Experiencing OBDII code P0136 can be frustrating for any car owner. This diagnostic trouble code signals a “Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) 2, Bank 1 – Circuit Malfunction”. It indicates a problem with the post-catalytic converter oxygen sensor on bank 1 of your engine. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the efficiency of your catalytic converter and ensuring optimal engine performance. Let’s delve into what this code means, its symptoms, potential causes, and how you can approach troubleshooting it.
Understanding the P0136 Code: Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction
The P0136 code specifically points to an issue within the circuit of the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor. In most vehicles, Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine where cylinder number 1 is located. Sensor 2 is the downstream oxygen sensor, positioned after the catalytic converter. This sensor’s job is to measure the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases after they’ve passed through the catalytic converter. The Engine Control Unit (ECU) uses this data to assess the converter’s efficiency. A “circuit malfunction” can mean various electrical problems preventing the sensor from sending accurate readings to the ECU.
Symptoms Associated with P0136
When your vehicle throws a P0136 code, you might notice several symptoms, including:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) Illumination: This is the most immediate sign. The ECU detects an anomaly and triggers the CEL to alert you.
- Rough Engine Performance: You may experience symptoms like choppy performance or a slight lack of throttle response.
- Increased Exhaust Fumes and Odor: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to inefficient combustion and potentially stronger exhaust fumes noticeable inside the cabin.
- Louder Exhaust Noise: In some cases, issues related to oxygen sensors and exhaust systems can lead to a noticeable change in exhaust volume, often described as louder or unusual.
- Other Related OBDII Codes: P0136 often appears alongside other oxygen sensor related codes, giving a broader picture of potential issues within the system.
Below are examples of sensor readings that can indicate issues with the oxygen sensors, as described in a real-world scenario:
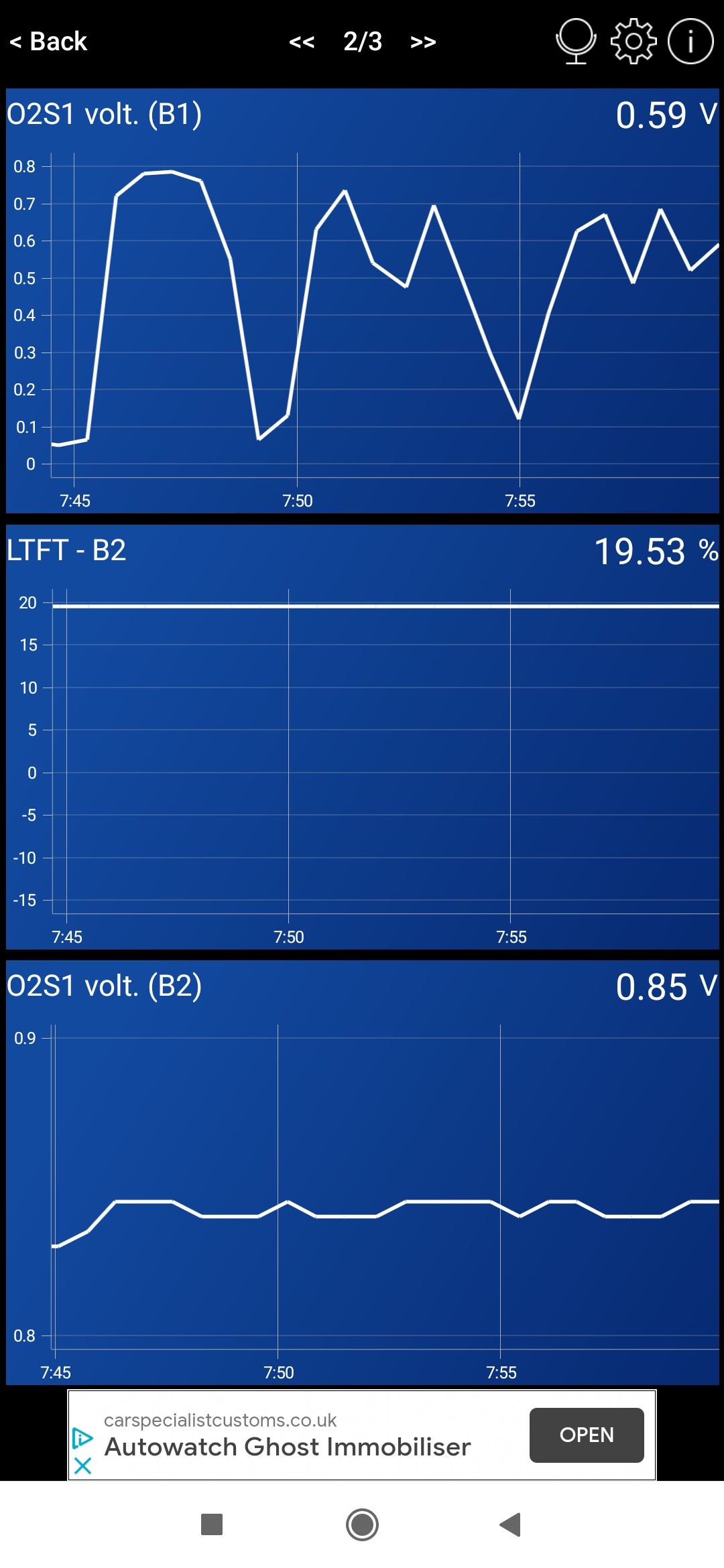 Initial O2 sensor readings showing Bank 2 sensor stuck on high voltage and lean condition
Initial O2 sensor readings showing Bank 2 sensor stuck on high voltage and lean condition
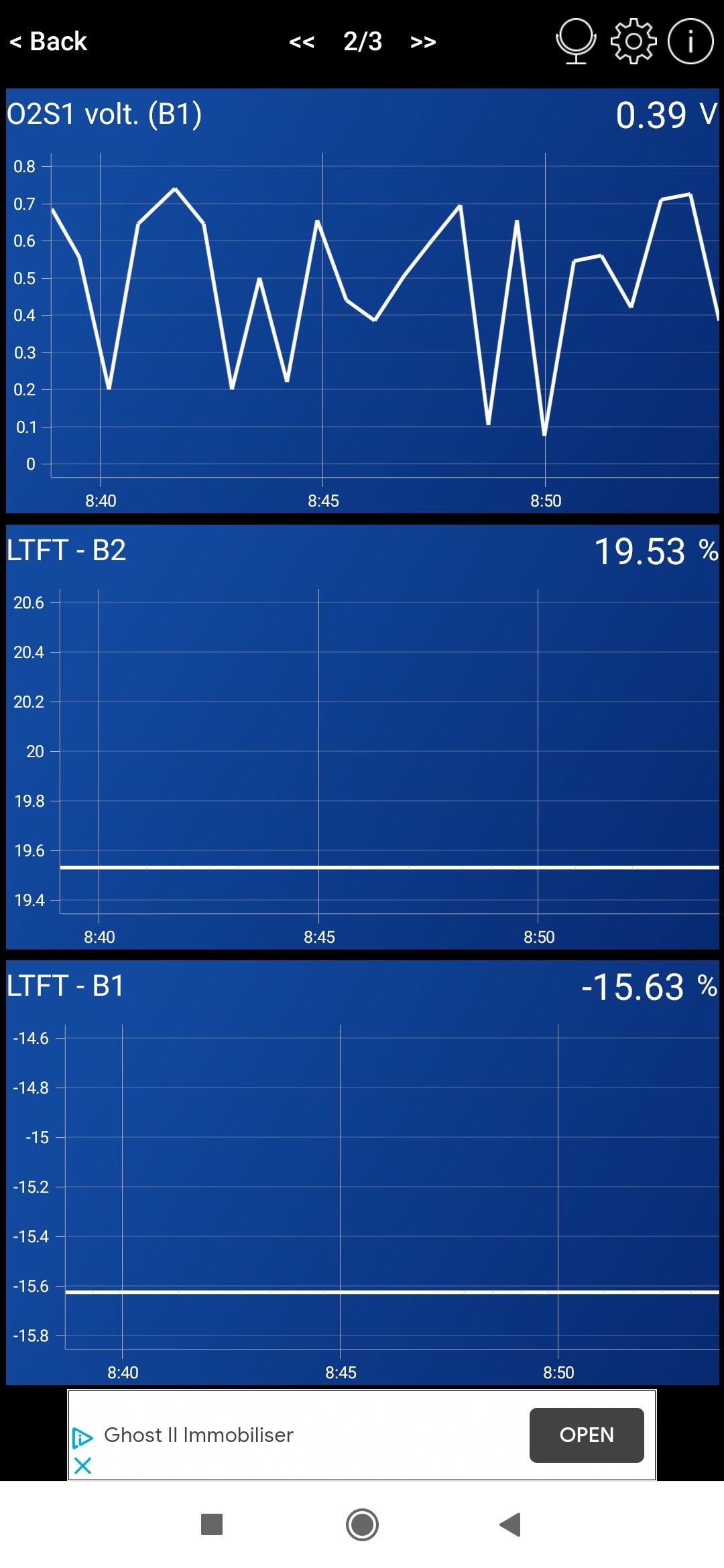 Further O2 sensor readings indicating worsening sensor behavior after driving
Further O2 sensor readings indicating worsening sensor behavior after driving
These readings highlight the erratic behavior of the oxygen sensors, a common symptom when experiencing a P0136 code and related issues.
Potential Causes of OBDII Code P0136
Several factors can trigger the P0136 code. Here are some common culprits:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The sensor itself may have failed due to age, contamination, or internal damage. This is often the primary suspect.
- Wiring Issues: Damage to the wiring harness leading to the sensor, including frayed wires, corrosion, or loose connections, can disrupt the sensor’s circuit.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly before or around the oxygen sensor, can introduce extra oxygen into the system and cause incorrect readings.
- ECU Malfunction (Less Likely): While less common, problems with the ECU itself could, in rare cases, lead to misinterpretation of sensor signals or circuit issues.
- Catalytic Converter Issues: Although P0136 directly points to the sensor circuit, underlying catalytic converter problems can sometimes indirectly affect sensor readings over time.
It’s worth noting that resetting the ECU, as mentioned in some cases, might temporarily clear codes, but it doesn’t fix the underlying problem. In fact, as seen in some situations, forcing an ECU reset without addressing the root cause can sometimes exacerbate existing issues.
Troubleshooting P0136: A Step-by-Step Approach
Diagnosing P0136 requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide you can follow:
-
Visual Inspection:
- Check Sensor Wiring: Carefully inspect the wiring and connectors leading to the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor. Look for any signs of damage, melting, fraying, or loose connections.
- Examine for Exhaust Leaks: Visually and audibly inspect the exhaust system around the sensor and upstream for any signs of leaks. Listen for hissing or unusual exhaust noises, especially at cold start.
-
Scan Tool Data Analysis:
- Read and Clear Codes: Use an OBDII scan tool to confirm the P0136 code and check for any other related codes (like P0153, P0150, as seen in some instances which relate to other oxygen sensors). Clear the codes and see if P0136 returns.
- Monitor Live Sensor Data: Use the scan tool to monitor the live data stream from the Bank 1 Sensor 2 O2 sensor. Check if the voltage readings are erratic, stuck high or low, or unresponsive to engine changes. Compare readings with other sensors if possible.
-
Oxygen Sensor Testing:
- Multimeter Testing: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s heater circuit resistance and signal voltage. Refer to your vehicle’s repair manual for specific test procedures and expected values for your sensor type.
- Sensor Replacement (If Necessary): If tests indicate a faulty sensor, replace the Bank 1 Sensor 2 oxygen sensor with a new, quality replacement. Ensure you use the correct sensor type for your vehicle.
-
Wiring Circuit Testing:
- Continuity and Voltage Checks: If the sensor itself seems functional, use a multimeter and wiring diagrams to check the continuity and voltage in the sensor’s wiring circuit back to the ECU. Identify any breaks, shorts, or open circuits.
- Repair Wiring Issues: Repair any identified wiring problems, such as replacing damaged wires or connectors.
-
Exhaust System Check and Repair:
- Professional Smoke Test: If exhaust leaks are suspected but not easily found, a professional smoke test can help pinpoint even small leaks in the system.
- Repair Exhaust Leaks: Address any exhaust leaks by repairing or replacing damaged exhaust components.
After performing any repairs, clear the OBDII codes and monitor if the P0136 code returns. It’s also advisable to take your vehicle for a test drive to ensure the issue is resolved under normal driving conditions.
If you are not comfortable performing these diagnostic steps yourself, it is always recommended to consult a qualified automotive technician. They have the expertise and tools to accurately diagnose and repair OBDII code P0136 and related issues, ensuring your vehicle runs efficiently and cleanly.
Here is an example of OBDII codes, including P0136, that were diagnosed in a real-world scenario, indicating a broader oxygen sensor related problem:
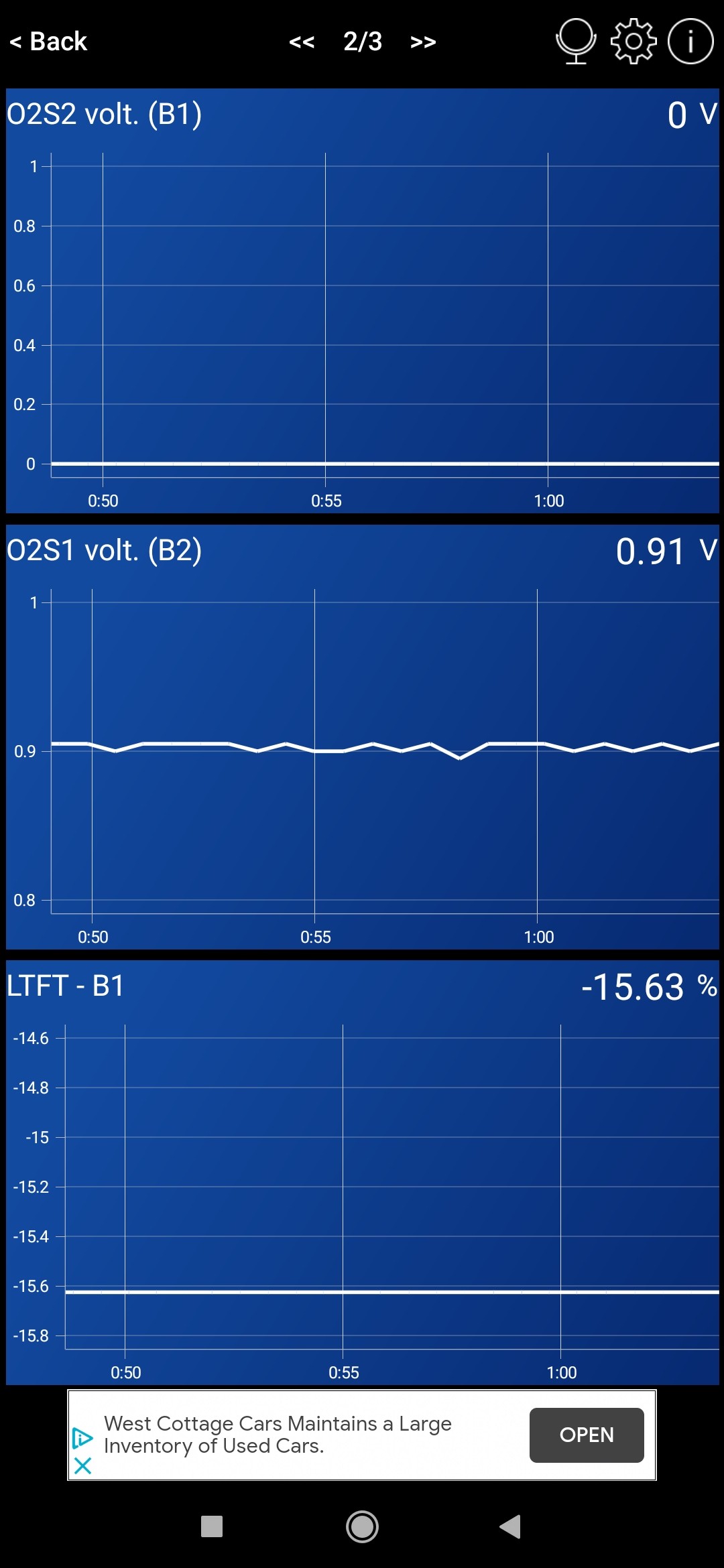 OBDII codes P0136, P0153, P0150 indicating oxygen sensor circuit malfunctions
OBDII codes P0136, P0153, P0150 indicating oxygen sensor circuit malfunctions
This example shows that P0136 can often be part of a larger set of related oxygen sensor codes, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
