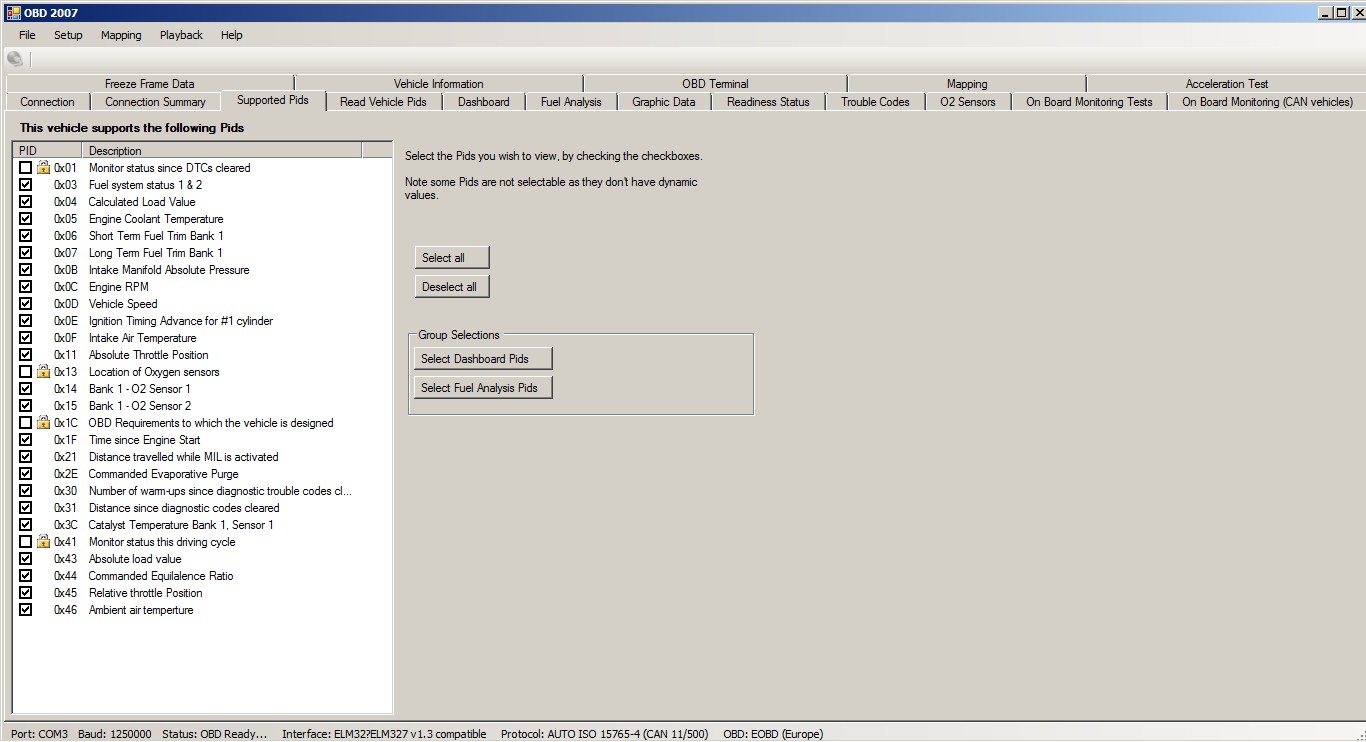 Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data – supported PIDs
Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data – supported PIDs
How PID 00 Works: A diagnostic tool sends a request for PID 00 (0100). The vehicle responds with four data bytes (4100XXXX), where XXXX represents the bit-encoded information about supported PIDs. Each bit, from most significant to least significant, corresponds to a specific PID. A “1” indicates the PID is supported, while a “0” indicates it is not.
Example: A response of 4100BE1FA813 indicates support for PIDs 01, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 0C, 0D, 0E, 0F, 10, 11, 13, 15, 1C, 1F, and 20.
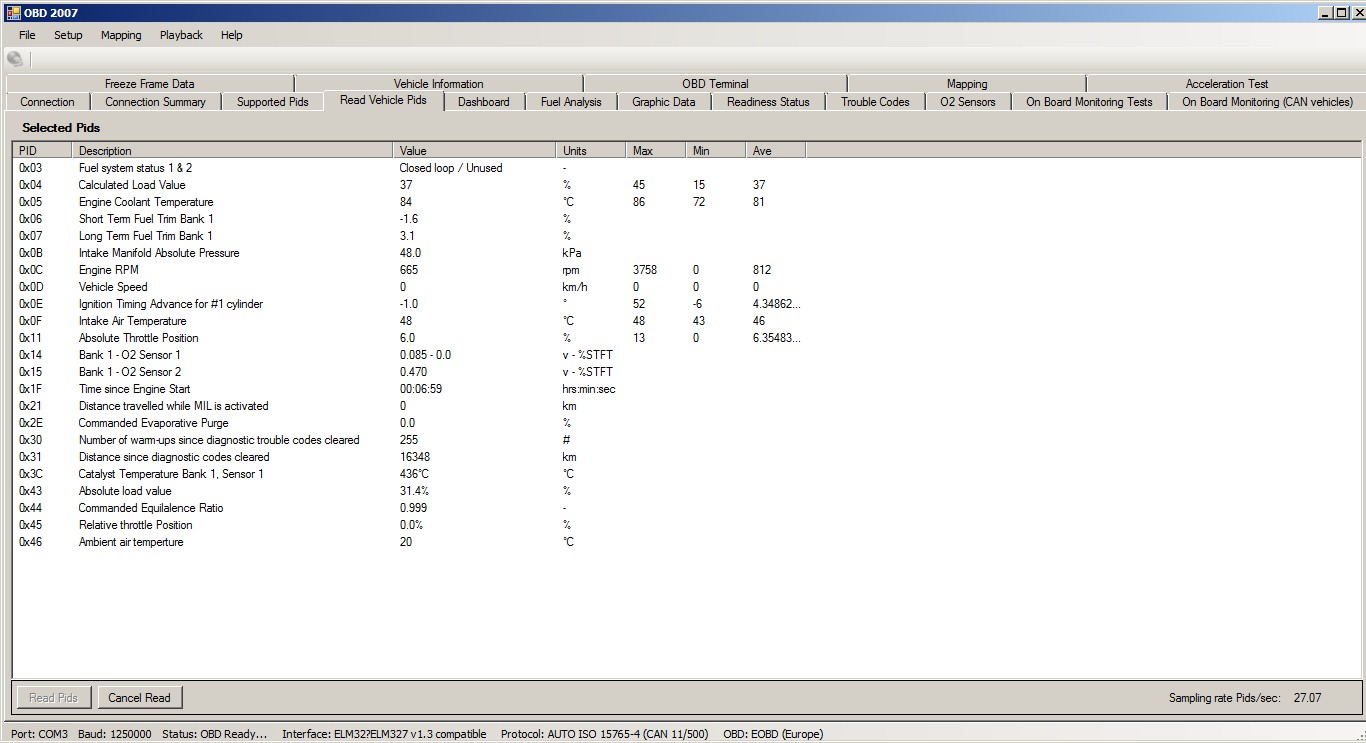 OBD diagnostic service (mode) 01 – Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data
OBD diagnostic service (mode) 01 – Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data
Beyond PID 00: Accessing Extended PID Support
PID 00 only covers PIDs 01-20. To discover support for higher-numbered PIDs, similar requests are made using:
- PID 20: Supported PIDs from 21 to 40
- PID 40: Supported PIDs from 41 to 60
- PID 60: Supported PIDs from 61 to 80
- PID 80: Supported PIDs from 81 to A0
- PID A0: Supported PIDs from A1 to C0
Practical Application of OBDII PID 00
Understanding which PIDs are supported is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics. By querying PID 00 first, diagnostic tools can tailor subsequent requests, ensuring they only target available data points. This streamlines the diagnostic process and prevents unnecessary communication overhead. For instance, a technician can determine if the vehicle supports PIDs for monitoring engine coolant temperature (PID 05), engine speed (PID 0C), or throttle position (PID 11).
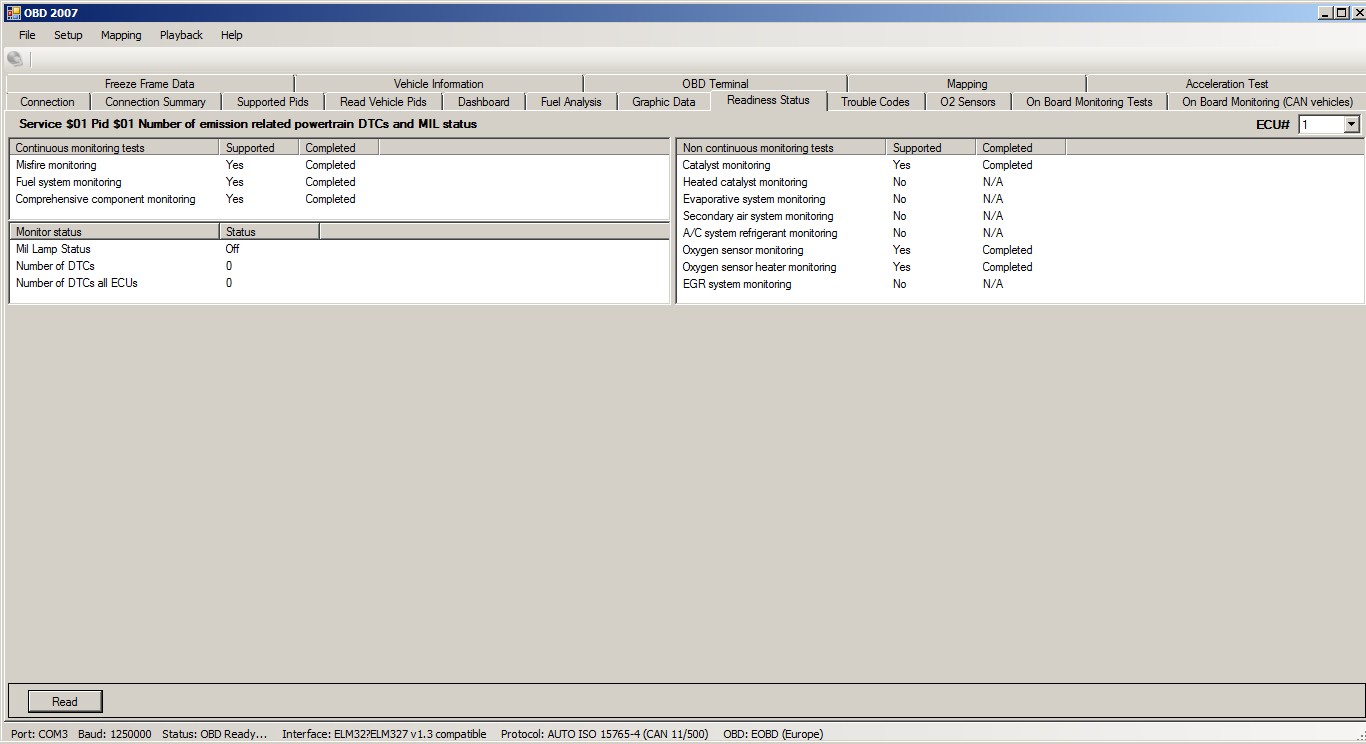 Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data – PID 01
Request Current Powertrain Diagnostic Data – PID 01
Conclusion: PID 00 – The Foundation of OBDII Diagnostics
OBDII PID 00 is more than just a simple request; it’s the foundation upon which effective vehicle diagnostics are built. By providing a clear picture of supported PIDs, it empowers technicians and diagnostic tools to efficiently access the wealth of information available through the OBDII system, enabling faster and more accurate troubleshooting. Knowing how to utilize PID 00 is essential for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics.
