Clearing OBDII error codes is simple with the right tools and knowledge, allowing you to address minor issues yourself. CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality OBDII scanners that make diagnosing and resolving car problems easier than ever. Learning how to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and using an OBDII code eraser can save you time and money.
1. Understanding OBDII Error Codes and Your Car
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) system is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured after 1996 to monitor the performance of the engine and other major components. When the system detects a problem, it generates an error code, also known as a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), which illuminates the check engine light on your dashboard. Understanding these codes is the first step in addressing the issue.
-
What are OBDII Error Codes? OBDII error codes are alphanumeric codes that provide information about the specific problem detected by your car’s onboard computer. These codes help mechanics and car owners diagnose and repair issues efficiently.
-
Importance of Addressing Error Codes: While some error codes may indicate minor issues, others can signal serious problems that can lead to further damage or safety risks if left unaddressed. Regularly checking and understanding these codes ensures your vehicle operates optimally and safely.
1.1 Common Categories of OBDII Error Codes
OBDII error codes are categorized into several groups, each representing a different system or component of the vehicle. Here’s a brief overview of the main categories:
- P0 Codes (Powertrain): These codes relate to the engine, transmission, and related components.
- P1 Codes (Manufacturer Specific Powertrain): These are powertrain codes specific to the vehicle manufacturer.
- B Codes (Body): These codes pertain to body-related systems, such as airbags, power windows, and seats.
- C Codes (Chassis): These codes refer to chassis systems, including ABS, brakes, and suspension.
- U Codes (Network): These codes indicate issues with the vehicle’s communication network.
1.2 Tools You’ll Need
Before you begin, make sure you have the necessary tools. The most important tool is an OBDII scanner, which you can purchase from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- OBDII Scanner: This device plugs into your car’s OBDII port and reads the error codes stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Code Reader/Eraser: Some basic code readers can only read codes but can’t erase trouble codes. So make sure to get a reader that can do both.
- Vehicle Repair Manual: This manual provides detailed information about your car’s systems and components, as well as repair procedures.
- Internet Access: Access to online databases and forums can help you research specific error codes and find solutions.
1.3 Safety Precautions
Before working on your vehicle, it’s important to take certain safety precautions to protect yourself and your car.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris and fluids.
- Use Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, grease, and chemicals.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- Disconnect the Battery: Disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery can prevent electrical shocks and damage to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Refer to the Vehicle’s Repair Manual: Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for specific repair procedures.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Clearing OBDII Error Codes
Clearing OBDII error codes involves several steps, from identifying the OBDII port to verifying that the issue has been resolved. Here is a comprehensive guide to help you through the process.
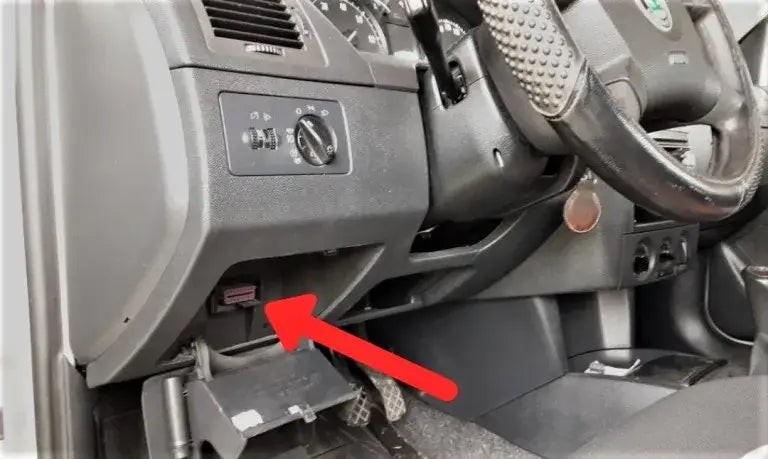
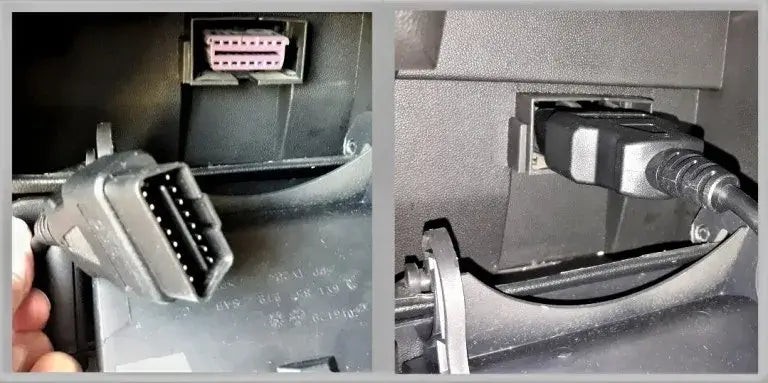
2.1 Locating the OBDII Port
The OBDII port is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It is a 16-pin connector and is easily identifiable.
- Typical Locations: Check under the steering wheel column, near the pedals, or in the glove compartment.
- Consult Your Vehicle’s Manual: If you can’t find the port, refer to your car’s manual for the exact location.
2.2 Connecting the OBDII Scanner
Once you’ve located the OBDII port, plug in your OBDII scanner.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Make sure the car’s ignition is turned off before plugging in the scanner.
- Firmly Insert the Scanner: Plug the scanner into the OBDII port until it is securely connected.
- Power On the Scanner: Some scanners will power on automatically, while others may require you to press a power button.
2.3 Reading the Error Codes
With the scanner connected, turn on the ignition to the “on” position without starting the engine. Follow the scanner’s prompts to read the error codes.
- Turn Ignition to “On” Position: This provides power to the vehicle’s computer without starting the engine.
- Navigate the Scanner Menu: Use the scanner’s menu to select the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option.
- Record the Codes: Write down all the error codes that appear on the scanner’s screen.
2.4 Interpreting the Error Codes
Interpreting the error codes is crucial to understanding the underlying issues.
- Use a Code Database: Refer to a reliable OBDII code database, either online or in your vehicle’s repair manual, to look up the meaning of each code.
- Understand the Severity: Determine the severity of each issue. Some codes may indicate minor problems, while others may point to more serious conditions.
- Prioritize Issues: Address the most critical issues first to prevent further damage to your vehicle.
Here’s an example of some common OBDII codes and their meanings:
| Code | Meaning | Potential Issue |
|---|---|---|
| P0101 | Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor Range/Performance | Dirty or faulty MAF sensor, intake leaks |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, fuel injectors |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Failing catalytic converter, exhaust leaks, faulty oxygen sensors |
| P0442 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected | Loose or damaged fuel cap, cracked hoses, faulty purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Air Control System Malfunction | Dirty or faulty idle air control valve, vacuum leaks |
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, MAF sensor issue, fuel delivery problem |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, MAF sensor issue, fuel delivery problem |
| P0301 | Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector |
| P0302 | Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected | Faulty spark plug, ignition coil, fuel injector |
| P0401 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Insufficient Detected | Clogged EGR valve, faulty EGR solenoid |
| P0402 | Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Flow Excessive Detected | Faulty EGR valve, faulty EGR solenoid |
| P0411 | Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect Flow Detected | Faulty air pump, vacuum leak |
| P0455 | Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large Leak) | Loose fuel cap, damaged fuel tank |
| P0507 | Idle Air Control (IAC) System RPM Higher Than Expected | Vacuum leak, faulty IAC valve |
| P0700 | Transmission Control System Malfunction | Faulty transmission control module (TCM) |
| P0741 | Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off | Faulty torque converter, solenoid |
| P1131 | Lack of HO2S Switch – Sensor Indicates Lean – Bank No. 1 Sensor No. 1 | Vacuum leak, faulty O2 sensor |
| P1132 | Lack of HO2S Switch – Sensor Indicates Rich – Bank No. 1 Sensor No. 1 | Faulty O2 sensor, fuel injector issue |



2.5 Addressing the Underlying Issues
Before clearing the error codes, it’s essential to address the underlying issues causing the codes.
- Perform Necessary Repairs: Depending on the error codes, perform the necessary repairs or replacements. This may involve replacing a faulty sensor, fixing a leak, or repairing a damaged component.
- Test the Fix: After making the repairs, test the vehicle to ensure the issue has been resolved. This may involve driving the car for a certain period or performing specific diagnostic tests.
2.6 Clearing the Error Codes
Once you’ve addressed the underlying issues, you can proceed to clear the error codes.
- Navigate to the “Clear Codes” Option: Use the scanner’s menu to select the “Clear Codes” or “Erase Codes” option.
- Confirm the Action: The scanner may ask you to confirm that you want to clear the codes. Select “Yes” to proceed.
- Wait for Confirmation: The scanner will clear the codes and display a confirmation message.
2.7 Verifying the Clear
After clearing the codes, verify that the check engine light has turned off and that the codes have been successfully cleared.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Turn off the car’s ignition and remove the OBDII scanner.
- Restart the Engine: Start the engine and check if the check engine light is off.
- Re-Scan for Codes: Use the OBDII scanner to re-scan the vehicle for any remaining or new error codes. If the check engine light comes back on or new codes appear, it indicates that the underlying issue has not been fully resolved.
3. Advanced Tips for Using OBDII Scanners
To get the most out of your OBDII scanner, consider these advanced tips:
- Live Data Streaming: Many advanced scanners offer live data streaming, allowing you to monitor various parameters in real-time. This can be useful for diagnosing intermittent issues or monitoring engine performance.
- Freeze Frame Data: Freeze frame data captures a snapshot of the vehicle’s operating conditions when an error code was triggered. This can provide valuable clues for diagnosing the problem.
- Software Updates: Keep your OBDII scanner’s software up to date to ensure it has the latest features and code definitions.
- Professional-Grade Scanners: Consider investing in a professional-grade scanner for more advanced diagnostics and features, such as bi-directional control and advanced system testing.
4. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Clearing OBDII Error Codes
Clearing OBDII error codes is a straightforward process, but it’s important to avoid common mistakes that can lead to further issues.
- Clearing Codes Without Addressing the Underlying Issue: Clearing codes without fixing the problem will only result in the check engine light coming back on. Always address the root cause of the error before clearing the codes.
- Using Low-Quality Scanners: Cheap, low-quality scanners may not provide accurate information or may damage your vehicle’s computer. Invest in a reputable OBDII scanner from CARDIAGTECH.NET to ensure accurate diagnostics.
- Ignoring Serious Error Codes: Some error codes indicate serious problems that require immediate attention. Ignoring these codes can lead to further damage and safety risks.
- Disconnecting the Battery Instead of Using a Scanner: While disconnecting the battery can clear some error codes, it can also reset other important systems in your vehicle, such as the radio and security system. It’s best to use an OBDII scanner to clear codes properly.
- Forcing the Connector: Forcing the OBDII scanner into the port can damage the connector. Ensure it aligns correctly and inserts smoothly.
- Not Consulting a Professional: If you’re unsure about how to interpret an error code or perform a repair, consult a professional mechanic.
5. The Benefits of Owning an OBDII Scanner
Owning an OBDII scanner can provide numerous benefits for car owners and enthusiasts.
- Early Problem Detection: Detect potential issues early, preventing costly repairs.
- Informed Decision-Making: Make informed decisions about car repairs, saving money on unnecessary mechanic visits.
- DIY Repairs: Perform simple repairs yourself, saving time and money.
- Vehicle Health Monitoring: Regularly monitor your vehicle’s health, ensuring optimal performance and safety.
- Negotiating Repairs: Use the information from the scanner to negotiate fair prices with mechanics.
6. Choosing the Right OBDII Scanner
Selecting the right OBDII scanner depends on your needs and budget. Here are some factors to consider:
- Functionality: Determine whether you need a basic code reader or a more advanced scanner with features like live data streaming and bi-directional control.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Ease of Use: Look for a scanner with an intuitive interface and clear instructions.
- Price: Set a budget and compare prices from different brands and models.
- Reviews: Read reviews from other users to get an idea of the scanner’s reliability and performance.
Some popular OBDII scanners available at CARDIAGTECH.NET include:
| Model | Features | Price | User Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGSULIT SC301 | Basic code reading and clearing, DTC lookup | $39.99 | Beginner |
| Autel MaxiCheck MX808 | Advanced diagnostics, bi-directional control, service resets | $349.00 | Intermediate |
| BlueDriver Pro | Smartphone-based, advanced diagnostics, live data | $119.95 | Intermediate |
| Launch X431 V+ | Professional-grade, comprehensive diagnostics, coding and programming | $1,299.00 | Professional |
| Innova 3100j | Code reading, clearing, battery and alternator check | $79.99 | Beginner |
7. Maintenance and Care for Your OBDII Scanner
Proper maintenance and care can extend the life of your OBDII scanner and ensure it continues to provide accurate readings.
- Store in a Safe Place: Store the scanner in a clean, dry place away from extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Keep the Connector Clean: Clean the connector regularly to remove dirt and debris that can interfere with the connection.
- Protect the Screen: Use a screen protector to prevent scratches and damage to the display.
- Update Software Regularly: Keep the scanner’s software updated to ensure it has the latest features and code definitions.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or mishandling the scanner, as this can damage the internal components.
- Check the Cable: Regularly inspect the cable for any signs of wear and tear. Replace it if necessary to ensure a reliable connection.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Do not leave the scanner in direct sunlight or in a hot car, as this can damage the electronics.
- Use the Correct Voltage: Ensure the scanner is compatible with the voltage of your vehicle’s electrical system.
8. When to Seek Professional Help
While an OBDII scanner can help you diagnose and fix many car problems, there are times when it’s best to seek professional help.
- Unfamiliar Error Codes: If you’re unsure about how to interpret an error code or perform a repair, consult a professional mechanic.
- Complex Repairs: Complex repairs that require specialized tools or knowledge should be left to a professional.
- Recurring Issues: If the check engine light keeps coming back on after clearing the codes, it may indicate a more serious underlying issue that requires professional attention.
- Safety Concerns: If you’re concerned about your safety or the safety of your vehicle, don’t hesitate to seek professional help.
- Emissions Problems: Issues related to emissions can be complex and may require specialized diagnostic equipment.
- Engine Problems: Engine-related issues can be serious and should be diagnosed and repaired by a qualified mechanic.
- Transmission Problems: Transmission issues often require specialized knowledge and tools to diagnose and repair.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Clearing OBDII Error Codes
To illustrate the practical application of clearing OBDII error codes, here are a few real-world case studies:
Case Study 1: Replacing a Faulty Oxygen Sensor
Problem: A car owner noticed the check engine light was on and used an OBDII scanner to read the code P0131, indicating a faulty oxygen sensor.
Solution: The car owner purchased a new oxygen sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET and followed the vehicle’s repair manual to replace the faulty sensor. After replacing the sensor, the car owner cleared the error code using the OBDII scanner. The check engine light turned off, and the car ran smoothly.
Outcome: The car owner saved money by performing the repair themselves and avoided a costly visit to the mechanic.
Case Study 2: Fixing a Loose Gas Cap
Problem: A driver saw the check engine light illuminate on their dashboard. They used an OBDII scanner and found the code P0455, indicating a large evaporative emission control system leak.
Solution: The driver checked the gas cap and found it was loose. They tightened the gas cap and cleared the error code using the OBDII scanner.
Outcome: The check engine light turned off, and the driver resolved the issue quickly and easily without any additional repairs.
Case Study 3: Diagnosing a Misfire
Problem: A vehicle was running rough, and the check engine light was flashing. An OBDII scan revealed a P0300 code, indicating a random misfire.
Solution: The owner checked the spark plugs, ignition coils, and fuel injectors. They found a faulty ignition coil on cylinder 3. After replacing the ignition coil, they cleared the code.
Outcome: The engine ran smoothly again, and the check engine light stayed off.
Case Study 4: MAF Sensor Issue
Problem: A car was experiencing poor fuel economy and had a rough idle. The OBDII scan showed a P0101 code, indicating a problem with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
Solution: The owner cleaned the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner. After cleaning the sensor and clearing the code, the car’s performance improved.
Outcome: The car’s fuel economy improved, and the rough idle was resolved.
10. FAQ About Clearing OBDII Error Codes
Here are some frequently asked questions about clearing OBDII error codes:
- Will clearing the OBDII error code pass the smog test? No, if the underlying problem is not fixed, clearing the code will only temporarily turn off the check engine light. The code will return, and the car will fail the smog test.
- How long does it take for the check engine light to go off after the fix? It depends on the problem and the car’s driving cycle. Some lights go off immediately after the fix and code clearing, while others take several driving cycles.
- Is it safe to drive with the check engine light on? It depends on the nature of the problem. If the light is flashing, it indicates a severe problem, and driving should be avoided. If the light is steady, it’s generally safe to drive, but the problem should be checked soon.
- Can I use any OBDII scanner for my car? Most OBDII scanners are compatible with all cars made after 1996, but it’s always a good idea to check the scanner’s compatibility with your car model.
- How often should I check for OBDII error codes? It’s a good practice to check for codes whenever you notice unusual behavior in your car or at least once a month.
- Can clearing the OBDII error code damage my car? Clearing the code itself won’t damage the car, but ignoring the underlying problem can lead to more damage.
- What does it mean if the check engine light comes back on after clearing the code? It means the underlying problem was not fixed, and the car’s computer has detected the issue again.
- Can I clear the OBDII error code myself? Yes, you can clear the code yourself with an OBDII scanner after fixing the underlying problem.
- Where can I find a reliable OBDII code database? There are many online databases, such as those provided by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and reputable automotive websites. Also, CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- What is the difference between OBD1 and OBD2? OBD1 is an older system used in cars before 1996, while OBD2 is a standardized system used in cars made after 1996. OBD2 provides more detailed and comprehensive diagnostics.
Conclusion: Empowering You to Clear OBDII Error Codes
Understanding and clearing OBDII error codes can save you time and money while keeping your vehicle running smoothly. By following this comprehensive guide and using the right tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can confidently diagnose and address many common car problems. Remember to always address the underlying issues before clearing the codes and seek professional help when needed. With the right knowledge and tools, you can empower yourself to take control of your car’s health and maintenance.
Ready to take control of your car’s diagnostics? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET to explore our wide range of OBDII scanners and diagnostic tools. Let us help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.

