Encountering OBDII codes can be perplexing, especially when you’re trying to understand what they mean and how to address them. In the realm of automotive diagnostics, code P0038, specifically “O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)”, points towards a potential issue within your vehicle’s emission control system. This article delves into the specifics of the P0038 code, helping you understand its implications, potential causes, and steps for diagnosis.
The P0038 code is related to the oxygen (O2) sensor located downstream of the catalytic converter, often referred to as Sensor 2 in Bank 1. “Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number one. This downstream sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the efficiency of the catalytic converter by measuring the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases after they have passed through the converter.
The O2 sensor itself needs to reach a certain operating temperature to function accurately. To achieve this quickly, especially during cold starts, it incorporates a heater circuit. The P0038 code indicates that the engine control unit (ECU) has detected an abnormally high voltage in the heater circuit of this downstream O2 sensor.
Several factors can trigger the P0038 code:
- Faulty O2 Sensor: The most common culprit is a malfunctioning downstream O2 sensor. The heater element within the sensor might have failed or is drawing excessive voltage.
- Wiring Issues: Problems in the wiring harness connecting to the O2 sensor can lead to a P0038 code. This includes:
- Short circuit to voltage: A wire in the heater circuit might be shorting to a voltage source, causing excessive voltage.
- Damaged wiring: Wires can be corroded, frayed, or broken, leading to electrical issues.
- Connector problems: Loose or corroded connectors can disrupt the circuit.
- ECU Malfunction: In rare cases, a fault within the ECU itself could incorrectly trigger the P0038 code.
When the P0038 code is present, you might experience the following:
- Check Engine Light (CEL): While not always the case, the CEL may illuminate on your dashboard. However, as seen in some instances, the code can be present without a visible CEL.
- Emissions Test Failure: Due to the potential impact on the catalytic converter monitoring, your vehicle might fail an emissions test.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: In some cases, issues with the O2 sensor system can slightly affect fuel economy.
Diagnosing the P0038 code requires a systematic approach. Here are steps you can take:
-
OBDII Code Scan: Use an OBDII scanner to confirm the presence of the P0038 code and check for any other related codes. Note down all codes present.
-
Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the downstream O2 sensor, its wiring, and connectors. Look for any signs of damage, such as:
- Melted or burnt wires
- Corrosion on connectors
- Physical damage to the sensor itself
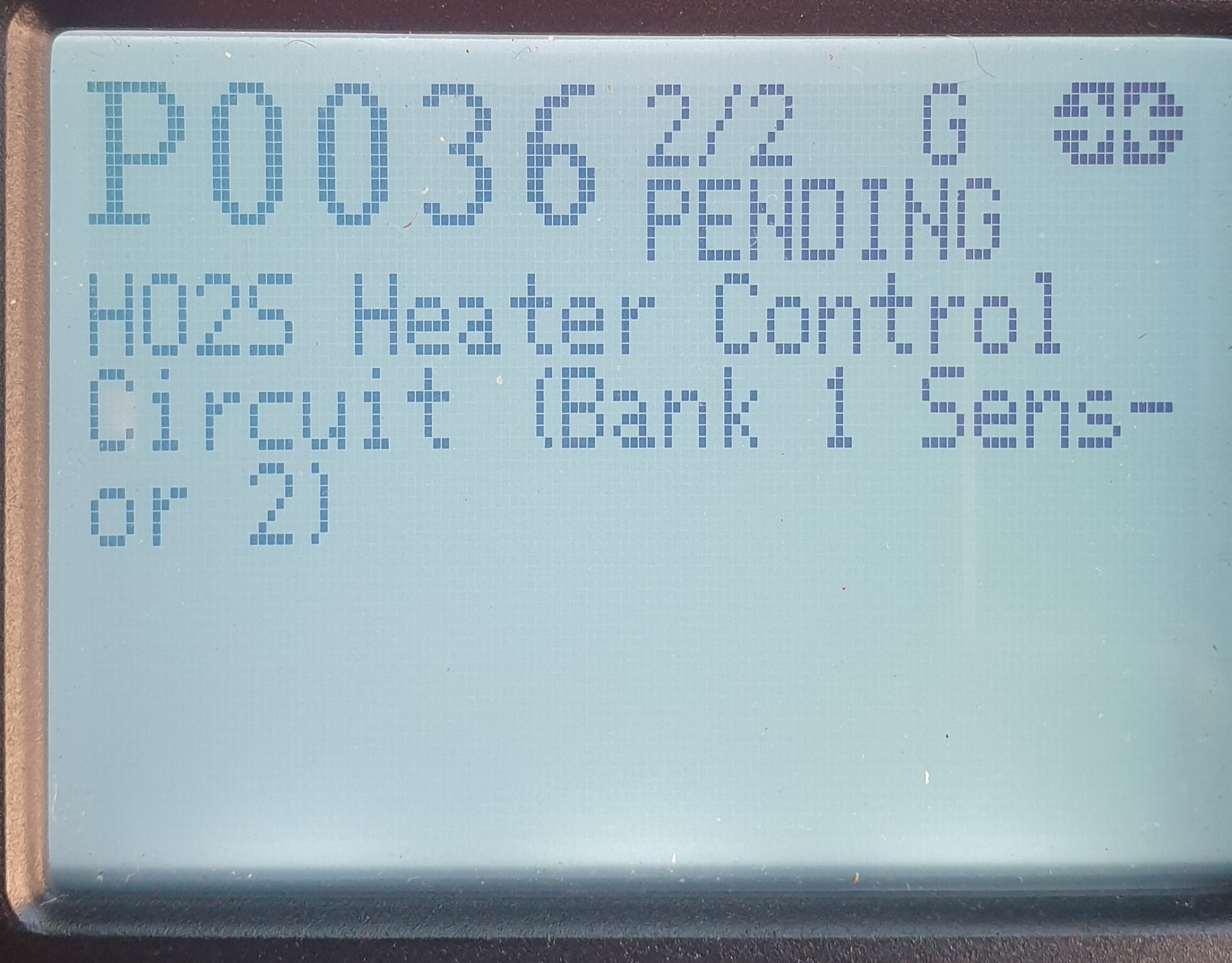 P0036.jpg
P0036.jpg -
Check Heater Circuit Resistance: Disconnect the O2 sensor and use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the heater circuit within the sensor. You’ll need to identify the correct pins for the heater circuit – typically, wiring diagrams for your specific vehicle model are essential here. A reading of infinite resistance (open circuit) or significantly different from the manufacturer’s specification indicates a faulty heater element.
 parts list.JPG
parts list.JPG -
Voltage and Ground Checks: With the sensor disconnected and the ignition ON, use a multimeter to check for voltage at the heater circuit connector in the vehicle’s wiring harness. You should typically see battery voltage. Also, check for a good ground connection on the other heater circuit wire. Consult your vehicle’s wiring diagram for the correct pins to test.
Close-up view of an O2 sensor location, relevant when diagnosing OBDII P0038.
-
Wiring Diagram and Pinout: Access the wiring diagram specific to your vehicle model and engine. This will provide crucial information about wire colors and pin assignments for the O2 sensor connector, which is essential for accurate testing, especially when dealing with non-standard wire colors.
 z20240313_185835.jpg
z20240313_185835.jpg
If your diagnosis points to a faulty O2 sensor, replacement is usually necessary. Ensure you use the correct replacement part for your vehicle make and model. If wiring issues are found, carefully repair or replace the damaged sections. After completing repairs, clear the P0038 code with your OBDII scanner and monitor if it returns.
While a faulty O2 sensor heater circuit might not always trigger a CEL immediately or drastically affect drivability, it’s important to address it to ensure your vehicle’s emission system functions correctly and to avoid potential issues with emissions testing and fuel efficiency in the long run. If you are unsure about any step in the diagnosis or repair process, consulting a qualified automotive technician is always recommended.

