Obdii Fuse Location 2011 Silverado is essential knowledge for maintaining your truck’s health. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides expert insights into identifying and troubleshooting fuse-related issues, ensuring your Silverado runs smoothly. Addressing electrical issues promptly can prevent costly repairs.
1. Introduction to OBDII Fuse Location in Your 2011 Silverado
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) system is a crucial component of your 2011 Chevrolet Silverado 1500, responsible for monitoring various engine and vehicle systems. The OBDII port allows technicians to access this data for diagnostics and repairs. A blown fuse can disable the OBDII port, preventing communication with diagnostic tools. Knowing the OBDII fuse location is essential for quick troubleshooting and resolution, ensuring your truck remains in top condition. Understanding how to maintain your vehicle’s electrical system protects your investment and ensures reliable performance.
2. Understanding the Importance of the OBDII System
The OBDII system in your 2011 Silverado is more than just a diagnostic port; it’s the gateway to understanding your vehicle’s health. It monitors emissions, engine performance, and various other systems, alerting you to potential issues before they become major problems. According to the EPA, OBDII systems have significantly reduced vehicle emissions since their introduction in the mid-1990s. Regular diagnostics through the OBDII port can help maintain optimal fuel efficiency and reduce your vehicle’s environmental impact. Keeping your OBDII system functional ensures accurate diagnostics and helps you address issues promptly, saving time and money in the long run.
3. Common Symptoms of a Blown OBDII Fuse
Several symptoms can indicate a blown OBDII fuse in your 2011 Silverado. The most obvious is the inability to connect a diagnostic scanner to the OBDII port. Other symptoms may include a check engine light that won’t reset, issues with emissions testing, or problems with features that rely on the OBDII system for data. According to a study by the National Institute for Automotive Service Excellence (ASE), electrical issues, including blown fuses, account for a significant percentage of vehicle repairs. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you address the problem quickly and prevent further complications.
4. Locating the OBDII Port in Your 2011 Silverado
Before you can check the OBDII fuse, you need to locate the OBDII port itself. In most 2011 Chevrolet Silverado 1500 models, the OBDII port is located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It’s usually near the steering column or the center console. The port is a 16-pin connector, easily identifiable by its trapezoidal shape. If you’re having trouble finding it, consult your owner’s manual for a precise location diagram. Knowing the exact location of the OBDII port is the first step in diagnosing and resolving any issues related to the OBDII system.
5. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding the OBDII Fuse Location 2011 Silverado
Finding the OBDII fuse location in your 2011 Silverado involves a few simple steps. Here’s a detailed guide:
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: The owner’s manual is your best resource for identifying the exact location of the fuse boxes and the specific fuse for the OBDII port.
- Locate the Fuse Boxes: Your 2011 Silverado has multiple fuse boxes. The primary fuse box is usually located under the hood, while additional fuse boxes may be found inside the cabin, typically on the driver’s side or under the dashboard.
- Identify the OBDII Fuse: Once you’ve located the fuse box, use the fuse box diagram in your owner’s manual to identify the fuse labeled for the OBDII port or diagnostic link connector (DLC).
- Check the Fuse: After locating the fuse, visually inspect it to see if the filament inside is broken. If it is, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage. Ensure the new fuse is securely seated in the fuse box.
By following these steps, you can quickly locate and replace the OBDII fuse in your 2011 Silverado, restoring functionality to the diagnostic port.
6. Detailed Look at the Underhood Fuse Block
The underhood fuse block in your 2011 Silverado houses many critical fuses and relays for various vehicle systems. This fuse box is typically located on the driver’s side of the engine compartment. Here’s a table detailing some of the key fuses and relays in this block:
| Fuse/Relay | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuse 1 (MINI) | Right Trailer Stop/Turn Lamp |
| Fuse 4 (MINI) | Engine Controls |
| Fuse 11 (MINI) | Driver Side Low-Beam Headlamp |
| Fuse 20 (MINI) | Fuel Pump |
| Fuse 29 (MINI) | Horn |
| Fuse 30 (MINI) | Passenger Side High-Beam Headlamp |
| Fuse 57 (FMX/JCase) | Cooling Fan 1 |
| Relay FAN HI | Cooling Fan High Speed |
| Relay FUEL PMP | Fuel Pump |
Understanding the layout and function of the fuses and relays in the underhood fuse block is essential for diagnosing and resolving various electrical issues in your 2011 Silverado.
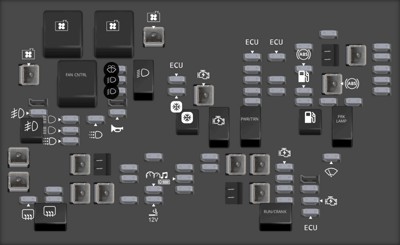 Underhood Fuse Block diagram
Underhood Fuse Block diagram
7. Exploring the Instrument Panel Fuse Block
The instrument panel fuse block is another critical fuse box in your 2011 Silverado. It is typically located inside the cabin, often on the driver’s side or under the dashboard. This fuse box houses fuses for interior components and accessories. Here’s a table detailing some of the key fuses in this block:
| Fuse (MICRO2) | Description |
|---|---|
| Fuse 5 | Dome Lamps, Driver Side Turn Signal |
| Fuse 6 | Driver Side Turn Signal, Stoplamp |
| Fuse 8 | Passenger Side Turn Signal, Stoplamp |
| Fuse 12 | Stoplamps, Center-High Mounted Stoplamp |
| Fuse 16 | Accessory Power Outlets |
| Fuse 17 | Interior Lamps |
| Fuse 22 | Driver Information Center |
Knowing the location and function of the fuses in the instrument panel fuse block can help you troubleshoot issues with interior lighting, power outlets, and other accessories in your 2011 Silverado.
 Instrument Panel Fuse Block diagram
Instrument Panel Fuse Block diagram
8. Examining the Center Instrument Panel Fuse Block
In some 2011 Silverado models, there may be a third fuse box located in the center instrument panel. This fuse box typically houses fuses for specific accessories or optional equipment. Consult your owner’s manual for the exact location and diagram of this fuse box, as it may vary depending on the vehicle’s configuration. Understanding the purpose of the fuses in this fuse box can help you address issues with specific features in your truck.
 Center Instrument Panel Fuse Block diagram
Center Instrument Panel Fuse Block diagram
9. Tools You’ll Need to Check and Replace Fuses
Checking and replacing fuses in your 2011 Silverado requires a few basic tools:
- Fuse Puller: A fuse puller is a small plastic tool designed to grip and remove fuses from the fuse box without damaging them.
- Spare Fuses: Keep a set of spare fuses of various amperages in your vehicle so you can quickly replace a blown fuse when needed.
- Multimeter (Optional): A multimeter can be used to test the continuity of a fuse to determine if it is blown.
- Owner’s Manual: Your owner’s manual contains essential information about the location of fuse boxes and the function of each fuse.
- Flashlight: A flashlight can help you see clearly inside the fuse box, especially in low-light conditions.
Having these tools on hand can make the process of checking and replacing fuses much easier and more efficient. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of diagnostic tools and equipment to help you maintain your vehicle’s electrical system.
10. How to Check a Fuse for Continuity
Checking a fuse for continuity is a reliable way to determine if it is blown. Here’s how to do it using a multimeter:
1. **Set Up the Multimeter:** Turn on your multimeter and set it to the continuity setting. This setting is usually indicated by a diode symbol or an audible signal.
2. **Remove the Fuse:** Use a fuse puller to remove the fuse from the fuse box.
3. **Test the Fuse:** Place one probe of the multimeter on each of the metal contacts on the fuse.
4. **Interpret the Results:** If the multimeter shows continuity (usually indicated by a beep or a reading of 0 ohms), the fuse is good. If the multimeter shows no continuity (usually indicated by no beep or a reading of infinite ohms), the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.This method provides a definitive way to determine the condition of a fuse, ensuring you only replace fuses that are actually blown.
11. Selecting the Correct Replacement Fuse
Choosing the correct replacement fuse for your 2011 Silverado is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electrical system. Fuses are rated in amps, indicating the amount of current they can handle before blowing. Always replace a blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage. Using a fuse with a higher amperage can overload the circuit and cause damage, while using a fuse with a lower amperage may cause it to blow prematurely. Consult your owner’s manual or the fuse box diagram to determine the correct amperage for each fuse.
12. What to Do If the OBDII Fuse Keeps Blowing
If the OBDII fuse in your 2011 Silverado keeps blowing, it indicates a more significant underlying problem. A consistently blowing fuse is usually a sign of a short circuit or an overloaded circuit. Here are some steps to take:
- Inspect the Wiring: Check the wiring connected to the OBDII port and the components it serves for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or exposed metal.
- Disconnect Components: Try disconnecting components connected to the OBDII circuit one at a time to see if the fuse stops blowing. This can help you identify the source of the problem.
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unable to identify the cause of the problem, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic or electrician. They have the tools and expertise to diagnose and repair complex electrical issues.
Ignoring a consistently blowing fuse can lead to more severe electrical problems and potentially damage your vehicle’s systems.
13. Understanding Fuse Types and Amperage
Fuses come in various types and amperages, each designed for specific applications. The most common fuse types in the 2011 Silverado include:
- MINI Fuses: These are small, rectangular fuses commonly used for low-current circuits.
- MICRO2 Fuses: These are even smaller than MINI fuses and are used in newer vehicles.
- FMX/JCase Fuses: These are larger, high-current fuses used for circuits like cooling fans and power distribution.
- ATO/ATC Fuses: These are standard blade-type fuses used in a wide range of applications.
Amperage ratings typically range from 5 amps to 40 amps or higher, depending on the circuit’s requirements. Always use the correct fuse type and amperage when replacing a blown fuse to ensure proper circuit protection.
14. Tips for Preventing Future Fuse Problems
Preventing future fuse problems in your 2011 Silverado involves a few simple maintenance practices:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect your vehicle’s wiring and electrical components for signs of damage or wear.
- Proper Fuse Replacement: Always replace blown fuses with the correct type and amperage.
- Avoid Overloading Circuits: Don’t overload circuits by plugging too many devices into a single power outlet.
- Professional Maintenance: Have your vehicle’s electrical system inspected by a qualified technician during routine maintenance.
By following these tips, you can minimize the risk of fuse-related problems and keep your 2011 Silverado running smoothly.
15. The Role of Relays in Your Silverado’s Electrical System
Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They play a crucial role in your 2011 Silverado’s electrical system, allowing low-current switches to control high-power devices like headlights, cooling fans, and fuel pumps. Relays can fail over time, leading to various electrical issues. If you suspect a relay is faulty, it can be tested using a multimeter or replaced with a new one. Understanding the function of relays and how to test them is essential for diagnosing and resolving electrical problems.
16. How to Test a Relay Using a Multimeter
Testing a relay using a multimeter involves checking both the coil and the switch circuits. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the Terminals: Relays typically have four or five terminals, including two for the coil and two or three for the switch.
- Test the Coil: Set the multimeter to the resistance setting and measure the resistance between the coil terminals. A good coil will have a resistance value, while a faulty coil will have either very high or very low resistance.
- Test the Switch: Set the multimeter to the continuity setting and check for continuity between the switch terminals. With the relay unenergized, there should be continuity between the normally closed (NC) terminal and the common terminal. When the relay is energized, there should be continuity between the normally open (NO) terminal and the common terminal.
- Energize the Relay: Apply voltage to the coil terminals and check for continuity between the switch terminals again. The continuity should switch from the NC terminal to the NO terminal.
If the relay fails any of these tests, it should be replaced.
17. Understanding Wiring Diagrams for Your 2011 Silverado
Wiring diagrams are essential tools for diagnosing and repairing electrical problems in your 2011 Silverado. These diagrams provide a detailed map of the vehicle’s electrical circuits, showing the location of fuses, relays, wiring harnesses, and components. Understanding how to read and interpret wiring diagrams can greatly simplify the troubleshooting process. Wiring diagrams are typically available in your vehicle’s service manual or online databases.
18. Common Electrical Problems in the 2011 Silverado
The 2011 Chevrolet Silverado 1500 is generally a reliable truck, but like any vehicle, it can experience electrical problems. Some common issues include:
- Blown Fuses: As discussed, blown fuses are a common electrical problem that can affect various systems.
- Faulty Relays: Relays can fail over time, leading to issues with headlights, cooling fans, and other components.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can cause shorts, open circuits, and other electrical issues.
- Battery Issues: A weak or dead battery can cause various electrical problems, including difficulty starting the engine.
- Sensor Failures: Faulty sensors can disrupt various systems, such as the engine management system and the anti-lock braking system.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent further damage and keep your Silverado running smoothly.
19. How to Troubleshoot a Non-Functional OBDII Port
If your OBDII port is not functioning, here’s a systematic approach to troubleshooting the problem:
- Check the OBDII Fuse: As discussed, start by checking the OBDII fuse to ensure it is not blown.
- Inspect the OBDII Connector: Examine the OBDII connector for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Check the Wiring: Inspect the wiring connected to the OBDII port for any signs of damage, such as frayed wires or exposed metal.
- Test the Power and Ground: Use a multimeter to check for power and ground at the OBDII port. There should be 12 volts between pin 16 (power) and pin 4 or 5 (ground).
- Consult a Professional: If you’re unable to identify the cause of the problem, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic or electrician.
20. The Importance of Professional Diagnostic Tools
Professional diagnostic tools, such as scan tools and multimeters, are essential for accurately diagnosing and repairing electrical problems in your 2011 Silverado. These tools allow technicians to access data from the vehicle’s computer, test components, and identify the root cause of the problem. While some basic troubleshooting can be done with simple tools, professional diagnostic tools are often necessary for complex electrical issues. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of professional diagnostic tools to help you maintain your vehicle’s electrical system.
21. Maintaining Your Silverado’s Battery for Optimal Performance
The battery is the heart of your 2011 Silverado’s electrical system. Maintaining it properly is crucial for optimal performance. Here are some tips:
- Regularly Clean the Terminals: Clean the battery terminals with a wire brush to remove corrosion.
- Check the Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Have the Battery Tested: Have the battery tested periodically to ensure it is still capable of holding a charge.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Avoid leaving the headlights or accessories on for extended periods, as this can deep discharge the battery.
- Use a Battery Tender: If you don’t drive your Silverado regularly, use a battery tender to keep the battery charged.
22. Understanding the Silverado’s Charging System
The charging system in your 2011 Silverado is responsible for keeping the battery charged while the engine is running. The main components of the charging system include the alternator, voltage regulator, and wiring. If the charging system is not functioning properly, the battery can become discharged, leading to various electrical problems. Symptoms of a charging system problem include a warning light on the dashboard, a weak battery, and dimming headlights.
23. The Role of the Alternator in Your Silverado
The alternator is a key component of the charging system in your 2011 Silverado. It is responsible for generating electricity to power the vehicle’s electrical system and recharge the battery while the engine is running. If the alternator fails, the battery will eventually become discharged, and the vehicle will not be able to start. Symptoms of a faulty alternator include a warning light on the dashboard, a weak battery, and dimming headlights.
24. How to Test Your Silverado’s Alternator
Testing your Silverado’s alternator involves checking its output voltage and current. Here’s how to do it:
- Check the Battery Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage with the engine off. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it idle.
- Check the Alternator Output Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the alternator output voltage at the battery terminals. The voltage should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
- Check the Alternator Output Current: Use an inductive amp clamp to measure the alternator output current. The current should increase as electrical loads are added to the system.
If the alternator fails these tests, it may need to be replaced.
25. Diagnosing and Repairing Short Circuits
A short circuit occurs when electrical current flows along an unintended path, typically due to damaged or exposed wiring. Short circuits can cause fuses to blow, damage components, and even start fires. Diagnosing and repairing short circuits requires careful inspection of the wiring and components. A multimeter can be used to identify the location of the short. Once the short is located, the damaged wiring or component must be repaired or replaced.
26. Addressing Open Circuits in Your Silverado
An open circuit occurs when there is a break in the electrical path, preventing current from flowing. Open circuits can be caused by broken wires, loose connections, or faulty components. Symptoms of an open circuit include a non-functional component or system. Diagnosing and repairing open circuits involves tracing the wiring to identify the location of the break. A multimeter can be used to check for continuity and identify the open circuit.
27. The Impact of Corrosion on Electrical Connections
Corrosion can have a significant impact on electrical connections in your 2011 Silverado. Corrosion can increase resistance in the circuit, leading to reduced performance and component failure. Corrosion is especially common in areas exposed to moisture and road salt. Regularly inspect and clean electrical connections to prevent corrosion. Use a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner to remove corrosion and protect the connections.
28. Using Dielectric Grease to Protect Electrical Connections
Dielectric grease is a non-conductive lubricant that can be used to protect electrical connections from moisture and corrosion. Applying dielectric grease to electrical connections can help prevent corrosion and ensure reliable performance. Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the terminals and connectors before assembling them.
29. Upgrading Your Silverado’s Electrical System
If you’re planning to add aftermarket accessories to your 2011 Silverado, such as lights, sound systems, or winches, you may need to upgrade the electrical system to handle the increased load. Upgrading the electrical system may involve installing a higher-output alternator, adding a secondary battery, and upgrading the wiring. Consult a qualified electrician to determine the best way to upgrade your Silverado’s electrical system.
30. Understanding the Body Control Module (BCM)
The Body Control Module (BCM) is a computer that controls various body functions in your 2011 Silverado, such as lighting, power windows, and door locks. The BCM receives inputs from various sensors and switches and controls the corresponding outputs. A faulty BCM can cause various electrical problems. Diagnosing and repairing BCM problems often requires professional diagnostic tools and expertise.
31. How to Reset Your Silverado’s Computer
Resetting your Silverado’s computer can sometimes resolve minor electrical problems. Here’s how to do it:
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable from the battery.
- Wait 15 Minutes: Wait for at least 15 minutes to allow the computer to reset.
- Reconnect the Battery: Reconnect the negative battery cable to the battery.
This process will reset the computer and clear any stored codes. Note that resetting the computer may also clear some of your vehicle’s settings, such as radio presets.
32. The Importance of Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is essential for the proper operation of your 2011 Silverado’s electrical system. Grounding provides a return path for electrical current and helps prevent electrical noise. Poor grounding can cause various electrical problems, such as erratic sensor readings and component failures. Ensure that all grounding connections are clean and tight. Add additional grounding straps if necessary.
33. Using a Multimeter to Diagnose Electrical Problems
A multimeter is an essential tool for diagnosing electrical problems in your 2011 Silverado. A multimeter can be used to measure voltage, current, resistance, and continuity. By using a multimeter to test various circuits and components, you can identify the root cause of the problem.
34. The Benefits of Using LED Lighting
LED lighting offers several benefits over traditional incandescent lighting in your 2011 Silverado. LED lights are brighter, more energy-efficient, and longer-lasting than incandescent lights. Upgrading to LED lighting can improve visibility and reduce the load on your electrical system.
35. Adding Auxiliary Lighting to Your Silverado
Adding auxiliary lighting to your 2011 Silverado can improve visibility and safety, especially when driving off-road or in low-light conditions. When adding auxiliary lighting, it’s important to choose lights that are compatible with your vehicle’s electrical system and to wire them properly. Use a relay to control the auxiliary lights and protect the switch.
36. Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes stored in your Silverado’s computer that indicate a problem with a specific system or component. DTCs can be retrieved using a scan tool. Understanding the meaning of DTCs can help you diagnose and repair electrical problems.
37. How to Use a Scan Tool to Retrieve DTCs
Using a scan tool to retrieve DTCs from your 2011 Silverado is a straightforward process:
- Connect the Scan Tool: Plug the scan tool into the OBDII port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “on” position, but do not start the engine.
- Select the Vehicle: Select your vehicle’s make, model, and year on the scan tool.
- Retrieve DTCs: Select the “Read Codes” or “Retrieve Codes” option on the scan tool.
- View DTCs: The scan tool will display any stored DTCs.
Record the DTCs and research their meaning to help diagnose the problem.
38. Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
After repairing the problem, you can clear the DTCs from your Silverado’s computer using a scan tool. Select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option on the scan tool. Clearing the DTCs will turn off the check engine light. Note that some DTCs may require multiple drive cycles to clear.
Maintaining your 2011 Chevrolet Silverado 1500’s electrical system is crucial for its overall performance and reliability. By understanding the location of the OBDII fuse and other key components, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve electrical issues. Remember, if you encounter complex problems or are unsure about any repair procedures, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic or electrician.
Are you facing electrical challenges with your 2011 Silverado? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today for expert advice and top-quality diagnostic tools to keep your truck running smoothly. Our team is ready to assist you with all your automotive needs. Reach out to us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or connect via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our extensive range of products and services.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About 2011 Silverado OBDII Fuse Location
-
Where is the OBDII port located in my 2011 Silverado?
The OBDII port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side, near the steering column or center console. -
Which fuse box contains the OBDII fuse in a 2011 Silverado?
The OBDII fuse is usually located in the instrument panel fuse box, which is inside the cabin on the driver’s side. -
What amperage is the OBDII fuse for a 2011 Silverado?
The amperage of the OBDII fuse can vary, but it’s typically a 10-amp or 15-amp fuse. Consult your owner’s manual for the exact rating. -
Can a blown OBDII fuse affect other systems in my 2011 Silverado?
Yes, a blown OBDII fuse can sometimes affect other systems that rely on the diagnostic link, such as the check engine light or emissions testing. -
What tools do I need to check and replace the OBDII fuse?
You’ll need a fuse puller, spare fuses of the correct amperage, and your owner’s manual. A multimeter is optional but helpful for testing the fuse. -
What should I do if the OBDII fuse keeps blowing?
If the OBDII fuse keeps blowing, it indicates a short circuit or an overloaded circuit. Inspect the wiring and consult a professional if needed. -
Is it safe to use a higher amperage fuse if the correct one is not available?
No, it is not safe to use a higher amperage fuse. This can overload the circuit and cause damage. -
How can I prevent corrosion on electrical connections in my Silverado?
Clean the connections regularly with a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner, and apply dielectric grease to protect them from moisture. -
What is the role of the Body Control Module (BCM) in my Silverado?
The BCM controls various body functions, such as lighting, power windows, and door locks. -
Where can I find wiring diagrams for my 2011 Silverado?
Wiring diagrams are typically available in your vehicle’s service manual or online databases.
