Connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII port unlocks a wealth of diagnostic data and customization options. This article, brought to you by CARDIAGTECH.NET, provides a detailed guide on how to connect your laptop to your car’s OBDII system, empowering you to diagnose issues, monitor performance, and gain deeper insights into your vehicle’s health. Learning how to connect your laptop to your car’s computer, opening a world of possibilities, from reading diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) to live data streaming, and even performing advanced vehicle customizations with the right software and interface. Unlock your car’s hidden potential using vehicle diagnostic tools and car diagnostic software.
1. Understanding the OBDII System
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) system is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured since 1996. It monitors various engine and vehicle parameters, providing valuable information for diagnostics and maintenance. Understanding the OBDII system is the first step in unlocking your vehicle’s hidden data.
1.1. What is OBDII?
OBDII is a standardized system that allows technicians and vehicle owners to access information about a vehicle’s engine, emissions, and other systems. It’s like having a direct line to your car’s computer, giving you insights into its performance and potential issues. According to the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), OBDII was mandated to ensure vehicles meet stringent emission standards.
1.2. Why Connect Your Laptop to OBDII?
Connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII port offers several advantages:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Identify the cause of the “check engine” light.
- Monitor Real-Time Data: Track engine performance, sensor readings, and other vital parameters.
- Perform Advanced Diagnostics: Access manufacturer-specific codes and data for in-depth analysis.
- Customize Vehicle Settings: Adjust certain vehicle parameters (depending on the software and vehicle).
- Save Money on Repairs: Diagnose issues yourself and potentially avoid costly trips to the mechanic.
1.3. Common OBDII Protocols
Several OBDII protocols exist, each with its own communication method. Some common protocols include:
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| SAE J1850 PWM | Used primarily by Ford vehicles. Employs a variable pulse width to transmit data. |
| SAE J1850 VPW | Used primarily by General Motors vehicles. Employs a variable pulse width with a higher data rate than J1850 PWM. |
| ISO 9141-2 | Used by European and Asian vehicles. Employs an asynchronous serial communication protocol. |
| ISO 14230-4 (KWP2000) | An evolution of ISO 9141-2. Features faster data transfer rates and more advanced diagnostic capabilities. |
| CAN (ISO 15765-4) | The most modern and widely used protocol. Offers high-speed data transfer and supports advanced diagnostics and control functions. Required in all vehicles sold in the US since 2008. |

1.4. Understanding the OBDII Connector
The OBDII connector is a standardized 16-pin diagnostic port typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It provides a physical interface for accessing the vehicle’s diagnostic data.
2. Essential Equipment for Connecting Your Laptop
To connect your laptop to your car’s OBDII system, you’ll need specific hardware and software. Choosing the right tools is crucial for a successful and safe connection. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of high-quality OBDII scanners and software to meet your diagnostic needs. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and personalized recommendations.
2.1. OBDII Scanner/Adapter
An OBDII scanner or adapter serves as the interface between your car’s OBDII port and your laptop. These devices translate the data from your car into a format your laptop can understand.
- Bluetooth OBDII Adapters: Wireless and convenient, these adapters connect to your laptop via Bluetooth.
- Wi-Fi OBDII Adapters: Similar to Bluetooth adapters, but connect via Wi-Fi.
- USB OBDII Adapters: Wired connection for a reliable and stable data transfer.
2.2. Diagnostic Software
Diagnostic software is essential for interpreting the data received from the OBDII scanner. Many software options are available, each with its own features and capabilities.
- Free Software: Basic functionality for reading DTCs and monitoring real-time data.
- Paid Software: Offers advanced features like enhanced diagnostics, custom parameter identification (PID) support, and bidirectional control.
2.3. Laptop Requirements
Most laptops running Windows, macOS, or Linux can be used for OBDII diagnostics. Ensure your laptop meets the minimum system requirements for your chosen diagnostic software.
- Operating System: Windows 7/8/10/11, macOS 10.10+, Linux (check software compatibility).
- Processor: Intel Pentium or equivalent.
- RAM: 2GB or more.
- Storage: 100MB free space (minimum).
- Connectivity: Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or USB port.
3. Step-by-Step Guide: Connecting Your Laptop to Your Car’s OBDII
Follow these steps to successfully connect your laptop to your car’s OBDII system and start diagnosing your vehicle.
3.1. Locating the OBDII Port
The OBDII port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. It may be exposed or hidden behind a small panel. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you’re unsure of its location.
Alt: Key ignition position showing the ‘ON’ position marked with Roman numeral II, a common step when connecting a laptop to car OBDII.
3.2. Connecting the OBDII Scanner/Adapter
Plug the OBDII scanner/adapter into the OBDII port. Ensure it’s securely connected.
3.3. Establishing a Connection (Bluetooth/Wi-Fi/USB)
Depending on the type of adapter you’re using, follow these steps to establish a connection with your laptop:
3.3.1. Bluetooth Connection
- Enable Bluetooth: Turn on Bluetooth on your laptop.
- Pair the Adapter: Put the OBDII adapter in pairing mode (refer to the adapter’s manual).
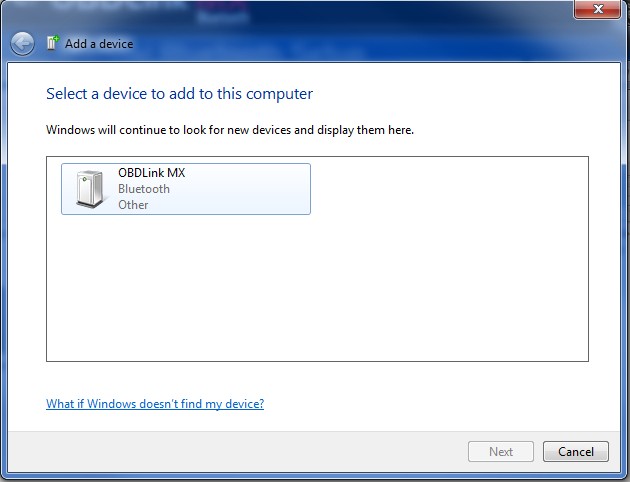
- Search for Devices: On your laptop, search for available Bluetooth devices.
- Select the Adapter: Select the OBDII adapter from the list of available devices.
- Enter PIN (if required): Enter the PIN code (usually “1234” or “0000”).
- Confirm Pairing: Confirm that the adapter is successfully paired.
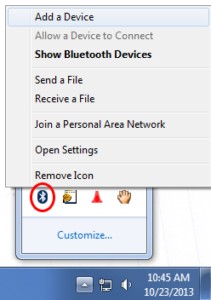
Alt: Opening the Windows System Tray to right-click the Bluetooth icon, a step in connecting a laptop to car OBDII via Bluetooth.
3.3.2. Wi-Fi Connection
- Turn on the Adapter: Plug the OBDII adapter into the OBDII port and turn it on.
- Connect to Wi-Fi Network: On your laptop, connect to the Wi-Fi network broadcasted by the OBDII adapter.
- Enter Password (if required): Enter the Wi-Fi password (refer to the adapter’s manual).
- Verify Connection: Verify that your laptop is successfully connected to the adapter’s Wi-Fi network.
3.3.3. USB Connection
- Install Drivers: Install the necessary USB drivers for the OBDII adapter (usually provided with the adapter or available on the manufacturer’s website).
- Connect the Adapter: Connect the OBDII adapter to your laptop using a USB cable.
- Verify Connection: Your laptop should automatically recognize the adapter.
3.4. Installing and Configuring Diagnostic Software
- Download Software: Download and install your chosen diagnostic software.
- Install Software: Follow the installation instructions provided by the software vendor.
- Configure Settings: Configure the software settings to match your OBDII adapter and vehicle.
- Select Communication Port: Select the correct communication port (COM port for USB, Bluetooth for Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi for Wi-Fi).
- Test Connection: Test the connection to ensure the software can communicate with the OBDII adapter.
3.5. Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
- Turn Ignition On: Turn your car’s ignition to the “ON” position (without starting the engine).
- Connect to Vehicle: In the diagnostic software, connect to your vehicle.
- Read DTCs: Select the option to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Interpret Codes: The software will display any stored DTCs. Use a DTC lookup tool or online resources to interpret the codes.
- Clear Codes (Optional): If desired, you can clear the DTCs after addressing the underlying issue.
4. Choosing the Right OBDII Scanner and Software
Selecting the appropriate OBDII scanner and software is crucial for accurate diagnostics and effective vehicle maintenance. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a diverse selection of high-quality tools to meet your specific needs. Here are some factors to consider when making your choice:
4.1. Compatibility
Ensure the OBDII scanner and software are compatible with your vehicle’s make, model, and year. Some scanners and software are designed for specific vehicle types or protocols.
4.2. Features and Functionality
Consider the features and functionality you need. Basic scanners can read and clear DTCs, while advanced scanners offer features like live data streaming, bidirectional control, and advanced diagnostics.
4.3. User Interface and Ease of Use
Choose a scanner and software with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and understand. A clear and intuitive interface can save you time and frustration.
4.4. Updates and Support
Ensure the scanner and software receive regular updates to support new vehicles and features. Also, check for reliable customer support in case you encounter any issues.
4.5. Budget
OBDII scanners and software range in price from affordable basic models to expensive professional-grade tools. Determine your budget and choose a scanner and software that offer the best value for your money.
4.6. Recommended OBDII Scanners and Software
Here are some recommended OBDII scanners and software options:
| Product | Description | Price (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | A versatile diagnostic scanner with a wide range of functions, including DTC reading/clearing, live data streaming, and bidirectional control. | $500 |
| Launch X431 V+ | A professional-grade diagnostic scanner with advanced features such as ECU coding, programming, and active testing. | $1,200 |
| BlueDriver Bluetooth Pro OBDII | A Bluetooth OBDII scanner that connects to your smartphone or tablet. Offers DTC reading/clearing, live data streaming, and repair reports. | $120 |
| OBDwiz (Free Software) | A free OBDII diagnostic software for Windows. Offers basic functionality for reading DTCs and monitoring real-time data. | Free |
| Torque Pro (Android App) | A popular Android app for OBDII diagnostics. Offers DTC reading/clearing, live data streaming, and customizable dashboards. | $5 |
| FORScan (Ford/Mazda Specific) | A powerful diagnostic software specifically designed for Ford and Mazda vehicles. Offers advanced features such as module programming, parameter resets, and custom configurations. | Free/Paid |
CARDIAGTECH.NET can help you find the perfect OBDII scanner and software for your needs. Contact us today at +1 (641) 206-8880 for a personalized consultation.
5. Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Encountering connection issues is not uncommon when connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII system. Here are some troubleshooting tips to help you resolve these problems:
5.1. Adapter Not Recognized
- Check Connection: Ensure the OBDII adapter is securely plugged into the OBDII port.
- Verify Power: Make sure the adapter is receiving power (check for LED lights).
- Install Drivers: Install the correct USB drivers for the adapter (if using a USB adapter).
- Restart Laptop: Restart your laptop and try again.
- Test on Another Vehicle: Test the adapter on another vehicle to rule out a faulty adapter.
5.2. Bluetooth Pairing Problems
- Enable Bluetooth: Ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your laptop.
- Put Adapter in Pairing Mode: Make sure the OBDII adapter is in pairing mode (refer to the adapter’s manual).
- Check PIN Code: Verify you’re using the correct PIN code (usually “1234” or “0000”).
- Remove and Re-Pair: Remove the adapter from the list of paired devices and re-pair it.
- Update Bluetooth Drivers: Update your laptop’s Bluetooth drivers.
Alt: Windows automatically discovering and displaying an OBDLink device, illustrating the pairing process of a laptop to car OBDII.
5.3. Software Connection Failures
- Select Correct Port: Ensure you’ve selected the correct communication port in the diagnostic software (COM port for USB, Bluetooth for Bluetooth, or Wi-Fi for Wi-Fi).
- Test Connection: Use the software’s built-in connection test to verify communication with the adapter.
- Firewall Issues: Temporarily disable your firewall to see if it’s blocking the connection.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your OBDII adapter and vehicle.
- Reinstall Software: Try reinstalling the diagnostic software.
5.4. No Data Displayed
- Turn Ignition On: Ensure your car’s ignition is turned to the “ON” position (without starting the engine).
- Select Correct Protocol: Some software requires you to manually select the correct OBDII protocol for your vehicle.
- Check Vehicle Compatibility: Verify that your vehicle is OBDII compliant.
- Faulty Sensor: A faulty sensor may prevent data from being displayed.
6. Safety Precautions and Best Practices
Connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII system can be a rewarding experience, but it’s essential to follow safety precautions and best practices to avoid damaging your vehicle or equipment.
6.1. Use Reliable Equipment
Only use high-quality OBDII scanners and software from reputable sources like CARDIAGTECH.NET. Cheap or counterfeit equipment can damage your vehicle’s computer system.
6.2. Follow Instructions Carefully
Read and follow the instructions provided with your OBDII scanner and software. Incorrectly connecting or configuring the equipment can lead to problems.
6.3. Avoid Distracted Driving
Never use your laptop or diagnostic software while driving. Pull over to a safe location before performing any diagnostics or adjustments.
6.4. Back Up Vehicle Data
Before making any changes to your vehicle’s settings, back up your vehicle’s data. This will allow you to restore the original settings if something goes wrong.
6.5. Understand the Risks
Be aware of the risks involved in modifying your vehicle’s settings. Incorrectly modifying certain parameters can damage your engine or other systems.
6.6. Seek Professional Help
If you’re unsure about any aspect of connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII system, seek professional help from a qualified mechanic or automotive technician.
7. Advanced OBDII Diagnostics and Customization
Once you’re comfortable connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII system and reading basic data, you can explore advanced diagnostics and customization options. However, proceed with caution and only attempt these procedures if you have a thorough understanding of your vehicle’s systems.
7.1. Bidirectional Control
Bidirectional control allows you to send commands to your vehicle’s computer system and control various components, such as:
- Activating Fuel Injectors: Test fuel injector operation.
- Controlling Cooling Fans: Verify cooling fan functionality.
- Cycling ABS Pump: Bleed the ABS system.
- Resetting адаптации: Reset learned values in the engine control unit (ECU).
7.2. Parameter Identification (PID) Support
Enhanced PID support allows you to access manufacturer-specific data and monitor parameters beyond the standard OBDII PIDs. This can provide valuable insights into your vehicle’s performance and potential issues.
7.3. ECU Coding and Programming
ECU coding and programming involve modifying the software in your vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU). This can be used to:
- Improve Performance: Optimize engine parameters for increased horsepower and torque.
- Enable Features: Activate features that were disabled by the manufacturer.
- Customize Settings: Adjust various vehicle settings to your preferences.
Warning: ECU coding and programming can be risky and should only be performed by experienced professionals. Incorrectly modifying the ECU can damage your engine or other systems.
8. Legal Considerations and Warranty Implications
Modifying your vehicle’s computer system can have legal and warranty implications. Be aware of the following:
8.1. Emissions Regulations
Modifying your vehicle’s engine or emissions system may violate emissions regulations. Check your local laws before making any modifications.
8.2. Warranty Coverage
Modifying your vehicle’s computer system may void your warranty. Check with your vehicle manufacturer or dealer before making any modifications.
8.3. Liability
You are responsible for any damages or injuries that result from modifying your vehicle’s computer system.
9. The Future of OBDII Diagnostics
OBDII diagnostics are constantly evolving, with new technologies and features being developed all the time. Here are some trends to watch for:
9.1. Cloud-Based Diagnostics
Cloud-based diagnostics allow you to access your vehicle’s data from anywhere in the world. This can be useful for remote diagnostics and fleet management.
9.2. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to analyze OBDII data and provide more accurate and insightful diagnostics. AI can also be used to predict potential problems before they occur.
9.3. Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates
OTA updates allow vehicle manufacturers to update your vehicle’s software remotely. This can be used to fix bugs, improve performance, and add new features.
10. CARDIAGTECH.NET: Your Partner in Automotive Diagnostics
At CARDIAGTECH.NET, we’re committed to providing you with the highest quality OBDII scanners, software, and support. We offer a wide range of products to meet your specific needs and budget.
10.1. Our Products
We offer a comprehensive selection of OBDII scanners, software, and accessories from leading manufacturers like Autel, Launch, and BlueDriver.
10.2. Our Expertise
Our team of experienced automotive technicians can provide you with expert advice and support. We can help you choose the right OBDII scanner and software for your needs and troubleshoot any issues you may encounter.
10.3. Our Commitment
We’re committed to providing you with the best possible customer experience. We offer fast shipping, easy returns, and a satisfaction guarantee.
Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more about our products and services.
FAQ: Connecting Laptop to Car OBDII
Here are some frequently asked questions about connecting your laptop to your car’s OBDII system:
-
What is OBDII?
- OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) is a standardized system used in most vehicles manufactured since 1996 to monitor engine and vehicle parameters for diagnostics and maintenance.
-
Why should I connect my laptop to my car’s OBDII port?
- Connecting your laptop allows you to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs), monitor real-time data, perform advanced diagnostics, customize vehicle settings, and potentially save money on repairs.
-
What equipment do I need to connect my laptop to OBDII?
- You’ll need an OBDII scanner/adapter (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or USB), diagnostic software, and a laptop that meets the software’s minimum system requirements.
-
Where is the OBDII port located in my car?
- The OBDII port is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual if you’re unsure of its location.
-
How do I connect a Bluetooth OBDII adapter to my laptop?
- Enable Bluetooth on your laptop, put the OBDII adapter in pairing mode, search for available devices, select the adapter, enter the PIN code (usually “1234” or “0000”), and confirm pairing.
-
What should I do if my OBDII adapter is not recognized by my laptop?
- Check the connection, verify power, install drivers (if using a USB adapter), restart your laptop, and test on another vehicle.
-
Is it safe to clear diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)?
- Yes, it’s generally safe to clear DTCs after addressing the underlying issue. However, be aware that clearing DTCs may reset certain vehicle systems.
-
Can I damage my car by connecting my laptop to the OBDII port?
- It’s unlikely to damage your car if you use reliable equipment and follow instructions carefully. However, avoid making changes to your vehicle’s settings unless you have a thorough understanding of the systems involved.
-
Will modifying my car’s computer system void my warranty?
- Modifying your vehicle’s computer system may void your warranty. Check with your vehicle manufacturer or dealer before making any modifications.
-
Where can I find reliable OBDII scanners and software?
- CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide selection of high-quality OBDII scanners and software from reputable manufacturers. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and personalized recommendations.
Are you ready to unlock the full potential of your vehicle? Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 for expert advice and personalized recommendations on OBDII scanners and software. Our team of experienced automotive technicians is here to help you diagnose issues, monitor performance, and gain deeper insights into your vehicle’s health. Don’t wait, take control of your car’s diagnostics today!
