Obdii Generic Code Definitions are your gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health, offering insights into potential issues and guiding effective repairs. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we empower you with the knowledge and tools to decipher these codes, ensuring your vehicle runs smoothly and efficiently. This detailed guide will explore the world of OBDII codes, helping you become proficient in diagnosing and resolving automotive problems. Let’s explore the world of car diagnostics and the best equipment for automotive repair to make your job easier.
1. Decoding the Language of Your Car: What are OBDII Generic Code Definitions?
On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) generic code definitions serve as a universal language for your car’s computer to communicate potential problems. Think of them as diagnostic messages that pinpoint malfunctions within various vehicle systems, from the engine to the transmission. These codes are standardized across all makes and models, allowing you to quickly identify and address issues regardless of your vehicle’s brand.
 Understanding OBD2 codes means deciphering complex diagnostics
Understanding OBD2 codes means deciphering complex diagnostics
1.1 The Importance of Standardized Diagnostics
Before OBDII, each car manufacturer had its own diagnostic systems, making it difficult for mechanics to work on different makes and models. The introduction of OBDII in the mid-1990s revolutionized the automotive industry by providing a standardized system for monitoring and reporting vehicle issues. This standardization has several benefits:
- Easier Diagnostics: Mechanics can use the same tools and procedures to diagnose problems on any OBDII-compliant vehicle.
- Faster Repairs: Standardized codes allow for quicker identification of issues, reducing repair time.
- Cost Savings: With faster and more accurate diagnostics, repair costs are often lower.
- Improved Emissions Control: OBDII systems monitor emissions-related components, helping to ensure vehicles meet environmental standards.
1.2 What Systems Do OBDII Codes Cover?
OBDII codes cover a wide range of vehicle systems, including:
- Engine: Issues related to the engine’s performance, such as misfires, fuel delivery problems, and sensor malfunctions.
- Transmission: Problems with the transmission’s operation, including slipping gears, incorrect gear ratios, and solenoid issues.
- Emissions System: Malfunctions in components like the catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, and evaporative emissions control system (EVAP).
- Fuel System: Issues with fuel delivery, such as faulty fuel injectors, fuel pump problems, and fuel pressure irregularities.
- Ignition System: Problems related to the ignition system, including faulty ignition coils, spark plugs, and crankshaft position sensors.
By understanding the scope of OBDII codes, you can better grasp the overall health and performance of your vehicle.
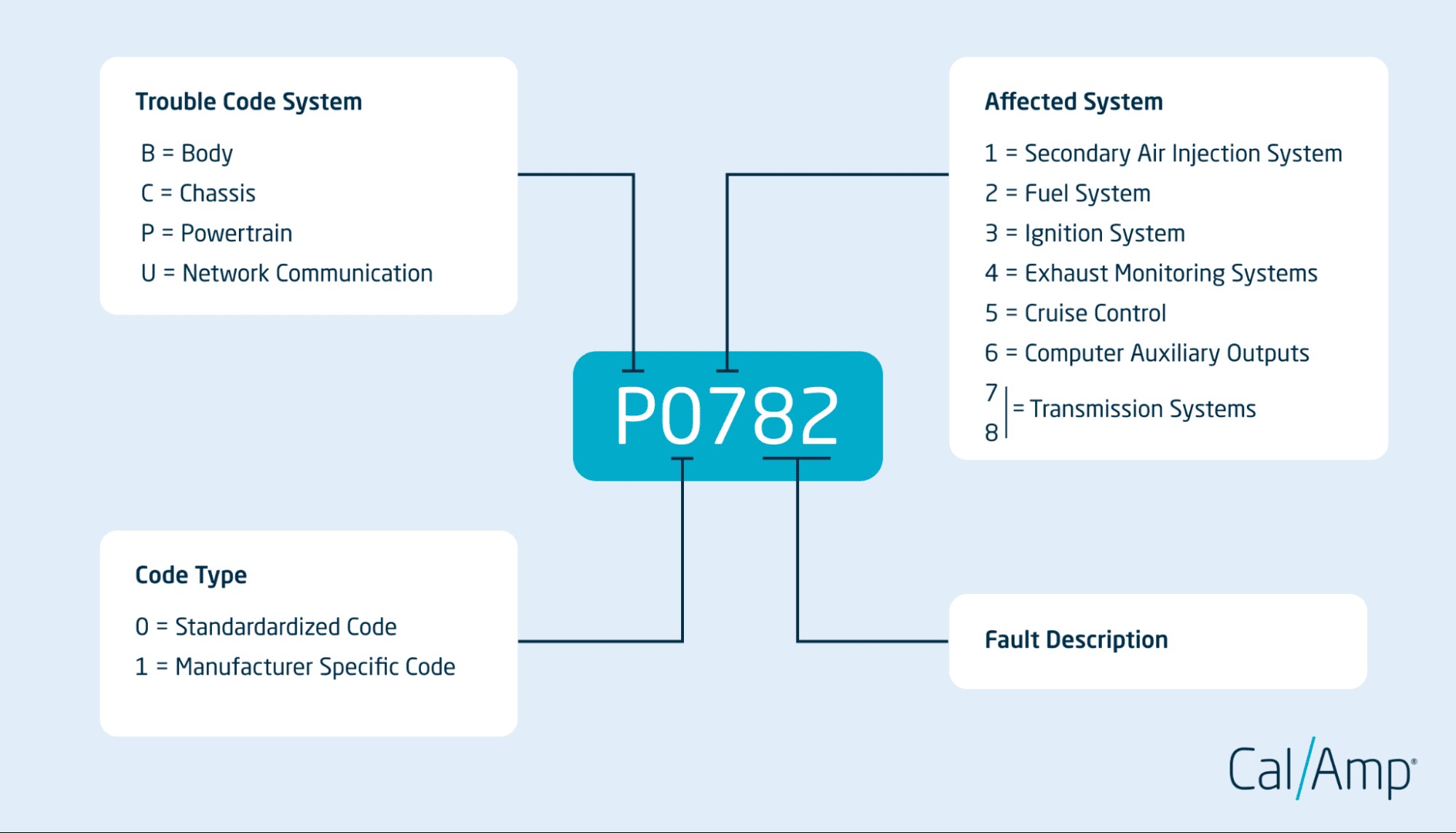
2. Decoding the Code: Understanding the Structure of OBDII Codes
OBDII codes are alphanumeric, consisting of five characters. Each character provides specific information about the issue. Let’s break down the structure of a typical OBDII code:
2.1 The First Character: Category
The first character indicates the system where the fault occurred:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, fuel system)
- B: Body (airbags, lighting, climate control)
- C: Chassis (brakes, suspension, steering)
- U: Network Communication (communication between onboard computers)
2.2 The Second Character: Code Type
The second character specifies whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE) code, common to all vehicles.
- 1: Manufacturer-specific code, unique to a particular make or model.
2.3 The Third Character: Subsystem
The third character identifies the specific subsystem involved:
- 0: Fuel and air metering and auxiliary emission controls.
- 1: Fuel and air metering.
- 2: Fuel and air metering – injector circuit.
- 3: Ignition system or misfire.
- 4: Auxiliary emission controls.
- 5: Vehicle speed control and idle control system.
- 6: Computer output system.
- 7: Transmission.
- 8: Transmission.
- 9: SAE Reserved.
- A: Hybrid Propulsion System.
- B: Hybrid Propulsion System.
- C: Hybrid Propulsion System.
2.4 The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Fault
The fourth and fifth characters provide a specific fault number within the subsystem. These numbers help pinpoint the exact component or circuit causing the issue. For example, in the code P0301, “01” indicates a misfire in cylinder 1.
2.5 Examples of Common OBDII Codes
To illustrate how these codes work, let’s look at a few common examples:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected. This code indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires across multiple cylinders, which could be due to various issues like faulty spark plugs, vacuum leaks, or a malfunctioning ignition coil.
- P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1). This code suggests that the engine is not receiving enough fuel or is receiving too much air, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture. Common causes include vacuum leaks, a faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor, or a clogged fuel filter.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1). This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently, which could be due to a worn-out converter, exhaust leaks, or faulty oxygen sensors.
- P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected. This code suggests a problem with the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, which could be due to a clogged EGR valve, vacuum leaks, or faulty sensors.
Understanding the structure and meaning of these codes empowers you to diagnose and address automotive issues more effectively.
3. Top 5 User Search Intentions for “OBDII Generic Code Definitions”
Understanding the user search intentions behind the keyword “OBDII generic code definitions” is crucial for providing relevant and valuable content. Here are the top 5 user search intentions:
3.1 Information Seeking
Users want to understand what OBDII generic code definitions are and how they work. They may be new to automotive diagnostics and looking for a basic explanation of the system. This is often the entry point for many users who encounter an OBDII code for the first time.
3.2 Code Interpretation
Users have encountered a specific OBDII code and need to understand its meaning. They are looking for accurate and reliable definitions of the code and possible causes of the problem. This is the most common search intention, as users often turn to search engines when a “Check Engine” light appears.
3.3 Troubleshooting and Repair Guidance
Users want to find out how to troubleshoot and repair the problem indicated by the OBDII code. They are looking for step-by-step guides, videos, and expert advice on fixing the issue. This intent goes beyond simply understanding the code; users want to take action.
3.4 Tool and Equipment Recommendations
Users are looking for recommendations on OBDII scanners, diagnostic tools, and other equipment needed to read and clear codes. They want to know which tools are reliable, accurate, and suitable for their needs and budget. This is a critical point where CARDIAGTECH.NET can offer valuable recommendations.
3.5 Preventative Maintenance and Best Practices
Users want to learn how to prevent OBDII codes from occurring in the first place. They are looking for tips on regular maintenance, best driving practices, and quality products that can help keep their vehicles running smoothly. This proactive approach appeals to users who want to avoid costly repairs.
4. Choosing the Right Tool: OBDII Scanners and Diagnostic Equipment
To effectively read and interpret OBDII codes, you need the right tools. OBDII scanners come in various types, each with its own features and capabilities. Here’s a guide to help you choose the right one:
4.1 Basic OBDII Scanners
These are the most affordable and straightforward options, designed primarily for reading and clearing OBDII codes. They typically display the code definition and may offer basic information about the vehicle’s status. Basic scanners are suitable for DIY enthusiasts and those who need a simple tool for quick diagnostics.
4.2 Enhanced OBDII Scanners
Enhanced scanners offer more advanced features, such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and the ability to perform some diagnostic tests. Live data streaming allows you to monitor various engine parameters in real-time, helping you identify intermittent issues. Freeze frame data captures the engine conditions when the code was triggered, providing valuable context for troubleshooting.
4.3 Professional-Grade Diagnostic Tools
These are the most comprehensive and feature-rich options, designed for professional mechanics and advanced DIYers. They offer advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes and data. Bi-directional control allows you to command the vehicle’s computer to perform specific tests, such as activating solenoids or turning on fans.
4.4 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Scanner
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Features: Determine which features are most important to you, such as live data streaming, bi-directional control, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Price: Set a budget and compare the features of different scanners within that range.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s reliability and performance.
4.5 CARDIAGTECH.NET Recommendations
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a range of high-quality OBDII scanners and diagnostic tools to meet your needs. Our top recommendations include:
- Autel MaxiCOM MK808: A versatile and affordable scanner with advanced features like bi-directional control and live data streaming.
- Launch X431 V+: A professional-grade diagnostic tool with comprehensive coverage and advanced diagnostic capabilities.
- BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool: A user-friendly Bluetooth scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet, offering a range of features and ease of use.
By choosing the right OBDII scanner, you can accurately diagnose and address automotive issues, saving time and money on repairs.
5. Step-by-Step Guide: Diagnosing and Repairing OBDII Code Issues
Once you have an OBDII scanner and a code to interpret, the next step is to diagnose and repair the issue. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
5.1 Read and Record the Code
Use your OBDII scanner to read the code and record it. Note any additional information provided by the scanner, such as freeze frame data or live data.
5.2 Research the Code Definition
Look up the code definition in a reliable database or online resource. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a comprehensive database of OBDII generic code definitions to help you understand the meaning of each code.
5.3 Gather Information
Collect as much information as possible about the issue. Ask yourself:
- What symptoms is the vehicle exhibiting?
- When did the problem start?
- Are there any other codes present?
- Has the vehicle had any recent repairs or maintenance?
5.4 Perform a Visual Inspection
Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the affected components and systems. Look for:
- Loose or damaged wires
- Cracked or leaking hoses
- Corroded connectors
- Damaged sensors or components
5.5 Perform Diagnostic Tests
Use your OBDII scanner to perform diagnostic tests on the affected components and systems. This may include:
- Testing sensors with a multimeter
- Checking fuel pressure
- Performing a compression test
- Inspecting the ignition system
5.6 Analyze the Data
Analyze the data collected from the diagnostic tests to identify the root cause of the problem. Use the code definition, symptoms, and test results to narrow down the possible causes.
5.7 Make the Repair
Once you have identified the root cause, make the necessary repair. This may involve replacing a faulty sensor, repairing a wiring harness, or cleaning a clogged component.
5.8 Clear the Code and Retest
After making the repair, clear the code with your OBDII scanner and retest the vehicle to ensure the problem is resolved. Monitor the vehicle for any recurring symptoms or codes.
5.9 When to Seek Professional Help
If you are unsure about any step in the diagnostic or repair process, or if you lack the necessary tools or expertise, it’s best to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic. CARDIAGTECH.NET can help you find a trusted mechanic in your area.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can effectively diagnose and repair OBDII code issues, saving time and money on repairs.
6. Common OBDII Codes and Their Solutions
To help you get started, let’s explore some common OBDII codes and their potential solutions:
6.1 P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- Symptoms: Rough idling, reduced power, poor fuel economy, “Check Engine” light.
- Possible Causes:
- Faulty spark plugs
- Faulty ignition coils
- Vacuum leaks
- Clogged fuel injectors
- Low fuel pressure
- Faulty crankshaft or camshaft position sensor
- Solutions:
- Replace spark plugs
- Replace ignition coils
- Repair vacuum leaks
- Clean or replace fuel injectors
- Check fuel pressure and replace fuel pump if necessary
- Replace crankshaft or camshaft position sensor
6.2 P0171: System Too Lean (Bank 1)
- Symptoms: “Check Engine” light, poor fuel economy, rough idling, hesitation upon acceleration.
- Possible Causes:
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty mass airflow (MAF) sensor
- Clogged fuel filter
- Low fuel pressure
- Faulty oxygen sensor
- Solutions:
- Repair vacuum leaks
- Replace MAF sensor
- Replace fuel filter
- Check fuel pressure and replace fuel pump if necessary
- Replace oxygen sensor
6.3 P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- Symptoms: “Check Engine” light, poor fuel economy, reduced power.
- Possible Causes:
- Worn-out catalytic converter
- Exhaust leaks
- Faulty oxygen sensors
- Engine misfires
- Solutions:
- Replace catalytic converter
- Repair exhaust leaks
- Replace oxygen sensors
- Address engine misfires
6.4 P0401: Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
- Symptoms: “Check Engine” light, rough idling, poor acceleration.
- Possible Causes:
- Clogged EGR valve
- Vacuum leaks
- Faulty EGR solenoid
- Faulty differential pressure feedback EGR (DPFE) sensor
- Solutions:
- Clean or replace EGR valve
- Repair vacuum leaks
- Replace EGR solenoid
- Replace DPFE sensor
6.5 P0101: Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Circuit Range/Performance Problem
- Symptoms: “Check Engine” light, poor fuel economy, stalling, hesitation.
- Possible Causes:
- Dirty or faulty MAF sensor
- Vacuum leaks
- Restricted air filter
- Wiring issues
- Solutions:
- Clean or replace MAF sensor
- Repair vacuum leaks
- Replace air filter
- Repair wiring issues
By understanding these common codes and their solutions, you can tackle many automotive issues with confidence.
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Your Diagnostic Journey
CARDIAGTECH.NET is your trusted partner in navigating the world of OBDII generic code definitions and automotive diagnostics. We provide a range of resources and services to help you succeed:
7.1 Comprehensive OBDII Code Database
Our website features a comprehensive database of OBDII generic code definitions, allowing you to quickly and accurately identify the meaning of any code. We regularly update our database to ensure it remains current and reliable.
7.2 Expert Advice and Guidance
Our team of experienced mechanics and automotive experts is here to provide you with expert advice and guidance. Whether you need help diagnosing a complex issue or choosing the right OBDII scanner, we’re here to assist you. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for immediate support.
7.3 High-Quality Diagnostic Tools and Equipment
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of high-quality OBDII scanners, diagnostic tools, and automotive equipment from trusted brands like Autel and Launch. We carefully select our products to ensure they meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
7.4 Step-by-Step Repair Guides and Videos
We provide step-by-step repair guides and videos to help you tackle common automotive issues. Our guides are designed to be easy to follow, even for those with limited mechanical experience.
7.5 Community Forum
Join our community forum to connect with other automotive enthusiasts, share your experiences, and get answers to your questions. Our forum is a great place to learn from others and get support from the CARDIAGTECH.NET community.
8. Tips for Preventing OBDII Codes
Preventing OBDII codes is always better than dealing with them. Here are some tips for keeping your vehicle running smoothly and avoiding unnecessary repairs:
8.1 Regular Maintenance
Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle. This includes:
- Changing the oil and filter regularly
- Replacing the air filter
- Replacing the fuel filter
- Checking and topping off fluids
- Inspecting and replacing spark plugs
- Rotating tires
- Inspecting brakes
8.2 Quality Fuel and Fluids
Use high-quality fuel and fluids that meet the manufacturer’s specifications. Avoid using low-quality or generic products, as they can damage your vehicle’s components.
8.3 Proper Driving Habits
Avoid aggressive driving habits, such as:
- Rapid acceleration and braking
- High-speed driving
- Towing heavy loads
- Ignoring warning lights
8.4 Prompt Repairs
Address any warning lights or symptoms promptly. Ignoring small problems can lead to more significant and costly repairs down the road.
8.5 Regular Inspections
Conduct regular inspections of your vehicle to identify potential problems before they become serious. This includes:
- Checking tire pressure
- Inspecting belts and hoses
- Checking fluid levels
- Looking for leaks or damage
By following these tips, you can keep your vehicle running smoothly and avoid many common OBDII codes.
9. OBDII Code Definitions: The Future of Automotive Diagnostics
OBDII code definitions are constantly evolving to keep pace with advancements in automotive technology. As vehicles become more complex, the diagnostic systems must also become more sophisticated. Here are some trends to watch for in the future of OBDII code definitions:
9.1 Increased Complexity
Future OBDII systems will likely incorporate more sensors and monitors to track a wider range of vehicle parameters. This will result in more complex and detailed OBDII codes.
9.2 Enhanced Data Analysis
Future diagnostic tools will be able to analyze OBDII data in more sophisticated ways, providing mechanics with more insights into the root causes of problems. This will lead to faster and more accurate diagnoses.
9.3 Integration with Telematics Systems
OBDII data will increasingly be integrated with telematics systems, allowing vehicle owners and fleet managers to monitor vehicle health in real-time. This will enable proactive maintenance and reduce downtime.
9.4 Remote Diagnostics
Future diagnostic tools will be able to perform remote diagnostics, allowing mechanics to troubleshoot problems without being physically present with the vehicle. This will be particularly useful for diagnosing issues in remote locations or on vehicles with complex problems.
9.5 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI will play an increasingly important role in automotive diagnostics, helping mechanics analyze OBDII data, identify patterns, and predict potential problems. This will lead to more efficient and effective repairs.
By staying up-to-date with the latest trends in OBDII code definitions, you can ensure you are prepared for the future of automotive diagnostics.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About OBDII Generic Code Definitions
To further enhance your understanding of OBDII generic code definitions, here are some frequently asked questions:
10.1 What is the difference between OBDII generic codes and manufacturer-specific codes?
OBDII generic codes are standardized codes that are common to all vehicles. Manufacturer-specific codes are unique to a particular make or model and provide more detailed information about the issue.
10.2 Can I clear OBDII codes without fixing the problem?
While you can clear OBDII codes without fixing the underlying problem, it is not recommended. The code will likely return if the issue is not addressed, and you may cause further damage to your vehicle.
10.3 How do I find the OBDII port in my vehicle?
The OBDII port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the exact location.
10.4 Can I use a smartphone app to read OBDII codes?
Yes, there are many smartphone apps available that can read OBDII codes using a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi OBDII adapter. However, be sure to choose a reputable app and adapter to ensure accurate and reliable results.
10.5 What does “Bank 1” and “Bank 2” mean in OBDII codes?
“Bank 1” refers to the side of the engine that contains cylinder number one. “Bank 2” refers to the other side of the engine, if applicable (V-shaped or horizontally opposed engines).
10.6 How often should I scan my vehicle for OBDII codes?
You should scan your vehicle for OBDII codes whenever the “Check Engine” light comes on or if you notice any unusual symptoms. Regular scanning can help you identify potential problems early and prevent more significant repairs.
10.7 Can a bad gas cap cause an OBDII code?
Yes, a loose or damaged gas cap can cause an OBDII code related to the evaporative emissions control system (EVAP).
10.8 Do I need a special tool to clear OBDII codes?
Yes, you need an OBDII scanner to clear OBDII codes. Basic scanners can clear codes, while enhanced scanners offer more advanced features.
10.9 Can OBDII codes indicate a problem with my transmission?
Yes, OBDII codes can indicate problems with your transmission, such as slipping gears, incorrect gear ratios, and solenoid issues.
10.10 Where can I find a reliable list of OBDII generic code definitions?
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides a comprehensive and reliable database of OBDII generic code definitions. You can also consult other online resources or your vehicle’s repair manual.
Conclusion: Empowering You with OBDII Knowledge
Understanding OBDII generic code definitions is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s health and performance. By deciphering these codes, you can diagnose and address automotive issues effectively, saving time and money on repairs. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we are committed to empowering you with the knowledge, tools, and support you need to succeed in your diagnostic journey.
Don’t let those cryptic codes intimidate you any longer. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, CARDIAGTECH.NET has everything you need to decode the language of your car. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our range of high-quality OBDII scanners, diagnostic tools, and expert resources. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently for years to come. Address: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880. Website: CARDIAGTECH.NET.
Ready to take control of your vehicle’s health? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET now and let our experts guide you toward the perfect diagnostic solution. Don’t wait for that “Check Engine” light to ruin your day – be prepared and stay informed with CARDIAGTECH.NET. Your car will thank you.
