For auto repair professionals and vehicle enthusiasts, understanding OBD-II codes is crucial for effective diagnostics and maintenance. While powertrain, chassis, and network codes address critical vehicle functions, OBD-II body codes are equally important, signaling issues within systems directly impacting safety, comfort, and convenience. This guide delves into the specifics of body codes, explaining their significance and how to interpret them for efficient vehicle repair.
Understanding OBD-II Codes: The Language of Your Vehicle
Onboard diagnostics (OBD-II) codes are standardized alphanumeric codes used by your vehicle’s computer system to communicate detected problems. Think of them as error messages from your car, alerting you to malfunctions within its various systems. Modern vehicles are equipped with an intricate network of sensors and modules monitoring everything from the engine’s performance to the functionality of your air conditioning. When a component or system operates outside of its expected parameters, the onboard computer generates an OBD-II code.
These codes are invaluable for pinpointing the source of a problem, whether it’s a minor sensor glitch or a more serious mechanical failure. To access these codes, you’ll need an OBD-II scanner, which connects to a port usually located under the dashboard. This scanner retrieves the diagnostic trouble code, providing a starting point for troubleshooting and repair decisions. For fleet managers and auto repair shops, understanding these codes is essential for maintaining vehicle health and operational efficiency.
Navigating the Types of OBD-II Codes: Focusing on Body Systems
When an OBD-II code appears, identifying its type is the first step in effective diagnosis. These codes are broadly categorized into four main types, each relating to a specific area of the vehicle. Understanding these categories helps narrow down the potential problem and streamlines the repair process.
Powertrain Codes: Engine and Transmission Issues
Powertrain codes, starting with the letter “P,” relate to problems within the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components. These are often performance-related, impacting how the vehicle drives and its fuel efficiency. For example, a P0101 code, as mentioned in the original article, indicates a potential issue with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, which can affect engine performance and fuel economy.
Body Codes: Addressing Comfort, Convenience, and Safety Systems
Body codes, identified by the letter “B,” are the focus of this guide. These codes signal problems within the vehicle’s body systems. This category encompasses a wide range of features, including:
- Lighting Systems: Headlights, taillights, signal lights, interior lighting.
- Airbag Systems (SRS): Deployment circuits, sensors, and indicators.
- Climate Control (HVAC): Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
- Power Windows and Locks: Electric window and door locking mechanisms.
- Wiper Systems: Front and rear wipers, washer fluid systems.
- Immobilizer and Security Systems: Anti-theft systems and components.
- Instrument Cluster and Gauges: Speedometer, tachometer, fuel gauge, and warning lights.
For instance, the example body code B0020 from the original article points to a problem with the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. This highlights the critical safety implications associated with body codes. Ignoring body codes can lead to malfunctions in safety systems, reduced driver comfort, and even legal compliance issues, especially concerning lighting and safety equipment.
 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Chassis Codes: Suspension, Steering, and Braking Concerns
Chassis codes, starting with “C,” indicate issues within the vehicle’s chassis systems, which are related to ride control and handling. This includes suspension, steering, and braking systems. The C1234 code, mentioned earlier, relating to a wheel speed sensor, illustrates how chassis codes can impact vehicle stability and braking effectiveness.
Network Communication Codes: Issues in Vehicle Communication
Network communication codes, beginning with “U,” point to problems within the vehicle’s communication network. Modern vehicles rely on complex communication networks to allow various modules and sensors to exchange information. U-codes indicate disruptions in this communication, potentially stemming from module failures, wiring issues, or even low battery voltage, as exemplified by the U0100 code and its potential link to battery problems.
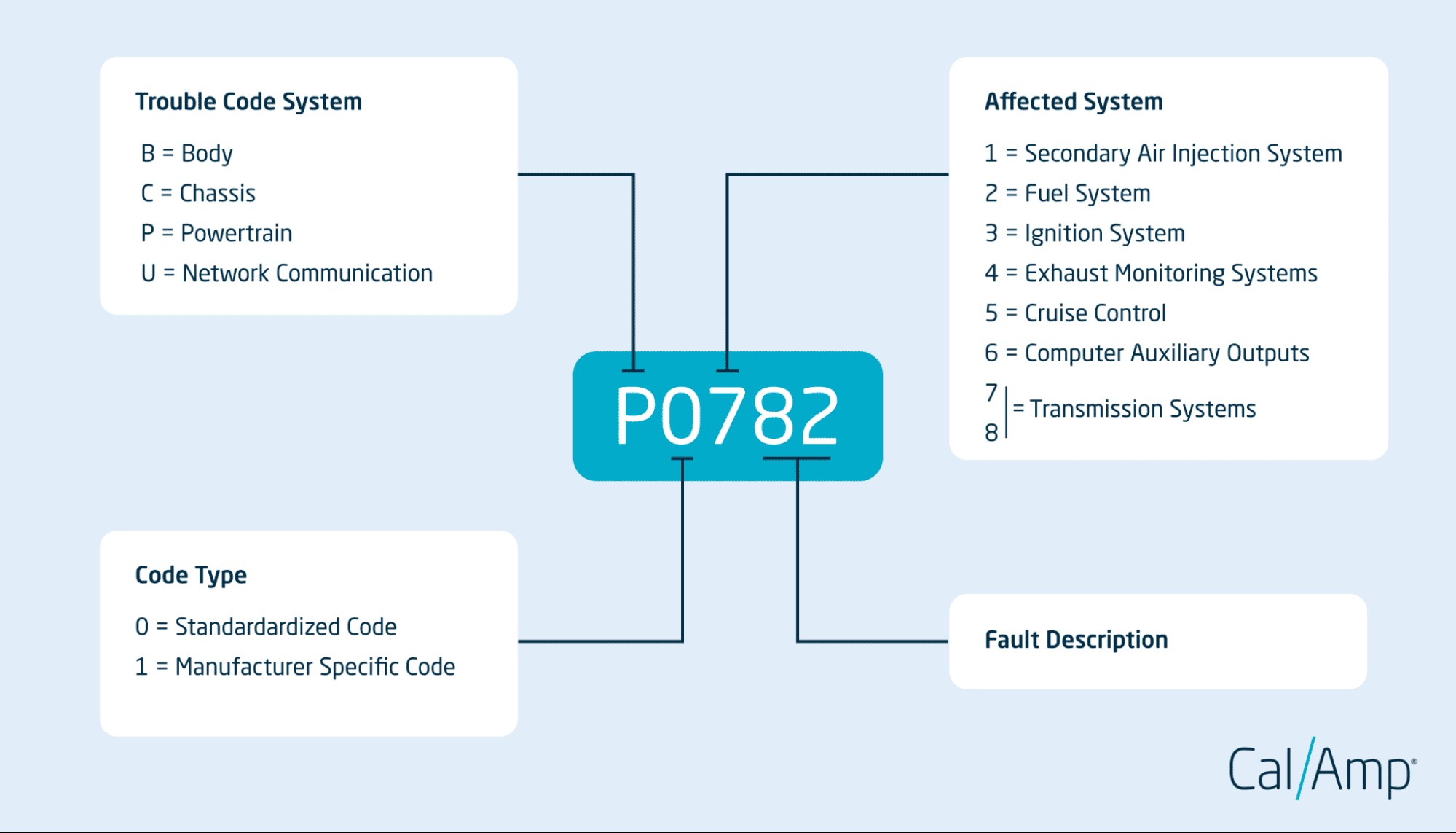
Decoding the Structure of OBD-II Codes: Understanding the Five Characters
Each OBD-II code is composed of five characters, providing a structured way to understand the nature and location of the problem. Breaking down this structure is key to effective diagnostics.
- First Character: Trouble Code System: Indicates the primary system affected (P=Powertrain, C=Chassis, B=Body, U=Network).
- Second Character: Code Type: “0” signifies a standardized (generic) code, while “1” indicates a manufacturer-specific code.
- Third Character: Affected System: A number representing a more specific subsystem within the primary system. For body codes, this could relate to lighting, airbags, or HVAC.
- Fourth and Fifth Characters: Specific Code: These two digits provide the most detailed information, pinpointing the specific fault within the affected system. For example, in “B0020,” the “20” specifies the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit.
Understanding this structure allows for a more informed interpretation of the code and guides diagnostic efforts towards the relevant vehicle systems.
Clearing OBD-II Codes: When and How
While clearing an OBD-II code might seem like a quick fix, it’s crucial to understand that it only removes the symptom, not the underlying problem. Generally, clearing codes without addressing the root cause is not recommended. However, there are situations where clearing codes might be necessary or occur naturally.
Utilizing an OBD-II Scanner for Code Clearing
OBD-II scanners are not only used to read codes but also to clear them. After diagnosing and repairing the issue indicated by a body code (or any other type), a scanner can be used to reset the system and turn off the “Check Engine” light or other warning indicators. This is essential after repairs to confirm that the problem is resolved and to allow the system to function normally.
Drive Cycles and Self-Clearing Codes
Some less severe or intermittent codes might clear themselves after a series of successful “drive cycles.” A drive cycle involves specific driving conditions that allow the vehicle’s computer to re-evaluate the system. If the fault is no longer detected during these cycles, the code may clear automatically. However, relying on self-clearing codes is not a substitute for proper diagnosis and repair, especially for critical body codes related to safety systems.
Seeking Professional Mechanic Assistance
For complex body code issues or when unsure about the diagnosis or repair process, consulting a qualified mechanic is always the best approach. Mechanics have the expertise, specialized tools, and diagnostic knowledge to accurately pinpoint the root cause of the code, perform necessary repairs, and ensure the system is functioning correctly. They can also properly clear codes after repairs and verify system functionality.
Preventing OBD-II Body Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Preventing OBD-II codes, including body codes, is far more cost-effective than dealing with repairs after a fault occurs. Regular vehicle maintenance plays a vital role in minimizing the likelihood of triggering these codes.
[Picture #5]
Alt text: A mechanic performing routine vehicle maintenance, emphasizing the importance of preventative care to avoid OBD-II codes and ensure vehicle reliability.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance: A Foundation for Prevention
Routine maintenance, as outlined in your vehicle’s owner’s manual, is crucial. This includes:
- Regular Inspections: Checking lights, wipers, and other body system components for proper function.
- Fluid Checks: Ensuring proper levels and condition of relevant fluids.
- Component Checks: Inspecting wiring, connectors, and sensors related to body systems for damage or corrosion.
- Addressing Minor Issues Promptly: Fixing small problems before they escalate and trigger codes.
Using Quality Components and Fluids: Ensuring System Longevity
Using high-quality replacement parts and fluids is also essential for preventing body codes. For example, using substandard bulbs in lighting systems or incompatible fluids in wiper systems can lead to premature failures and trigger body-related diagnostic codes.
Managing OBD-II Body Codes for Fleets: Efficiency and Systematization
For fleet managers, handling OBD-II codes efficiently across a fleet of vehicles is critical. Centralized tracking and proactive monitoring are key strategies.
Centralized Code Tracking: Streamlining Data Management
Implementing a system to centralize OBD-II code data from all fleet vehicles provides a comprehensive overview of vehicle health. Tools like CalAmp iOn, as mentioned in the original article, can facilitate real-time code tracking and provide insights into maintenance needs. This centralized approach simplifies data analysis, allowing fleet managers to identify trends, recurring issues, and prioritize maintenance tasks.
Ongoing Fleet Monitoring: Real-Time Diagnostics
Utilizing telematics systems for ongoing fleet monitoring allows for the proactive detection of OBD-II codes, including body codes, as they occur. Real-time alerts enable swift responses, minimizing downtime and preventing minor issues from becoming major problems.
Prioritizing Repairs: Severity-Based Approach
Establishing a system for prioritizing repairs based on the severity of the OBD-II code is essential for efficient resource allocation. Body codes related to safety systems, such as airbag malfunctions or lighting failures, should be prioritized for immediate attention. Codes related to convenience features might be scheduled for repair during routine maintenance intervals.
In Conclusion: Mastering OBD-II Body Codes for Vehicle Health
OBD-II body codes are vital indicators of the health and functionality of your vehicle’s comfort, convenience, and safety systems. Understanding these codes, their structure, and their implications is crucial for effective vehicle diagnostics and maintenance, whether you are a professional technician or a vehicle owner. By focusing on preventative maintenance, utilizing diagnostic tools effectively, and understanding the nuances of body codes, you can ensure vehicle reliability, safety, and longevity.
For advanced fleet management and comprehensive OBD-II code solutions, exploring tools like CalAmp iOn or Autel’s professional diagnostic scanners can significantly enhance your ability to manage and maintain vehicle health effectively. Request a demo today to discover how these technologies can streamline your diagnostic processes and improve vehicle maintenance outcomes.
