The landscape of automotive technology is rapidly evolving, and with it, the possibilities for car hacking and customization are expanding. As vehicles become increasingly connected and software-driven, tools that allow enthusiasts and professionals to interact directly with their car’s systems are more valuable than ever. Enter the Macchina M2, a device designed from the ground up for automotive tinkering, offering a powerful and versatile platform that goes far beyond basic OBDII scanners. This article provides an in-depth look at the Macchina M2 Obdii, exploring its features, capabilities, and why it stands out as a premier tool for anyone serious about understanding and modifying their vehicle.
Macchina M2 OBDII: Redefining Automotive Hacking Hardware
Building on the foundation of the original Macchina M1, the Macchina M2 OBDII represents a significant leap forward in automotive interface technology. Macchina recognized the need for a more compact, modular, and feature-rich device, resulting in the M2’s innovative two-board design. Where the M1 provided a solid starting point with its Arduino compatibility, the M2 refines the concept, packing a comprehensive feature set into a smaller, OBDII dongle-friendly form factor. This makes the Macchina M2 OBDII not just a tool for the workbench, but a device readily deployable in-vehicle for real-world automotive exploration.
Two-Board Architecture: Power and Flexibility
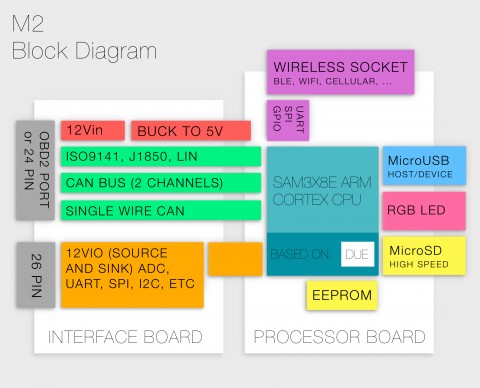 Block diagram of Macchina M2 hardware
Block diagram of Macchina M2 hardware
The core of the Macchina M2 OBDII’s design philosophy lies in its two-board hardware architecture. This modular approach separates the interface functionalities from the processing unit, offering both flexibility and performance.
-
Interface Board: This board is the communication hub, equipped with the necessary hardware to interface with a wide array of automotive protocols. It boasts dual high-speed CAN (Controller Area Network) interfaces, essential for modern vehicle communication, along with a single-wire CAN interface for specialized applications. Support for LIN (Local Interconnect Network), and legacy OBD protocols like ISO 9141 and J1850 ensures compatibility with virtually any vehicle manufactured after 1996, covering a broad spectrum of automotive systems. Furthermore, a dedicated header provides access to the microcontroller’s GPIOs (General Purpose Input/Output) and ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters), expanding the hardware’s potential for custom applications and sensor integration.
-
Processor Board: At the heart of the M2 OBDII resides a powerful processor board, effectively an Arduino Due. This integration provides a familiar and accessible platform for developers and hobbyists alike. The inclusion of a USB port simplifies programming and data transfer, while onboard LEDs offer visual feedback. An SD card slot enables data logging directly on the device, crucial for capturing vehicle data for analysis. EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) provides non-volatile storage for configuration settings or custom code. The modularity of the processor board is a key advantage, allowing for future upgrades or replacements as processing technology advances, ensuring the longevity of your Macchina M2 OBDII investment. An XBee-compatible socket further enhances connectivity options, supporting Bluetooth, WiFi, or even cellular data modules, opening up possibilities for wireless communication and remote vehicle interaction.
The Macchina M2 OBDII is available in two form factors: an under-the-dash version designed to plug directly into the standard OBDII port, and an under-the-hood variant with a connector for custom wiring harnesses for more permanent or concealed installations. The under-the-dash model provides convenient power and connectivity, mirroring the simplicity of standard OBDII dongles, while the under-the-hood option caters to users requiring a more integrated and robust setup.
Software Ecosystem: Arduino and Beyond
The Macchina M2 OBDII leverages the widely adopted Arduino ecosystem for its software development environment. The “getting started guide” clearly outlines the process of installing the Arduino IDE and configuring it to recognize the M2 board, making the initial setup process straightforward for anyone with Arduino experience. Working with automotive protocols necessitates specialized libraries, and while some were still under development at the time of the original article, the goal was to provide comprehensive Arduino library support for all the M2’s communication interfaces. This ambition to enable protocol access through simple Arduino sketches underscores Macchina’s commitment to user-friendliness and accessibility.
For users who prefer to interface with the Macchina M2 OBDII from a PC, several options are available. Support for SavvyCAN, a popular open-source CAN analysis tool, is readily provided. Furthermore, the integration of SocketCAN is in progress, promising compatibility with standard Linux tools such as Wireshark, expanding the range of software options for network analysis and diagnostics. The open nature of the Macchina M2 OBDII platform is a significant strength. Its capacity to emulate various devices through software opens the door to compatibility with a wide range of existing car hacking tools, further enhancing its versatility and utility within the automotive hacking community.
Despite the hardware’s robust capabilities, the software landscape was still evolving at the time of the initial launch. Macchina actively sought to engage developers to contribute to the software ecosystem, recognizing that community contributions would be crucial to unlocking the full potential of the Macchina M2 OBDII. The open-source nature of the project serves as a catalyst for expanding the device’s software functionalities and ensuring its ongoing development and adaptation to the ever-changing automotive technology landscape.
Macchina M2 OBDII: A Step Above ELM327 Dongles
 An ELM327 Device
An ELM327 Device
It’s common for discussions about OBDII dongles to quickly bring up ELM327 devices, praised for their affordability and accessibility. While ELM327 dongles serve a purpose, particularly for basic code reading and clearing “check engine” lights (or “Malfunction Indication Lamps” in automotive engineering terminology), the Macchina M2 OBDII occupies a different tier of functionality and capability.
ELM327 devices, while inexpensive, have inherent limitations. Their reliance on ASCII communication over Bluetooth Serial Port Profile (SPP) creates bottlenecks in data throughput and incompatibility with iOS devices. Customization is virtually non-existent, and they lack onboard storage for data logging. Security concerns also arise, with default Bluetooth PINs like “1234” posing a risk of unauthorized access.
The Macchina M2 OBDII addresses these shortcomings directly. While it comes at a higher price point than basic ELM327 dongles, the M2 delivers a vastly superior platform for serious automotive work. Its hardware is designed for high-speed communication across multiple protocols, its open-source nature fosters software customization and expansion, and its modular design ensures future adaptability. The Macchina M2 OBDII is not just an OBDII reader; it’s a comprehensive automotive interface and development platform.
Conclusion: Unleashing Automotive Innovation with Macchina M2 OBDII
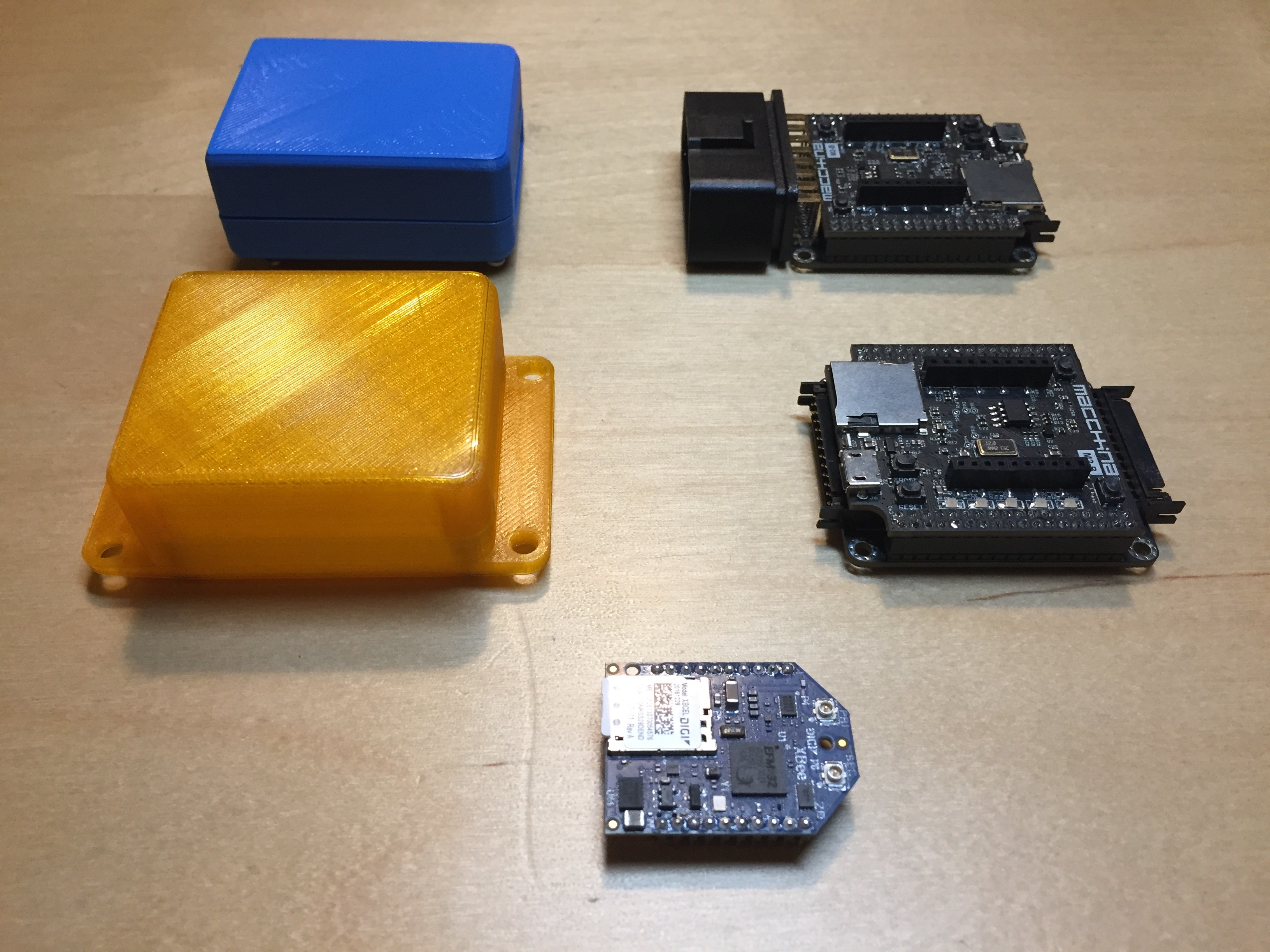 img_0032
img_0032
The Macchina M2 OBDII emerges as a compelling piece of hardware for individuals passionate about automotive hacking and customization. While the software side was still under active development during its initial release, the fundamental hardware platform is robust and ready for developers and enthusiasts to explore its potential. The developer release, initially priced at $99, provided early access to this innovative hardware, encouraging community involvement and software development.
The potential applications of the Macchina M2 OBDII are extensive. It can function as a high-speed, standalone vehicle data recorder, capturing critical vehicle parameters for performance analysis or diagnostics. The under-the-dash model can act as a bridge to integrate aftermarket components seamlessly into a vehicle’s CAN bus, enabling features like advanced head unit integration with steering wheel controls and vehicle speed-sensitive volume adjustments. With the addition of Bluetooth, the M2 OBDII can form the basis of custom vehicle immobilizer and remote control systems. Furthermore, cellular connectivity unlocks possibilities for vehicle tracking and even remote vehicle shutdown capabilities.
Macchina’s proven track record of delivering hardware and its commitment to open-source principles position the M2 OBDII as a valuable asset for the automotive hacking community. It’s a tool that empowers users to delve deeper into their vehicles’ systems, innovate new functionalities, and contribute to the growing field of automotive technology. For anyone seeking to move beyond basic OBDII diagnostics and truly understand and interact with their car’s inner workings, the Macchina M2 OBDII is a powerful and versatile platform worth exploring.
