The Bmw E46 Obdii Compliant system is your gateway to understanding and maintaining your vehicle’s health through its onboard diagnostic capabilities, and CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to guide you. Ensuring your E46 complies with OBDII standards unlocks a wealth of diagnostic data, enabling precise troubleshooting and informed maintenance decisions. Equip yourself with the right tools and knowledge to keep your BMW running smoothly for years to come, enhanced by the superior equipment available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
1. Understanding OBDII Compliance for Your BMW E46
The On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) system is a standardized system implemented in vehicles to monitor and report on various vehicle systems, primarily emissions-related components. For BMW E46 owners, understanding OBDII compliance is crucial for effective vehicle maintenance and diagnostics. Let’s dive into what OBDII compliance means for your E46.
1.1. What is OBDII?
OBDII, short for On-Board Diagnostics Second Generation, is a set of standards for vehicle on-board diagnostic systems. It was introduced in the United States in 1996 as a requirement for all new cars and light trucks. The primary goal of OBDII is to monitor the performance of the engine and related components, ensuring they operate within acceptable emission standards. When a problem is detected, the OBDII system stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that can be accessed using a scan tool.
1.2. Why is OBDII Important?
OBDII is important for several reasons:
- Emissions Control: OBDII helps ensure that vehicles meet emission standards, contributing to cleaner air.
- Diagnostics: It provides a standardized way to diagnose vehicle problems, making it easier for technicians to identify and fix issues.
- Maintenance: OBDII data can help owners monitor their vehicle’s health and perform preventative maintenance.
1.3. OBDII Compliance and the BMW E46
The BMW E46, produced from 1997 to 2006, generally adheres to OBDII standards, but compliance can vary based on the production year and the market where the vehicle was originally sold. In the United States, all E46 models from 1999 onwards are fully OBDII compliant. European models began incorporating OBDII (EOBD) in the early 2000s, with full compliance achieved by 2001 for gasoline vehicles and 2004 for diesel vehicles.
1.4. Identifying OBDII Compliance
To determine if your BMW E46 is OBDII compliant, check the following:
- Model Year: US models from 1996 and later are typically OBDII compliant. European models may vary, with gasoline cars from 2001 and diesel cars from 2004 being fully compliant.
- Under-Hood Label: Look for a sticker under the hood that explicitly states the vehicle is OBDII compliant. This label may also reference OBD II, EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics), or JOBD (Japanese On-Board Diagnostics).
- Owner’s Manual: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for information on OBDII compliance.
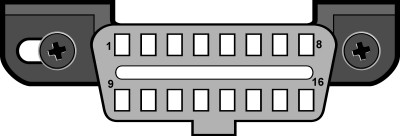
- DLC Connector: Check for a 16-pin Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC), which is a standard feature of OBDII-compliant vehicles. This connector is usually located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
 OBD-II port under the dashboard of a car
OBD-II port under the dashboard of a car
Figure 2. J1962 Vehicle Connector, Type A
1.5. Non-Compliance Issues
If your BMW E46 is not fully OBDII compliant, you may encounter issues when trying to use generic OBDII scan tools. Some early models may have a 16-pin connector but lack full OBDII functionality. In such cases, you may need to use specialized BMW diagnostic tools to access vehicle data.
1.6. Benefits of OBDII Compliance
OBDII compliance offers several benefits:
- Easy Diagnostics: Standardized diagnostic codes and data parameters make it easier to diagnose and repair vehicle issues.
- Wide Tool Compatibility: A wide range of OBDII scan tools and software are compatible with compliant vehicles, providing flexibility in diagnostic approaches.
- Emissions Monitoring: OBDII helps ensure that your vehicle meets emission standards, reducing its environmental impact.
1.7. Regulations and Standards
OBDII standards are mandated by governmental regulations. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) requires all new cars and light trucks from 1996 onwards to be OBDII compliant. Europe has similar regulations under the EOBD standard, and Japan has the JOBD standard.
1.8. OBDII Connectors and Protocols
OBDII uses a standardized 16-pin connector (SAE J1962) to access vehicle data. Several communication protocols are used, including:
- SAE J1850 PWM and VPW: Used primarily by Ford and GM.
- ISO 9141-2: Used by European and Asian manufacturers.
- ISO 14230 (KWP2000): Also used by European and Asian manufacturers.
- SAE J1939: Used by heavy-duty vehicles.
- CAN (Controller Area Network): The most modern and widely used protocol.
1.9. Common OBDII Codes for BMW E46
Here are some common OBDII codes you might encounter with your BMW E46:
| Code | Description | Possible Causes |
|---|---|---|
| P0171 | System Too Lean (Bank 1) | Vacuum leak, MAF sensor, fuel pump, fuel filter |
| P0174 | System Too Lean (Bank 2) | Vacuum leak, MAF sensor, fuel pump, fuel filter |
| P0300 | Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected | Ignition system, fuel system, vacuum leaks, engine compression |
| P0420 | Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold | Catalytic converter, oxygen sensors, exhaust leaks |
| P0440 | Evaporative Emission Control System Fault | Gas cap, vacuum lines, charcoal canister, purge valve |
| P0505 | Idle Control System Malfunction | Idle air control valve, throttle body, vacuum leaks |
| P1624 | EWS Manipulation Signal | Immobilizer system, DME (Digital Motor Electronics) |
| P1188 | Fuel Control (Bank 1 Sensor 1) | Oxygen sensor, fuel pressure regulator, fuel injectors |
| P1189 | Fuel Control (Bank 2 Sensor 1) | Oxygen sensor, fuel pressure regulator, fuel injectors |
| P0720 | Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction | Speed sensor, wiring, transmission |
1.10. Using OBDII Scan Tools with Your E46
To use an OBDII scan tool with your BMW E46:
- Locate the DLC Connector: It’s usually under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug in the Scan Tool: Connect the scan tool to the DLC connector.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
- Follow the Scan Tool Instructions: Use the scan tool to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and view live data.
- Interpret the Data: Research the DTCs to understand the underlying problem and take appropriate action.
1.11. Advanced Diagnostics with OBDII
Beyond reading basic DTCs, OBDII can provide valuable live data, including:
- Engine RPM: Revolutions per minute.
- Engine Load: Percentage of maximum engine power being used.
- Coolant Temperature: Engine coolant temperature.
- Fuel Trim: Adjustments made to the fuel mixture by the engine control unit (ECU).
- Oxygen Sensor Readings: Data from the oxygen sensors indicating the air-fuel ratio.
1.12. Maintenance Tips for OBDII Systems
To keep your OBDII system functioning properly:
- Regular Check-Ups: Periodically scan your vehicle for DTCs, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
- Proper Repairs: Address any detected issues promptly to prevent further damage and maintain emissions compliance.
- Quality Parts: Use high-quality replacement parts, especially for sensors and emission control components.
Understanding and utilizing the OBDII system in your BMW E46 can greatly enhance your ability to maintain and diagnose your vehicle. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a DIY enthusiast, leveraging OBDII data will help you keep your E46 running smoothly and efficiently.
2. Step-by-Step Guide: Checking OBDII Compliance on Your BMW E46
Verifying OBDII compliance on your BMW E46 is essential for effective diagnostics and maintenance. Follow this step-by-step guide to ensure your vehicle meets the necessary standards and learn how to use OBDII tools for optimal performance.
2.1. Gather Necessary Tools and Information
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- BMW E46 Vehicle: The car you intend to check.
- OBDII Scan Tool: A tool that can read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data. Consider a reliable tool from CARDIAGTECH.NET.
- Vehicle’s Owner’s Manual: For reference information.
- Under-Hood Label: The vehicle emission control information label.
- Internet Access: For researching DTCs and troubleshooting.
2.2. Locate the Diagnostic Link Connector (DLC)
The DLC is a 16-pin connector used to access the vehicle’s OBDII system. It is typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Check Under the Dashboard: Look for a rectangular, trapezoidal connector, usually black or blue.
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: If you can’t find the DLC, refer to the owner’s manual for its exact location.
2.3. Inspect the Under-Hood Label
The under-hood label provides critical information about the vehicle’s emission control systems and OBDII compliance.
- Open the Hood: Securely open the hood of your BMW E46.
- Locate the Label: Look for a sticker, usually on the underside of the hood or on the engine compartment.
- Read the Label: The label should explicitly state whether the vehicle is OBDII compliant. It may also reference OBD II, EOBD (European On-Board Diagnostics), or JOBD (Japanese On-Board Diagnostics).
Figure 1. Vehicle Emission Control Information Label
2.4. Verify the Model Year
The model year of your BMW E46 is a key indicator of OBDII compliance.
- Check the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): The VIN is located on the dashboard (driver’s side) and on the vehicle’s title and registration.
- Decode the VIN: Use an online VIN decoder to determine the model year. Generally, US models from 1996 onward are OBDII compliant. European models may vary.
2.5. Connect the OBDII Scan Tool
Once you’ve located the DLC, connect the OBDII scan tool to begin the diagnostic process.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Ensure the ignition is turned off before connecting the scan tool.
- Plug in the Scan Tool: Connect the scan tool to the DLC. Ensure it is firmly seated.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “ON” position without starting the engine.
2.6. Power Up the Scan Tool
Most OBDII scan tools will power on automatically once connected. If not, follow the tool’s instructions to power it up.
- Check the Display: The scan tool should display a welcome screen or a prompt to begin.
- Follow On-Screen Instructions: Use the scan tool’s buttons or touchscreen to navigate the menus.
2.7. Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Reading DTCs is the first step in diagnosing any potential issues.
- Select “Read Codes”: Navigate to the “Read Codes” or “Diagnostic Codes” option in the scan tool menu.
- Wait for the Scan: The scan tool will communicate with the vehicle’s computer and retrieve any stored DTCs.
- Record the Codes: Write down all the DTCs that are displayed. Note the code numbers and their descriptions.
2.8. Interpret the Diagnostic Trouble Codes
Understanding the DTCs is crucial for identifying the underlying problems.
- Consult the Owner’s Manual: Some owner’s manuals provide basic information on common DTCs.
- Use Online Resources: Search the internet for the DTC descriptions. Websites like OBD-Codes.com and reputable automotive forums can provide detailed information.
- Refer to a Repair Manual: A repair manual specific to your BMW E46 can offer in-depth explanations and troubleshooting steps.
2.9. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (Optional)
If you want to clear the DTCs after recording them, follow these steps. Note: Only clear codes if you understand the underlying issue and have addressed it.
- Select “Erase Codes”: Navigate to the “Erase Codes” or “Clear Codes” option in the scan tool menu.
- Confirm the Erase: The scan tool may ask you to confirm that you want to erase the codes. Follow the on-screen instructions.
- Verify the Clear: After erasing the codes, read them again to ensure they have been cleared.
2.10. Check Live Data (Optional)
Checking live data can provide additional insights into the vehicle’s performance.
- Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” option in the scan tool menu.
- Choose Parameters: Select the parameters you want to monitor, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Monitor the Data: Observe the data stream while the engine is running. Look for any abnormal readings.
2.11. Verify OBDII Compliance Based on Results
Based on the steps above, verify your BMW E46’s OBDII compliance:
- US Models: If your E46 is a US model from 1996 onward and the scan tool connects successfully and retrieves DTCs, it is likely OBDII compliant.
- European Models: Compliance varies. Gasoline cars from 2001 and diesel cars from 2004 are generally compliant. Check the under-hood label for confirmation.
- Non-Compliant Models: If the scan tool cannot connect or retrieve data, and the under-hood label does not indicate OBDII compliance, your E46 may not be fully OBDII compliant.
2.12. Take Action Based on Findings
Depending on your findings, take the appropriate action:
- OBDII Compliant: Use the scan tool to diagnose and address any issues indicated by the DTCs or live data.
- Non-Compliant: Consider using specialized BMW diagnostic tools or consult with a professional mechanic to diagnose and repair any issues.
By following this step-by-step guide, you can confidently check the OBDII compliance of your BMW E46 and take the necessary steps to maintain its performance and emissions standards. Remember to rely on trusted resources like CARDIAGTECH.NET for your diagnostic tools and automotive needs.
3. Advanced OBDII Diagnostics for BMW E46: Beyond the Basics
Taking your OBDII diagnostics to the next level can provide deeper insights into your BMW E46’s performance and help you tackle complex issues. Here’s how to perform advanced diagnostics using OBDII tools, leveraging the resources available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
3.1. Understanding OBDII Modes
OBDII systems operate using several modes, each designed to access specific types of diagnostic information. Knowing these modes can help you perform more targeted diagnostics.
- Mode $01 – Show Current Data: Displays real-time data parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings.
- Mode $02 – Show Freeze Frame Data: Displays the data parameters recorded at the moment a DTC was set. This can provide valuable context for troubleshooting.
- Mode $03 – Show Stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Displays the current DTCs stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Mode $04 – Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes and Reset Emission Monitors: Clears DTCs and resets the emission monitors.
- Mode $05 – Oxygen Sensor Monitoring Test Results: Displays the results of on-board oxygen sensor tests.
- Mode $06 – Non-Continuously Monitored Systems Test Results: Displays the results of on-board tests for systems that are not continuously monitored.
- Mode $07 – Show Pending Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Displays DTCs that have been detected but not yet confirmed.
- Mode $08 – Request Control of On-Board System, Test, or Component: Allows you to control certain on-board systems for testing purposes (use with caution).
- Mode $09 – Request Vehicle Information: Displays vehicle information such as the VIN and calibration IDs.
- Mode $0A – Permanent Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Displays DTCs that cannot be cleared by simply erasing codes.
3.2. Using Advanced Scan Tools
Advanced scan tools offer enhanced capabilities beyond basic code reading and clearing.
- Bi-Directional Control: Allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to activate specific components for testing purposes. For example, you can activate the fuel pump, injectors, or cooling fan to check their functionality.
- Data Logging: Records live data parameters over time, allowing you to analyze trends and identify intermittent issues.
- Graphing: Visualizes live data in graphical form, making it easier to spot anomalies and correlations between different parameters.
- Actuator Testing: Performs specific tests on actuators such as the idle air control valve or the throttle position sensor.
- Module Programming: Allows you to reprogram certain vehicle modules with updated software (use with caution and proper training).
3.3. Interpreting Freeze Frame Data
Freeze frame data captures the conditions present when a DTC was set, providing valuable context for troubleshooting.
- Access Freeze Frame Data: Use your scan tool to access the freeze frame data associated with a specific DTC.
- Analyze Key Parameters: Pay attention to parameters such as engine RPM, engine load, coolant temperature, and fuel trim.
- Identify the Trigger: Look for any abnormal readings or conditions that may have triggered the DTC. For example, if the DTC was set at high RPM and high load, it may indicate an issue with the fuel system or ignition system under those conditions.
3.4. Performing Oxygen Sensor Tests
Oxygen sensors play a crucial role in fuel management and emissions control.
- Access Oxygen Sensor Data: Use your scan tool to access the oxygen sensor data.
- Monitor Sensor Readings: Observe the voltage readings from the oxygen sensors. The readings should fluctuate rapidly between approximately 0.1 volts and 0.9 volts.
- Check for Sensor Response: Perform a “snap throttle” test by quickly opening and closing the throttle. The oxygen sensor readings should respond quickly to the change in engine load.
- Interpret the Results: A slow or non-responsive oxygen sensor may indicate a faulty sensor or an issue with the wiring.
3.5. Analyzing Fuel Trim Data
Fuel trim data indicates the adjustments made by the engine control unit (ECU) to the fuel mixture.
-
Access Fuel Trim Data: Use your scan tool to access the fuel trim data.
-
Monitor Short-Term and Long-Term Fuel Trim: Short-term fuel trim (STFT) represents immediate adjustments to the fuel mixture, while long-term fuel trim (LTFT) represents adjustments made over time.
-
Interpret the Results:
- Positive Fuel Trim: Indicates that the ECU is adding fuel to compensate for a lean condition (too much air, not enough fuel).
- Negative Fuel Trim: Indicates that the ECU is reducing fuel to compensate for a rich condition (too much fuel, not enough air).
- High Fuel Trim Values: Values above +10% or below -10% may indicate a significant issue.
-
Troubleshooting Based on Fuel Trim:
- Lean Condition (Positive Fuel Trim): Check for vacuum leaks, faulty MAF sensor, low fuel pressure, or clogged fuel injectors.
- Rich Condition (Negative Fuel Trim): Check for leaking fuel injectors, high fuel pressure, faulty oxygen sensor, or a restricted air intake.
3.6. Performing Component Tests
Advanced scan tools allow you to perform component tests to verify the functionality of specific components.
- Access Component Tests: Use your scan tool to access the component tests menu.
- Select the Component: Choose the component you want to test, such as the fuel pump, injectors, or cooling fan.
- Follow the On-Screen Instructions: The scan tool will provide instructions on how to perform the test.
- Interpret the Results: The scan tool will display the results of the test, indicating whether the component is functioning properly.
3.7. Reading BMW-Specific Codes
While OBDII provides standardized diagnostic codes, BMW also uses proprietary codes that can provide more specific information about vehicle issues.
- Use a BMW-Specific Scan Tool: To read BMW-specific codes, you will need a scan tool that supports the BMW diagnostic protocol.
- Access the BMW Diagnostic Menu: Navigate to the BMW diagnostic menu in the scan tool.
- Read the Codes: The scan tool will display any BMW-specific codes that are stored in the vehicle’s computer.
- Interpret the Codes: Refer to a BMW repair manual or online resources to understand the meaning of the BMW-specific codes.
3.8. Data Logging and Analysis
Data logging involves recording live data parameters over time, allowing you to analyze trends and identify intermittent issues.
- Set Up Data Logging: Use your scan tool to set up data logging. Select the parameters you want to record and set the logging interval.
- Record the Data: Drive the vehicle under the conditions that you want to analyze.
- Download the Data: Download the data from the scan tool to your computer.
- Analyze the Data: Use graphing software or a spreadsheet program to analyze the data. Look for any abnormal trends or correlations between different parameters.
3.9. Using BMW Diagnostic Software
BMW offers diagnostic software such as INPA, DIS, and ISTA that provide advanced diagnostic and programming capabilities.
- Install the Software: Install the BMW diagnostic software on your computer.
- Connect to the Vehicle: Connect your computer to the vehicle using a compatible interface cable.
- Perform Diagnostics: Use the software to perform advanced diagnostics, including reading BMW-specific codes, performing component tests, and programming modules.
- Follow the Instructions: Follow the software instructions carefully and use caution when performing programming functions.
3.10. Seeking Professional Help
If you are unsure about performing advanced diagnostics or if you encounter complex issues that you cannot resolve on your own, seek help from a professional mechanic.
- Consult a BMW Specialist: Find a mechanic who specializes in BMW vehicles.
- Provide Detailed Information: Provide the mechanic with as much information as possible about the issue, including any DTCs, freeze frame data, and data logging results.
- Follow the Mechanic’s Recommendations: Follow the mechanic’s recommendations for diagnosis and repair.
By mastering these advanced OBDII diagnostic techniques, you can gain a deeper understanding of your BMW E46’s performance and tackle even the most challenging issues. Rely on CARDIAGTECH.NET for your advanced diagnostic tools and expert support.
4. Selecting the Right OBDII Scanner for Your BMW E46
Choosing the correct OBDII scanner for your BMW E46 is critical for effective diagnostics and maintenance. With a plethora of options available, it’s important to select a scanner that meets your specific needs and budget. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a wide range of OBDII scanners to help you keep your BMW in top condition.
4.1. Understanding Your Diagnostic Needs
Before purchasing an OBDII scanner, assess your diagnostic needs.
- Frequency of Use: How often will you use the scanner? Occasional users may need a basic model, while frequent users should invest in a more advanced tool.
- Types of Repairs: What types of repairs do you typically perform? If you handle complex issues, you’ll need a scanner with advanced features like bi-directional control and data logging.
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend? Basic scanners can be quite affordable, while advanced models can be a significant investment.
4.2. Types of OBDII Scanners
There are several types of OBDII scanners, each offering different features and capabilities.
- Basic Code Readers: These are the most affordable options, capable of reading and clearing diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). They are suitable for basic diagnostics and simple repairs.
- Mid-Range Scanners: These scanners offer additional features such as live data streaming, freeze frame data, and O2 sensor testing. They are suitable for more in-depth diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Advanced Scanners: These scanners offer advanced features such as bi-directional control, data logging, component testing, and module programming. They are suitable for professional mechanics and advanced DIYers.
- Smartphone-Based Scanners: These scanners consist of a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that connects to your smartphone or tablet. They use a mobile app to display diagnostic data. They can be a cost-effective option, but their capabilities vary widely.
4.3. Key Features to Consider
When selecting an OBDII scanner, consider these key features.
- Compatibility: Ensure the scanner is compatible with your BMW E46. Some scanners are designed to work with specific makes and models.
- Ease of Use: Choose a scanner with a user-friendly interface and clear instructions.
- Code Definitions: The scanner should provide clear and accurate code definitions.
- Live Data Streaming: This feature allows you to monitor real-time data parameters such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and O2 sensor readings.
- Freeze Frame Data: This feature captures the data parameters recorded at the moment a DTC was set.
- Bi-Directional Control: This advanced feature allows you to send commands to the vehicle’s computer to activate specific components for testing purposes.
- Data Logging: This feature allows you to record live data parameters over time for later analysis.
- Software Updates: Ensure the scanner supports software updates to stay current with the latest vehicle models and diagnostic protocols.
- Customer Support: Choose a scanner from a reputable brand with good customer support.
4.4. Top OBDII Scanner Recommendations for BMW E46
Here are some recommended OBDII scanners for the BMW E46, available at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
| Scanner | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Autel MaxiCOM MK808 | Reads and clears codes, live data, bi-directional control, special functions (oil reset, EPB, TPMS), supports multiple languages, software updates | $500 – $600 |
| Launch X431 V+ | Reads and clears codes, live data, bi-directional control, special functions, supports a wide range of vehicle models, software updates | $800 – $1,200 |
| BlueDriver Bluetooth Professional OBDII Scan Tool | Reads and clears codes, live data, freeze frame data, enhanced diagnostics for BMW, repair reports, Bluetooth connectivity | $120 |
| INPA / Ediabas K+DCAN USB Interface | BMW-specific diagnostics, reads and clears BMW-specific codes, live data, coding, programming, requires software installation on a computer | $50 – $100 |
| Carly for BMW | Smartphone-based scanner, reads and clears codes, live data, coding, supports BMW-specific functions, subscription-based | $80 per year |
4.5. Using Smartphone-Based Scanners
Smartphone-based scanners are a convenient and affordable option for basic diagnostics.
- Purchase a Compatible Adapter: Choose a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi adapter that is compatible with your smartphone and your BMW E46.
- Download the App: Download the scanner app from the App Store or Google Play.
- Connect the Adapter: Plug the adapter into the DLC and connect it to your smartphone via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- Pair the Devices: Follow the app instructions to pair the adapter with your smartphone.
- Perform Diagnostics: Use the app to read and clear codes, view live data, and perform other diagnostic functions.
4.6. Considerations for BMW-Specific Diagnostics
For advanced diagnostics and BMW-specific functions, consider using a BMW-specific scanner or software.
- BMW INPA / Ediabas: This is a popular BMW diagnostic software that requires a K+DCAN USB interface cable.
- BMW DIS / ISTA: These are more advanced BMW diagnostic software used by professional mechanics.
- Carly for BMW: This smartphone-based scanner offers BMW-specific diagnostics and coding functions.
4.7. Keeping Your Scanner Updated
Keeping your OBDII scanner updated is essential for accurate and reliable diagnostics.
- Check for Updates Regularly: Check the scanner manufacturer’s website for software updates.
- Download and Install Updates: Follow the instructions to download and install the updates.
- Update Firmware: In addition to software updates, some scanners may also require firmware updates.
4.8. Seeking Expert Advice
If you are unsure which OBDII scanner is right for you, seek expert advice from CARDIAGTECH.NET. Our knowledgeable staff can help you choose the best scanner for your needs and budget.
Selecting the right OBDII scanner for your BMW E46 is an investment in the longevity and performance of your vehicle. Whether you need a basic code reader or an advanced diagnostic tool, CARDIAGTECH.NET has the perfect solution for you.
5. Decoding Common BMW E46 OBDII Error Codes
Understanding common OBDII error codes in your BMW E46 is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. This guide breaks down frequent codes, their potential causes, and how to address them, all while highlighting the value CARDIAGTECH.NET brings to your diagnostic process.
5.1. P0171 and P0174: System Too Lean (Bank 1 & Bank 2)
These codes indicate that the engine is running lean, meaning there’s too much air or not enough fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
-
Possible Causes:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in vacuum hoses, intake manifold gaskets, or the crankcase ventilation (CCV) system.
- Mass Airflow (MAF) Sensor: A faulty MAF sensor can provide incorrect readings, leading to a lean condition.
- Fuel Pump: A weak fuel pump may not provide enough fuel to the engine.
- Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow.
- Fuel Injectors: Clogged or faulty fuel injectors can reduce the amount of fuel delivered to the cylinders.
- Oxygen Sensors: Faulty oxygen sensors can provide incorrect feedback to the ECU.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Check all vacuum hoses and intake manifold gaskets for cracks or leaks. Use a smoke tester to identify hard-to-find leaks.
- Clean or Replace MAF Sensor: Clean the MAF sensor with a MAF sensor cleaner. If cleaning doesn’t help, replace the sensor.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to check the fuel pressure. If the pressure is low, replace the fuel pump or fuel filter.
- Inspect Fuel Injectors: Inspect the fuel injectors for clogs or leaks. Clean or replace the injectors as needed.
- Check Oxygen Sensors: Use a scan tool to monitor the oxygen sensor readings. Replace any faulty oxygen sensors.
5.2. P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
This code indicates that the engine is experiencing misfires in multiple cylinders.
-
Possible Causes:
- Ignition System: Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or ignition wires.
- Fuel System: Clogged or faulty fuel injectors, low fuel pressure.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in vacuum hoses or intake manifold gaskets.
- Engine Compression: Low compression in one or more cylinders.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Spark Plugs: Inspect the spark plugs for wear, damage, or fouling. Replace as needed.
- Check Ignition Coils: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the ignition coils. Replace any faulty coils.
- Check Fuel Injectors: Inspect the fuel injectors for clogs or leaks. Clean or replace the injectors as needed.
- Check Compression: Use a compression tester to check the compression in each cylinder. Low compression may indicate a more serious engine problem.
5.3. P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
This code indicates that the catalytic converter is not functioning efficiently.
-
Possible Causes:
- Faulty Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter is worn out or damaged.
- Faulty Oxygen Sensors: Faulty oxygen sensors can provide incorrect feedback to the ECU, leading to inefficient catalytic converter operation.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system can affect the performance of the catalytic converter.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Oxygen Sensors: Use a scan tool to monitor the oxygen sensor readings. Replace any faulty oxygen sensors.
- Inspect Exhaust System: Check the exhaust system for leaks. Repair any leaks as needed.
- Test Catalytic Converter Efficiency: Use a scan tool to monitor the catalytic converter efficiency. If the efficiency is below the threshold, replace the catalytic converter.
5.4. P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the evaporative emission control (EVAP) system.
-
Possible Causes:
- Gas Cap: A loose or damaged gas cap.
- Vacuum Lines: Leaks in the EVAP system vacuum lines.
- Charcoal Canister: A damaged or clogged charcoal canister.
- Purge Valve: A faulty purge valve.
-
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Gas Cap: Ensure the gas cap is properly tightened and not damaged.
- Inspect Vacuum Lines: Check all EVAP system vacuum lines for cracks or leaks.
- Check Charcoal Canister: Inspect the charcoal canister for damage or clogs.
- Check Purge Valve: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the purge valve. Replace the purge valve if it is faulty.
5.5. P0505: Idle Control System Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the idle control system.
-
Possible Causes:
- Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve: A faulty IAC valve.
- Throttle Body: A dirty or damaged throttle body.
- **Vacuum Leaks

