Eobd/obdii Error P2017, signaling “Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor/Switch Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 1),” can lead to diminished engine performance and fuel economy. At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we understand the urgency of addressing such issues, offering cutting-edge diagnostic tools and equipment to pinpoint and resolve these problems efficiently. Ignoring the P2017 code could potentially result in more significant engine complications; therefore, prompt diagnosis and repair are vital.
1. Understanding the EOBD/OBDII Error Code P2017
The P2017 error code indicates that the engine control unit (ECU) has detected an issue with the intake manifold runner control (IMRC) system, specifically relating to the runner position sensor or switch circuit for bank 1. This system is designed to optimize airflow into the engine based on driving conditions, and a malfunction can have adverse effects.
1.1. Decoding the Error Code
- P2017: Designates the specific error code within the OBDII system.
- Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor/Switch Circuit: Identifies the component and circuit in question.
- Range/Performance: Signals that the sensor’s signal is outside the expected range or that the system is not performing as expected.
- Bank 1: Refers to the side of the engine containing cylinder number 1.
1.2. Role of the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) System
The IMRC system utilizes valves or flaps within the intake manifold to adjust the length of the intake runners. At low engine speeds, the runners are lengthened to increase air velocity and improve cylinder filling, enhancing torque and fuel efficiency. At higher speeds, the runners are shortened to maximize airflow and boost horsepower.
1.3. Symptoms Associated with Error Code P2017
- Illuminated check engine light.
- Decreased engine performance.
- Reduced fuel economy.
- Rough idling.
- Hesitation during acceleration.
- Potential stalling.
- Failed emissions test.
2. Common Causes of the P2017 Error Code
Several factors can trigger the P2017 error code, ranging from electrical issues to mechanical failures. Let’s explore some of the primary causes behind this OBDII trouble code, offering insights that help you understand and tackle these issues effectively.
2.1. Defective Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor
The sensor itself may be faulty, providing inaccurate readings to the ECU.
2.2. Wiring and Connector Issues
Damaged, corroded, or loose wiring and connectors in the sensor circuit can disrupt the signal.
2.3. Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks in the IMRC system can cause the valves to operate incorrectly.
2.4. Malfunctioning IMRC Actuator
The actuator that controls the movement of the intake manifold runners may be failing or stuck.
2.5. Carbon Buildup
Excessive carbon buildup on the intake manifold runners and valves can impede their movement.
2.6. Faulty ECU
In rare cases, a malfunctioning ECU can generate false error codes.
3. Diagnostic Steps to Identify the Root Cause
Diagnosing the P2017 error code requires a systematic approach to pinpoint the underlying issue. Here’s a detailed guide to help you effectively troubleshoot the problem.
3.1. Visual Inspection
Inspect the intake manifold, wiring, and connectors for any visible signs of damage, corrosion, or disconnection. Ensure that all vacuum lines are properly connected and free from cracks or leaks.
3.2. Scan Tool Diagnosis
- Connect an OBDII scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Retrieve all stored error codes and freeze frame data.
- Clear the P2017 error code and perform a test drive to see if it returns.
- Monitor the IMRC system’s data using the scanner to check the sensor’s readings and actuator’s performance.
3.3. Sensor Testing
- Locate the intake manifold runner position sensor.
- Use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage and resistance, comparing the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check the sensor’s signal while manually moving the intake manifold runners to ensure the signal changes accordingly.
3.4. Actuator Testing
- Locate the IMRC actuator.
- Use a scan tool to activate the actuator and observe its movement.
- Manually move the intake manifold runners to ensure they move freely.
- Check the actuator’s wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion.
3.5. Vacuum Leak Testing
- Use a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner to check for vacuum leaks around the intake manifold, vacuum lines, and IMRC system components.
- Listen for hissing sounds that may indicate a vacuum leak.
4. Step-by-Step Repair Procedures for P2017 Error Code
Addressing the P2017 error code involves specific repair procedures depending on the root cause identified during the diagnostic process. Below are comprehensive repair steps to effectively resolve the issue, ensuring your vehicle’s engine operates optimally.
4.1. Replacing the Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the faulty sensor.
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the sensor mounting bolts or screws.
- Install the new sensor, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the error codes and perform a test drive.
4.2. Repairing Wiring and Connectors
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Inspect the wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Repair any damaged wires by splicing and soldering new sections.
- Clean corroded connectors with a wire brush or electrical contact cleaner.
- Apply dielectric grease to the connectors to prevent future corrosion.
- Reconnect the wiring and connectors.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the error codes and perform a test drive.
4.3. Addressing Vacuum Leaks
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the vacuum leak using a smoke machine or carburetor cleaner.
- Replace any cracked or damaged vacuum lines.
- Tighten any loose connections.
- Seal any leaks in the intake manifold with a suitable sealant.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the error codes and perform a test drive.
4.4. Replacing the IMRC Actuator
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Locate the faulty actuator.
- Disconnect the electrical connector.
- Remove the actuator mounting bolts or screws.
- Install the new actuator, ensuring it is properly aligned.
- Reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the error codes and perform a test drive.
4.5. Cleaning Carbon Buildup
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Remove the intake manifold.
- Clean the intake manifold runners and valves with a carbon cleaner or solvent.
- Use a brush or scraper to remove stubborn carbon deposits.
- Reinstall the intake manifold.
- Reconnect the negative battery cable.
- Clear the error codes and perform a test drive.
Table: Common Tools and Equipment for Repairing P2017 Error
| Tool/Equipment | Description | Approximate Cost |
|---|---|---|
| OBDII Scanner | Reads and clears diagnostic trouble codes, monitors engine data. | $50 – $500+ |
| Multimeter | Tests voltage, resistance, and continuity in electrical circuits. | $20 – $200+ |
| Smoke Machine | Detects vacuum leaks by injecting smoke into the intake system. | $100 – $500+ |
| Carburetor Cleaner | Spray solvent used to locate vacuum leaks. | $5 – $20 |
| Socket Set | Used to remove and install bolts and nuts. | $20 – $200+ |
| Wrench Set | Used to tighten and loosen nuts and bolts. | $20 – $200+ |
| Screwdriver Set | Used to remove and install screws. | $10 – $100+ |
| Electrical Contact Cleaner | Cleans and protects electrical connections. | $5 – $20 |
| Dielectric Grease | Prevents corrosion on electrical connections. | $5 – $15 |
| Carbon Cleaner/Solvent | Cleans carbon deposits from intake manifold runners and valves. | $10 – $30 |






5. Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For more complex cases, advanced diagnostic techniques may be necessary to accurately diagnose the P2017 error code.
5.1. Oscilloscope Testing
An oscilloscope can be used to analyze the waveform of the intake manifold runner position sensor signal. This can help identify intermittent issues or subtle deviations that may not be apparent with a multimeter.
5.2. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording the IMRC system’s data over a period of time while driving. This data can be analyzed to identify patterns or anomalies that may be contributing to the error code.
5.3. ECU Testing
If all other components have been ruled out, the ECU may need to be tested to ensure it is functioning correctly. This typically requires specialized equipment and expertise.
6. Preventive Maintenance to Avoid P2017 Error Code
Preventive maintenance is crucial to avoid the P2017 error code and maintain the optimal performance of your vehicle’s engine. Here are some essential maintenance tips.
6.1. Regular Inspection of Vacuum Lines and Connections
Regularly inspect vacuum lines and connections for cracks, leaks, and loose fittings. Replace any damaged or worn components to prevent vacuum leaks.
6.2. Cleaning the Intake Manifold Regularly
Clean the intake manifold regularly to prevent carbon buildup on the runners and valves. Use a carbon cleaner or solvent to remove deposits and ensure smooth operation.
6.3. Using High-Quality Fuel and Additives
Use high-quality fuel and fuel additives to minimize carbon buildup and maintain the cleanliness of the intake system.
6.4. Periodic Sensor and Actuator Testing
Periodically test the intake manifold runner position sensor and IMRC actuator to ensure they are functioning correctly. Replace any faulty components promptly.
6.5. Following Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedule
Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for the intake system and related components. This includes replacing air filters, spark plugs, and other parts as needed.
Table: Preventive Maintenance Schedule for IMRC System
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inspect Vacuum Lines and Connections | Every 6 Months | Check for cracks, leaks, and loose fittings; replace as necessary. |
| Clean Intake Manifold | Every 2 Years | Remove carbon deposits from runners and valves using a carbon cleaner. |
| Test Sensor and Actuator | Every Year | Ensure proper function; replace if faulty. |
| Replace Air Filter | Every 12,000 – 15,000 Miles | Maintain optimal airflow and prevent debris from entering the intake system. |
| Use Fuel Additives | Every 3,000 Miles | Help prevent carbon buildup and keep the intake system clean. |
7. The Role of CARDIAGTECH.NET in Resolving P2017 Errors
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we offer a comprehensive range of diagnostic tools and equipment to assist you in resolving P2017 errors efficiently. Our products are designed to meet the needs of both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts, providing accurate and reliable results.
7.1. High-Quality Diagnostic Tools
We provide top-of-the-line OBDII scanners, multimeters, and other diagnostic tools to help you pinpoint the root cause of the P2017 error.
7.2. Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance throughout the diagnostic and repair process.
7.3. Comprehensive Training Resources
We offer a variety of training resources, including online tutorials, videos, and workshops, to help you improve your diagnostic and repair skills.
7.4. Reliable Parts and Components
We stock a wide selection of reliable parts and components for the IMRC system, including sensors, actuators, and vacuum lines, ensuring you have everything you need to complete the repair.
7.5. Cost-Effective Solutions
We offer cost-effective solutions to help you resolve P2017 errors without breaking the bank, providing affordable diagnostic tools and quality parts.
8. The Importance of Addressing the P2017 Error Code Promptly
Ignoring the P2017 error code can lead to various complications, affecting your vehicle’s performance and potentially causing more extensive damage. Addressing this issue promptly is crucial for several reasons.
8.1. Maintaining Optimal Engine Performance
The Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) system optimizes airflow into the engine, ensuring efficient combustion and peak performance. When the P2017 error occurs, it disrupts this process, leading to reduced power and acceleration. Addressing the issue promptly restores the engine’s optimal performance.
8.2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
A malfunctioning IMRC system can negatively impact fuel efficiency, causing the engine to consume more fuel than necessary. By fixing the P2017 error, you can restore the engine’s fuel efficiency, saving money on gas and reducing your carbon footprint.
8.3. Preventing Further Damage
If left unaddressed, the P2017 error can lead to more severe engine damage. For instance, the malfunctioning IMRC system can cause excessive carbon buildup, leading to valve damage and other issues. Addressing the error promptly prevents these complications.
8.4. Ensuring Vehicle Reliability
A properly functioning IMRC system is essential for the overall reliability of your vehicle. By addressing the P2017 error, you ensure that your vehicle operates smoothly and dependably, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
8.5. Enhancing Vehicle Longevity
By maintaining the IMRC system and addressing the P2017 error, you can extend the life of your vehicle. Proper maintenance and timely repairs help prevent wear and tear, ensuring your vehicle remains in good condition for years to come.
Table: Benefits of Addressing P2017 Error Promptly
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Optimal Engine Performance | Restores engine power and acceleration by ensuring efficient combustion. |
| Improved Fuel Efficiency | Reduces fuel consumption by optimizing airflow and combustion processes. |
| Prevents Further Damage | Avoids costly engine damage caused by carbon buildup and malfunctioning components. |
| Ensures Vehicle Reliability | Reduces the risk of breakdowns and ensures smooth operation. |
| Enhances Vehicle Longevity | Extends the life of the vehicle by preventing wear and tear and maintaining critical systems. |
9. Real-World Examples of P2017 Error Resolution
To illustrate the practical application of the diagnostic and repair procedures discussed, let’s examine a couple of real-world examples of how the P2017 error can be resolved.
9.1. Case Study 1: Faulty Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor
Scenario:
A 2015 Ford Mustang with 80,000 miles on it displayed a check engine light with the P2017 error code. The vehicle exhibited reduced engine performance and poor fuel economy.
Diagnosis:
Using an OBDII scanner, the technician confirmed the P2017 error code and monitored the intake manifold runner position sensor data. The sensor readings were erratic and did not correlate with the actual position of the intake manifold runners. A multimeter was used to test the sensor, revealing that it was providing incorrect voltage and resistance values.
Resolution:
The faulty intake manifold runner position sensor was replaced with a new, OEM-quality sensor from CARDIAGTECH.NET. After installation, the technician cleared the error codes and performed a test drive. The engine performance was restored, and the fuel economy improved significantly.
9.2. Case Study 2: Vacuum Leak in the IMRC System
Scenario:
A 2012 Chevrolet Cruze with 120,000 miles on it displayed a check engine light with the P2017 error code. The vehicle had a rough idle and hesitated during acceleration.
Diagnosis:
The technician used a smoke machine to check for vacuum leaks in the IMRC system. A significant leak was detected in a cracked vacuum line connecting to the intake manifold. The OBDII scanner showed that the IMRC actuator was not functioning correctly due to the vacuum leak.
Resolution:
The cracked vacuum line was replaced with a new, high-quality vacuum line from CARDIAGTECH.NET. After replacing the line, the technician cleared the error codes and performed a test drive. The rough idle and hesitation during acceleration were resolved, and the vehicle’s overall performance improved.
10. Why Choose CARDIAGTECH.NET for Your Automotive Needs?
Choosing the right supplier for your automotive diagnostic tools and parts is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable repairs. CARDIAGTECH.NET stands out as a trusted provider, offering numerous benefits that cater to both professional technicians and DIY enthusiasts.
10.1. Extensive Product Range
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of automotive diagnostic tools, equipment, and parts, ensuring you can find everything you need to address the P2017 error and other automotive issues.
10.2. High-Quality Products
We source our products from reputable manufacturers, ensuring they meet the highest standards of quality and reliability. Our tools and parts are designed to provide accurate results and long-lasting performance.
10.3. Competitive Pricing
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers competitive pricing on all our products, making it affordable for both professionals and DIYers to access high-quality tools and parts.
10.4. Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced technicians is available to provide expert technical support and guidance. We can help you diagnose issues, select the right tools and parts, and guide you through the repair process.
10.5. Fast Shipping and Delivery
We understand the importance of getting your tools and parts quickly. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers fast shipping and delivery options to ensure you receive your order promptly.
10.6. Customer Satisfaction Guarantee
CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to customer satisfaction. We offer a hassle-free return policy and stand behind the quality of our products.
Table: Advantages of Choosing CARDIAGTECH.NET
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Extensive Product Range | Wide selection of diagnostic tools, equipment, and parts for various automotive needs. |
| High-Quality Products | Products sourced from reputable manufacturers, ensuring reliability and accuracy. |
| Competitive Pricing | Affordable pricing for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. |
| Expert Technical Support | Experienced technicians available to provide guidance and support. |
| Fast Shipping and Delivery | Quick and efficient shipping options to ensure timely delivery of orders. |
| Customer Satisfaction Guarantee | Commitment to customer satisfaction with a hassle-free return policy. |
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About EOBD/OBDII Error P2017
Here are some frequently asked questions about the P2017 error code to provide you with a better understanding of the issue and its solutions.
9.1. What Does the P2017 Code Mean?
The P2017 code indicates a problem with the intake manifold runner position sensor/switch circuit range/performance for bank 1. It means the engine control unit (ECU) has detected that the sensor’s signal is outside the expected range or that the intake manifold runner control system is not performing as expected.
9.2. Can I Drive with the P2017 Code?
While it is possible to drive with the P2017 code, it is not recommended. The issue can lead to reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, and potential damage to the engine. It is best to diagnose and repair the problem as soon as possible.
9.3. How Do I Fix the P2017 Code?
To fix the P2017 code, you need to diagnose the root cause of the problem and perform the appropriate repair. This may involve replacing the intake manifold runner position sensor, repairing wiring and connectors, addressing vacuum leaks, replacing the IMRC actuator, or cleaning carbon buildup.
9.4. How Much Does It Cost to Fix the P2017 Code?
The cost to fix the P2017 code can vary depending on the root cause of the problem and the repair procedures required. Replacing a faulty sensor may cost between $100 and $300, while addressing vacuum leaks or replacing the IMRC actuator may cost between $200 and $500. More complex repairs, such as cleaning carbon buildup or replacing the intake manifold, may cost more.
9.5. Can a Dirty Air Filter Cause the P2017 Code?
While a dirty air filter is not a direct cause of the P2017 code, it can contribute to poor engine performance and increased carbon buildup in the intake system, which can indirectly affect the IMRC system. Replacing the air filter regularly is a good preventive maintenance practice.
9.6. Can a Faulty Oxygen Sensor Cause the P2017 Code?
A faulty oxygen sensor is not a direct cause of the P2017 code, but it can affect the engine’s air-fuel mixture and combustion process, leading to increased carbon buildup in the intake system. This can indirectly affect the IMRC system and potentially trigger the P2017 code.
9.7. How Do I Test the Intake Manifold Runner Position Sensor?
To test the intake manifold runner position sensor, you can use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage and resistance, comparing the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. You can also monitor the sensor’s signal while manually moving the intake manifold runners to ensure the signal changes accordingly.
9.8. Can I Clean the Intake Manifold Without Removing It?
While it is possible to clean the intake manifold without removing it using chemical cleaners, it is not as effective as removing the manifold and cleaning it thoroughly. Removing the manifold allows you to access all the runners and valves for a more comprehensive cleaning.
9.9. What Are the Common Symptoms of a Vacuum Leak?
Common symptoms of a vacuum leak include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, poor fuel economy, hissing sounds, and the check engine light illuminating.
9.10. How Often Should I Clean My Intake Manifold?
The frequency of cleaning your intake manifold depends on your driving conditions and the quality of fuel you use. In general, it is recommended to clean the intake manifold every 2 years or 30,000 miles to prevent carbon buildup and maintain optimal engine performance.
Do you have any questions about the P2017 error code? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, or call us on Whatsapp at +1 (641) 206-8880. Visit our website CARDIAGTECH.NET for more information and to explore our range of diagnostic tools and equipment.
Alt: A mechanic carefully inspects an engine bay during an automotive repair, showcasing the complexity involved.
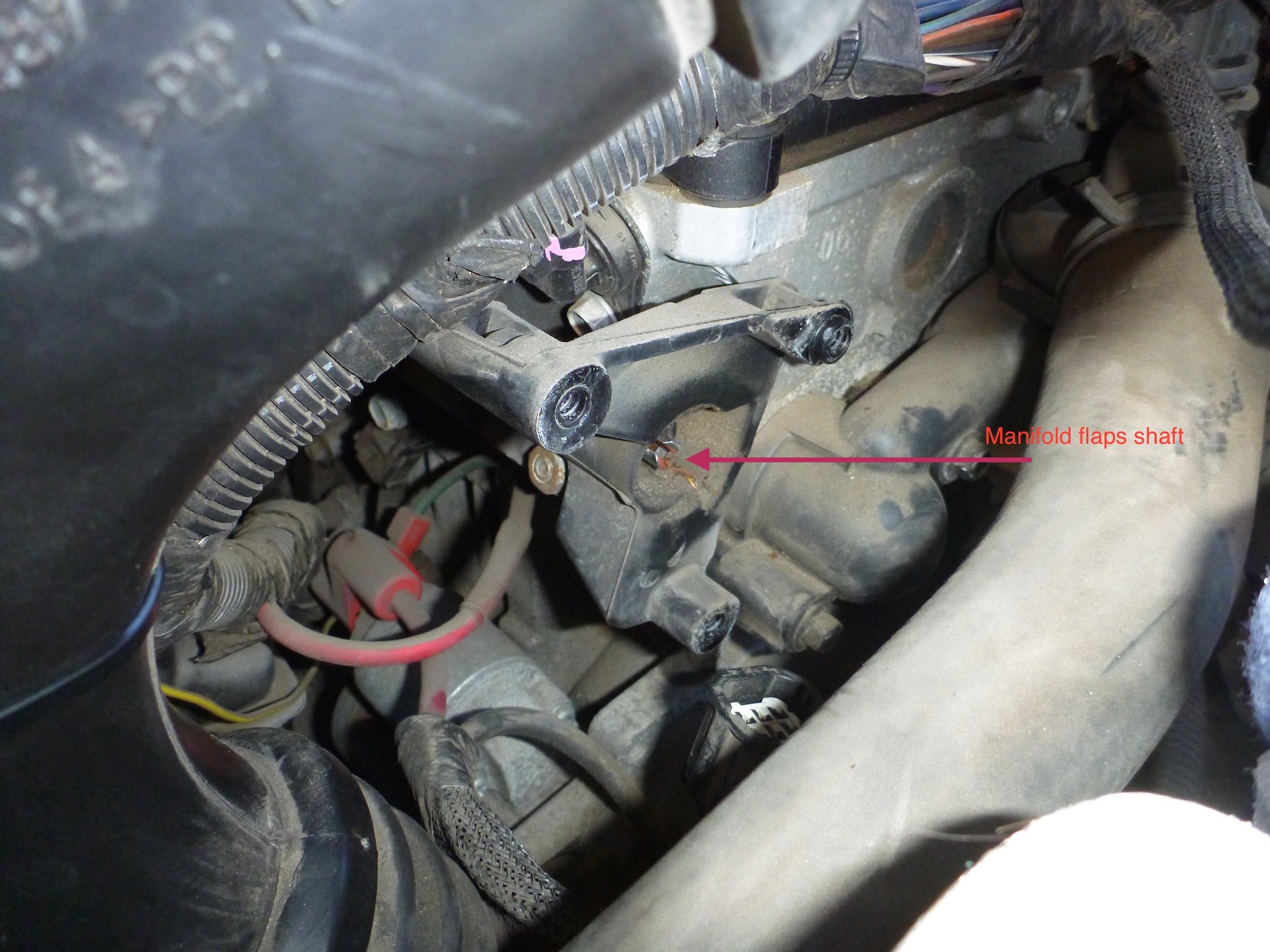
Alt: Close-up of intake manifold flaps reveals their role in controlling airflow for optimal engine performance.
Alt: A technician unscrews the air pipe to access the intake manifold for maintenance and diagnostics.
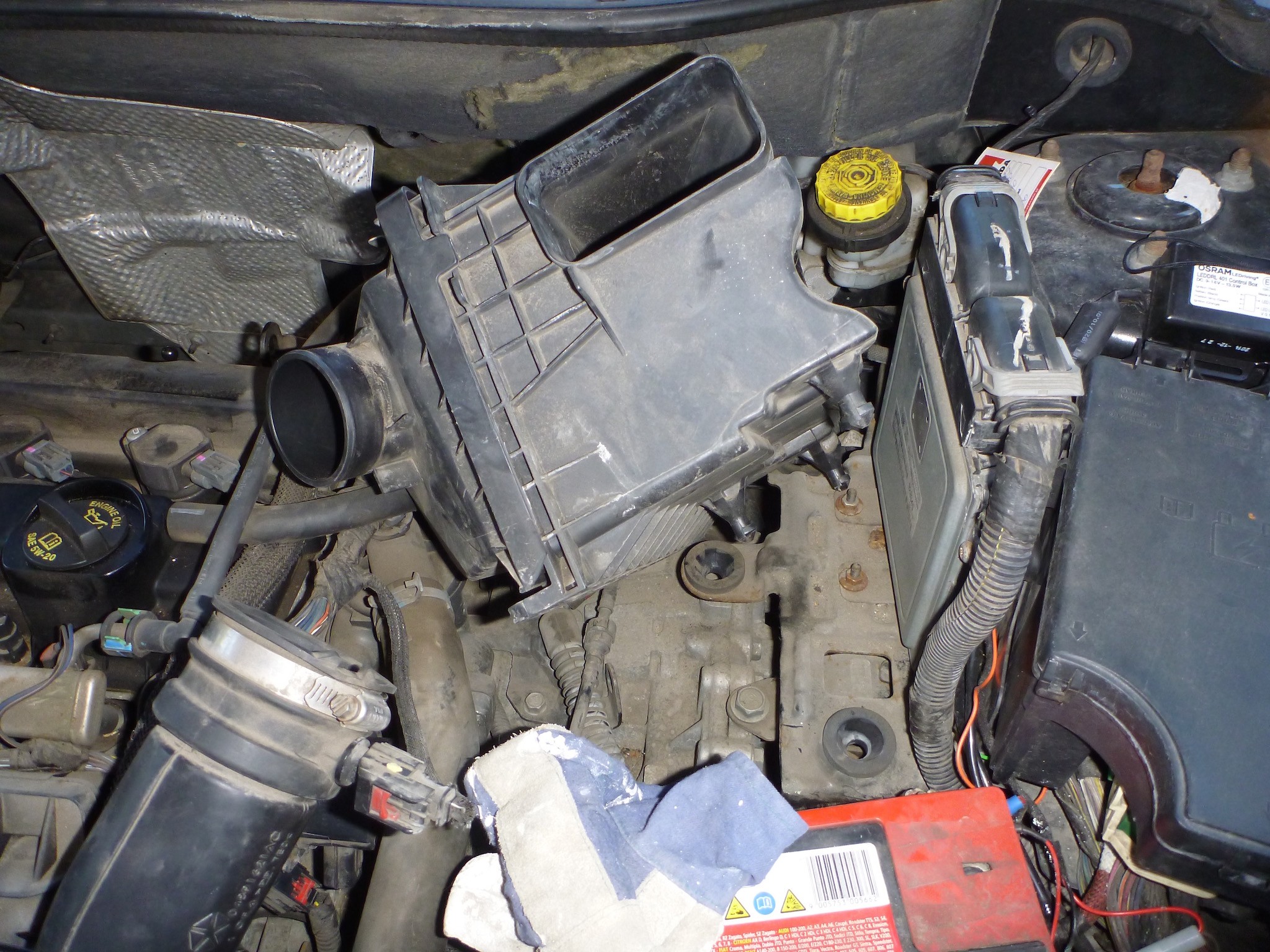
Alt: The airbox is removed to expose the engine components, essential for diagnosing intake manifold issues.
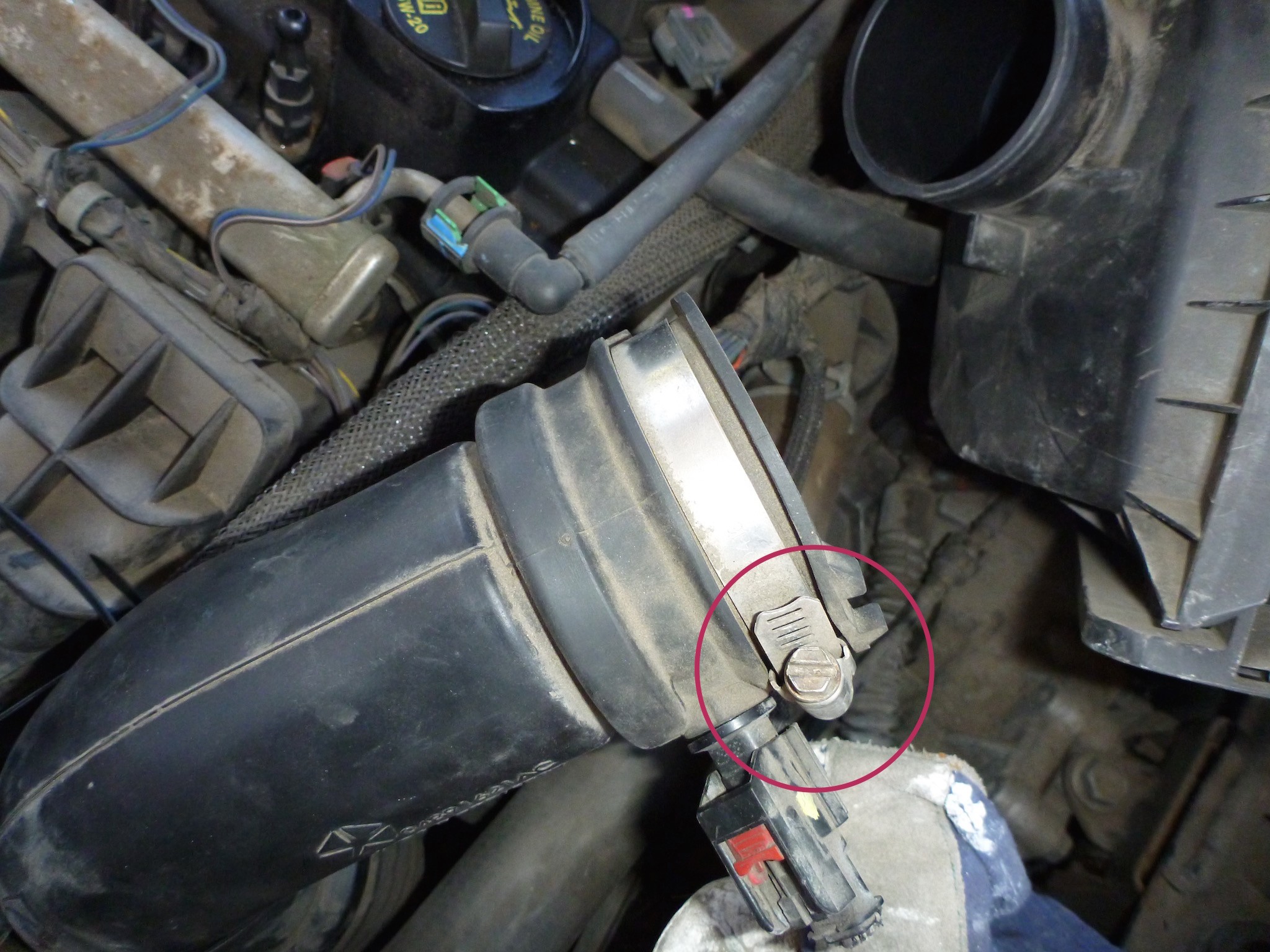
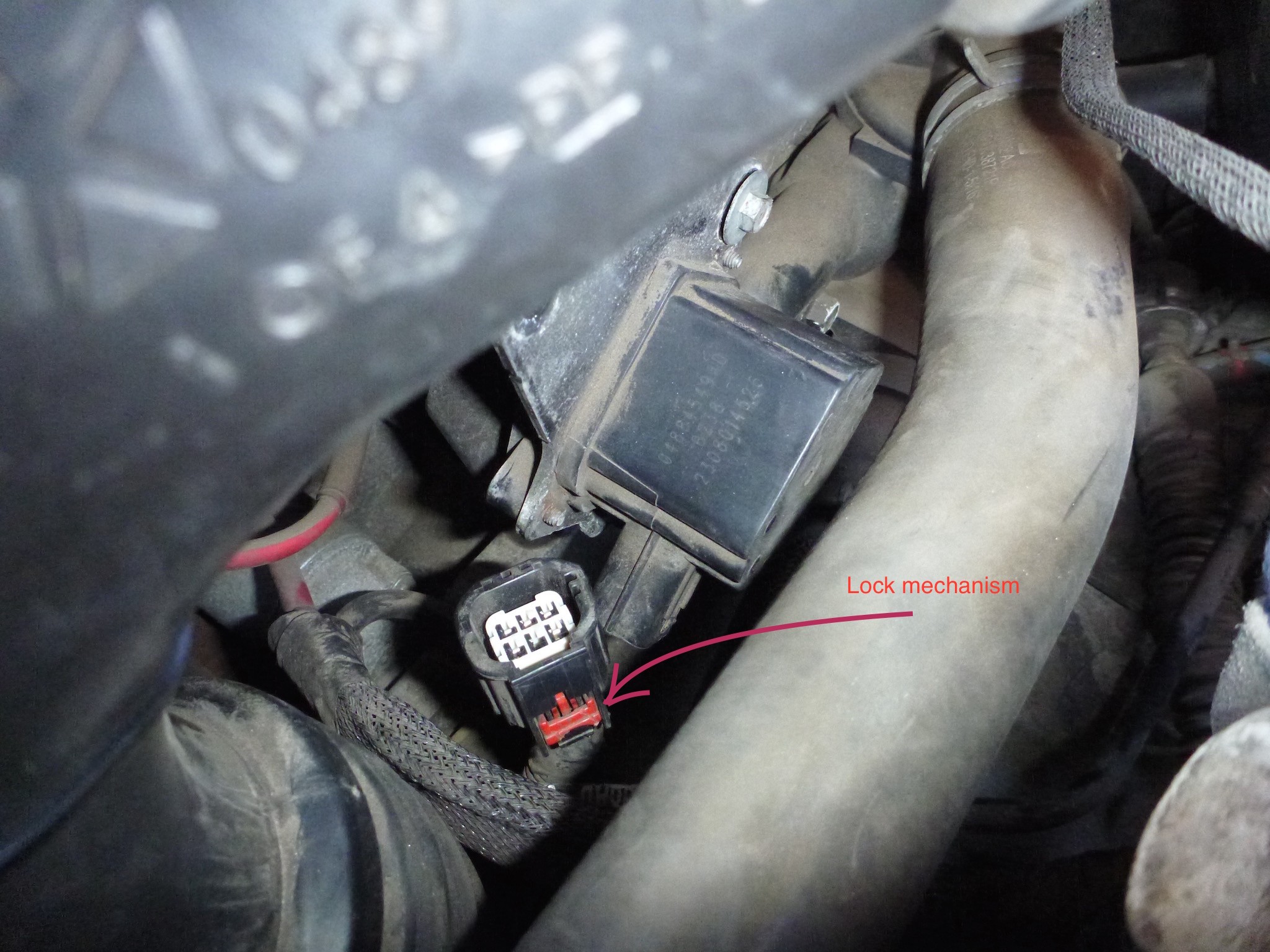
Alt: A close view of a faulty engine part, highlighting the electrical connector and spring mechanism involved in the intake manifold system.
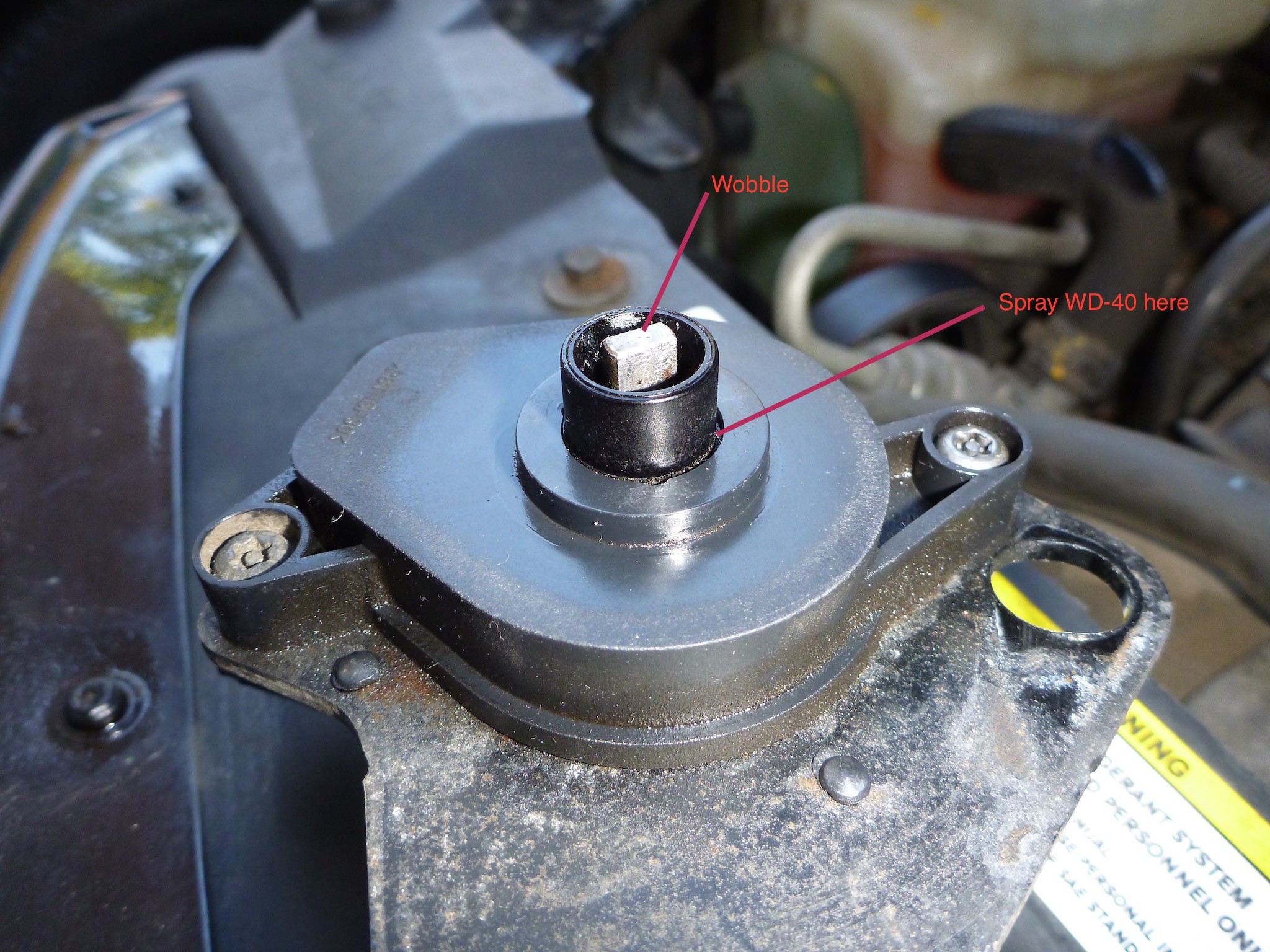
Alt: Inspection of the intake manifold flaps shaft for smooth rotation using a flat screwdriver, key to diagnosing P2017.
Alt: WD-40 lubricant being applied to the engine mechanism to loosen jammed parts during the repair process, crucial for unsticking components.
