When your OBDII scanner fails to detect ignition, it can be a frustrating roadblock in diagnosing vehicle issues. This communication failure prevents you from accessing crucial diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data, hindering your ability to pinpoint problems. For automotive professionals and enthusiasts alike, understanding why this happens and how to troubleshoot it is essential.
Several factors can lead to an OBDII scanner’s inability to detect ignition. These range from simple issues like a faulty connection to more complex problems within the vehicle’s electrical or computer systems. Let’s explore the common causes and systematic steps to resolve this diagnostic challenge.
Potential Causes of OBDII Not Detecting Ignition
Before assuming a major malfunction, it’s crucial to rule out the simpler, more common causes. Here’s a breakdown of potential culprits:
- Faulty OBDII Scanner or Cable: The scanner itself or the cable connecting it to the vehicle might be defective. Internal scanner malfunctions or damaged cables can disrupt communication.
- OBDII Port Issues: The OBDII port on your vehicle could be damaged, corroded, or have bent pins. This physical damage can prevent a proper connection and signal transmission.
- Ignition System Problems: While seemingly obvious, ensure the vehicle’s ignition is actually turned to the “ON” or “RUN” position. Some scanners require the ignition to be fully engaged to establish communication.
- Vehicle Battery Issues: A weak or dead battery can prevent the vehicle’s computer systems (including the ECM/PCM and OBDII port) from powering up correctly, hindering ignition detection.
- Power and Ground Issues to the OBDII Port: The OBDII port requires power and ground to function. Fuses, wiring harnesses, or ground connections related to the OBDII port might be faulty, cutting off the necessary electrical supply.
- CAN Bus Communication Problems: The Controller Area Network (CAN bus) is the communication network within your vehicle. Issues within the CAN bus system, such as wiring problems or module malfunctions, can disrupt OBDII communication.
- ECM/PCM (Engine Control Module/Powertrain Control Module) Malfunctions: In more severe cases, a malfunctioning ECM/PCM can be the root cause. If the vehicle’s computer is failing, it may not properly communicate with the OBDII scanner.
- TIPM (Totally Integrated Power Module) Issues: In vehicles like Dodge/Chrysler/Jeep, the TIPM acts as a central electrical hub. Problems within the TIPM can affect power distribution to various systems, including the OBDII port and ECM.
Diagnostic Steps to Resolve OBDII Ignition Detection Issues
A systematic approach is key to efficiently diagnosing and resolving OBDII ignition detection problems. Follow these steps:
-
Verify Scanner and Cable Functionality:
- Test your OBDII scanner on a known-good vehicle to confirm it’s working correctly.
- Inspect the OBDII cable for any visible damage, such as cuts or frayed wires. Try a different cable if available.
-
Inspect the OBDII Port:
- Visually examine the OBDII port on your vehicle for any signs of damage, corrosion, or bent pins.
- Use a flashlight to get a better view inside the port.
- If you suspect corrosion, use a contact cleaner specifically designed for electronics.
-
Check Vehicle Ignition Switch Position:
- Ensure the ignition switch is in the correct “ON” or “RUN” position as required by your OBDII scanner’s instructions.
- Try cycling the ignition switch to different positions and re-attempting scanner connection.
-
Assess Vehicle Battery Condition:
- Check the vehicle’s battery voltage using a multimeter. A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts at rest.
- If the voltage is low, try jump-starting the vehicle or charging the battery and then re-test the OBDII scanner.
-
Check OBDII Port Power and Ground:
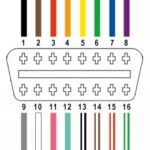
- Use a multimeter to check for power and ground at the OBDII port.
- Pin 16 should have battery voltage (12V+).
- Pins 4 and 5 should be ground.
- Refer to an OBDII port pinout diagram for your specific vehicle to confirm pin assignments.
- If power or ground is missing, check the relevant fuses and wiring diagrams for the OBDII port circuit.
-
Scan for CAN Bus Issues:
- If you have access to a more advanced scan tool, check for CAN bus communication errors.
- Look for DTCs related to CAN bus malfunction or communication loss with modules.
-
Consider ECM/PCM or TIPM Problems (If Other Steps Fail):
- If all other steps fail, and especially if you suspect other electrical issues, consider the possibility of an ECM/PCM or TIPM malfunction.
- These components are complex, and diagnosing them often requires specialized tools and expertise.
Case Study: Dodge Ram 2500 OBDII No Ignition Detection
Let’s examine a real-world scenario to illustrate the troubleshooting process. A user reported issues with their 2007.5 Dodge Ram 2500 where multiple OBDII scanners and programmers failed to detect ignition.
Initially, the vehicle presented other symptoms, including a P1222 code and limp mode, which led a dealer to replace injectors, FCA, and PRV. While those repairs addressed the original symptoms, the OBDII communication issue persisted. The user suspected an ECM problem and even tried swapping a used ECM (though from a different engine type, which is not recommended without proper programming).
Alt text: Location of the OBDII port, typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side of a vehicle.
Troubleshooting Steps Applied:
While the original user’s post didn’t detail all the systematic steps, we can infer some of the process and what could have been done:
- Scanner Verification: The user tried multiple scanners (Can/OBDII reader, Superchips Cortex, Smarty JR, Matco Interceptor), suggesting the issue was likely not scanner-specific.
- OBDII Port Inspection: No explicit mention of port inspection in the original post, but this should always be a standard first step.
- Ignition Position: Assumed to be correct, but always worth double-checking.
- Battery Condition: Not explicitly mentioned, but battery issues are common and should be ruled out.
- Power/Ground Check: This is a critical step that wasn’t detailed in the original post but is essential for diagnosing OBDII port issues.
- CAN Bus/Module Issues: The Matco Interceptor scan revealed “B1A28 – ECM mismatch with Sentry Stored Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM)” and “B104B – Floor/Defrost Mode Door Travel Range Too Large” codes, hinting at potential broader communication or module problems, although the relevance to OBDII detection is less direct for the latter.
- ECM Suspect: The user’s suspicion of the ECM was understandable given the symptoms and prior repairs.
Resolution:
In this specific case, the user ultimately replaced the TIPM (Totally Integrated Power Module) based on dealer recommendation, which resolved the OBDII detection issue. This highlights that in some cases, especially in Chrysler/Dodge/Jeep vehicles, TIPM problems can be the underlying cause of seemingly unrelated issues, including OBDII communication failures.
Alt text: A vehicle’s Totally Integrated Power Module (TIPM), a central electrical control unit that can affect OBDII port functionality.
Conclusion
When faced with an OBDII scanner not detecting ignition, a methodical diagnostic approach is crucial. Start with the simple checks – scanner functionality, port condition, and basic electrical supply. Progress to more complex investigations like CAN bus diagnostics and potential ECM/PCM or TIPM issues if necessary.
Remember to consult vehicle-specific repair information and wiring diagrams for accurate troubleshooting. In complex cases, seeking assistance from a qualified automotive technician is recommended to ensure proper diagnosis and repair. By systematically eliminating potential causes, you can effectively resolve OBDII communication problems and get back to diagnosing and repairing vehicles efficiently.