The OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) system in your vehicle uses Controller Area Network (CAN) communication to transmit data between various modules. One common communication error within this system is represented by the hexadecimal code 0x660. While not a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) itself, 0x660 often indicates a problem with CAN communication, specifically related to the reception of data. This article explores potential causes and troubleshooting steps for issues related to Obdii Can 0x660.
Common Causes of OBDII CAN 0x660 Issues
The 0x660 error typically points to a breakdown in communication between the OBDII port and other Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in the vehicle. This disruption can stem from several sources:
- Incorrect Baud Rate: The baud rate refers to the speed of data transmission on the CAN bus. A mismatch between the OBDII tool or device (e.g., a data logger) and the vehicle’s CAN bus can lead to 0x660 errors. Common baud rates for OBDII are 250kbps and 500kbps.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring within the CAN bus network can interrupt communication and trigger the error. This includes wiring within the OBDII connector itself, as well as the wiring harness connecting various ECUs.
- Faulty OBDII Port: In some cases, the OBDII port itself may be malfunctioning, preventing proper communication. This could be due to damaged pins or internal circuitry issues.
- ECU Malfunction: A malfunctioning ECU can also contribute to CAN communication problems. If an ECU is unable to transmit or receive data correctly, it can result in a 0x660 error.
- Incompatible Hardware or Software: Using an incompatible OBDII scanning tool, data logger, or software can prevent proper communication and lead to the 0x660 error. Ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s make and model.
Troubleshooting OBDII CAN 0x660
Addressing a 0x660 error requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause:
- Verify Baud Rate Settings: Confirm that the baud rate of your OBDII tool or device matches the vehicle’s CAN bus speed. Consult your vehicle’s service manual or use a diagnostic tool capable of identifying the correct baud rate.
- Inspect Wiring and Connectors: Carefully examine the wiring and connectors associated with the OBDII port and the CAN bus system. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace any faulty components.
- Test with a Known-Good OBDII Tool: If possible, try connecting a different OBDII scanning tool or data logger to rule out a problem with your existing equipment.
- Check for ECU Trouble Codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to check for any DTCs stored in the vehicle’s ECUs. These codes can provide valuable clues about potential underlying issues.
- Consult Vehicle-Specific Resources: Refer to your vehicle’s service manual or online forums dedicated to your specific make and model. These resources may offer specific troubleshooting guidance related to CAN communication problems.
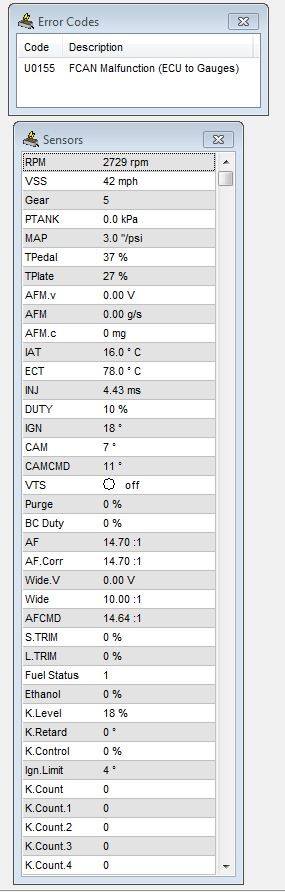 alt text describing image of Hondata Flashpro data log showing various sensor readings
alt text describing image of Hondata Flashpro data log showing various sensor readings
Conclusion
OBDII CAN 0x660 errors can be frustrating, but with a methodical approach to troubleshooting, the underlying cause can often be identified and resolved. By checking the baud rate, inspecting wiring, testing with different equipment, and consulting vehicle-specific resources, you can effectively address communication issues within your vehicle’s OBDII system. If the problem persists after these steps, consulting a qualified automotive technician with expertise in vehicle electronics is recommended.

