Audi 3.0 Tdi Turbo Actuator Adaptation Vcds is a crucial procedure for maintaining optimal engine performance. If you’re experiencing issues with your Audi’s turbocharger, like error codes or reduced boost, CARDIAGTECH.NET can help you diagnose and resolve these problems. Utilizing VCDS for turbo actuator adaptation ensures your Audi 3.0 TDI operates efficiently, delivering the power and responsiveness you expect.
1. Understanding the Audi 3.0 TDI Turbo Actuator
The turbo actuator controls the vanes inside the turbocharger, regulating boost pressure based on engine demand. A malfunctioning actuator can lead to poor performance, error codes, and potential engine damage. Understanding its function is the first step in effective diagnostics and repair.
1.1 What is a Turbo Actuator?
A turbo actuator is a critical component that regulates the turbocharger’s performance. It controls the position of the vanes inside the turbocharger, which in turn adjusts the amount of exhaust gas that flows over the turbine. This regulation is essential for managing boost pressure and ensuring the engine delivers the required power efficiently.
1.2 Function and Importance in Audi 3.0 TDI Engines
In Audi 3.0 TDI engines, the turbo actuator plays a vital role in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency. Accurate control of the turbocharger ensures the engine produces the necessary boost at different RPMs and load conditions. A properly functioning actuator contributes to smooth acceleration, reduced emissions, and overall engine longevity. When the actuator fails, it can lead to significant performance issues, triggering error codes and potentially causing damage to other engine components.
1.3 Symptoms of a Faulty Turbo Actuator
Recognizing the symptoms of a faulty turbo actuator is crucial for timely diagnosis and repair. Here are some common indicators:
- Reduced Engine Power: A noticeable decrease in acceleration and overall engine performance.
- Error Codes: The engine control unit (ECU) may display error codes related to the turbocharger, such as “19804/P3348/013128 – Control Circuit for Controller for Turbocharger 1 (J724): Electrical Malfunction.”
- Limp Mode: The vehicle may enter limp mode, restricting engine power to prevent further damage.
- Inconsistent Boost Pressure: Fluctuations in boost pressure can cause erratic engine behavior.
- Unusual Noises: Whining or whistling sounds from the turbocharger area.
2. Identifying the Root Cause
Before attempting any adaptation, it’s essential to pinpoint the exact cause of the turbo actuator issue. This involves checking for electrical faults, vacuum leaks, and mechanical problems. A systematic approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective repair.
2.1 Common Causes of Turbo Actuator Failure
Several factors can contribute to the failure of a turbo actuator. Understanding these causes can help in diagnosing the problem accurately:
- Electrical Malfunctions: Faulty wiring, damaged connectors, or internal electrical issues within the actuator.
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the vacuum lines that control the actuator can prevent it from functioning correctly.
- Mechanical Problems: Wear and tear, corrosion, or damage to the actuator’s internal components.
- Sensor Issues: Problems with sensors that provide feedback to the ECU about the actuator’s position.
- Carbon Buildup: Accumulation of carbon deposits can restrict the movement of the turbocharger vanes.
2.2 Checking for Electrical Faults
Electrical faults are a common cause of turbo actuator problems. Here’s how to check for them:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, such as fraying, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring between the actuator and the ECU.
- Voltage Test: Verify that the actuator is receiving the correct voltage from the ECU. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the specified voltage range.
2.3 Examining Vacuum Lines and Connections
Vacuum leaks can significantly impact the performance of the turbo actuator. Follow these steps to check for vacuum leaks:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect all vacuum lines connected to the actuator for cracks, splits, or loose connections.
- Vacuum Tester: Use a vacuum tester to check the vacuum pressure at the actuator. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Smoke Test: Introduce smoke into the vacuum system to identify any leaks. The smoke will escape from any points where there is a leak.
2.4 Assessing Mechanical Issues
Mechanical problems within the actuator can also lead to its failure. Here’s how to assess mechanical issues:
- Manual Movement: Try to move the actuator arm manually. It should move smoothly without any binding or resistance.
- Visual Inspection: Look for any signs of corrosion, damage, or wear on the actuator arm and its connecting components.
- Actuator Test: Use VCDS to perform an actuator test and observe its movement. If the actuator moves erratically or not at all, it may have internal mechanical issues.
2.5 Verifying Sensor Functionality
The turbo actuator relies on feedback from various sensors to operate correctly. Verify the functionality of these sensors:
- MAF Sensor: Ensure the mass airflow (MAF) sensor is functioning correctly, as it provides crucial data for boost control. Clean or replace the MAF sensor if necessary.
- Boost Pressure Sensor: Check the boost pressure sensor for accurate readings. A faulty sensor can provide incorrect data to the ECU, affecting actuator performance.
- Position Sensor: If the actuator has a position sensor, verify that it is providing accurate feedback to the ECU about the actuator’s position.
By thoroughly investigating these potential causes, you can accurately diagnose the root of the problem and proceed with the appropriate repair or adaptation. CARDIAGTECH.NET offers a range of diagnostic tools that can assist in these checks, ensuring a precise and efficient troubleshooting process.
 sDeT9Us.jpeg
sDeT9Us.jpeg
3. Preparing for Adaptation
Before diving into the adaptation process, it’s important to gather the necessary tools and information. Ensure you have a reliable VCDS interface, the correct software version, and access to your vehicle’s service manual. This preparation will streamline the adaptation process and minimize potential issues.
3.1 Essential Tools and Software
To perform the Audi 3.0 TDI turbo actuator adaptation, you’ll need the following tools and software:
- VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System): This is the primary software used for diagnosing and adapting VW, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles. Ensure you have a genuine VCDS interface for reliable communication with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Laptop: A laptop with a stable internet connection is necessary for running the VCDS software and accessing online resources.
- Vehicle Service Manual: The service manual provides specific instructions and specifications for your vehicle model.
- Multimeter: A multimeter is useful for checking electrical connections and voltage levels.
- Basic Hand Tools: Wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers may be needed for accessing and inspecting the turbo actuator.
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality VCDS interfaces and diagnostic tools, ensuring you have the right equipment for the job.
3.2 Ensuring Correct VCDS Version
Using the correct version of VCDS is crucial for successful adaptation. Here’s how to ensure you have the right version:
- Check Compatibility: Verify that your VCDS version is compatible with your vehicle model and year. Refer to the Ross-Tech website for compatibility information.
- Update Software: Regularly update your VCDS software to the latest version. Updates often include bug fixes, improved functionality, and support for newer vehicle models.
- Genuine Interface: Use a genuine VCDS interface to ensure access to all features and updates. Cloned or pirated interfaces may not function correctly and can potentially damage your vehicle’s ECU.
3.3 Gathering Vehicle Information
Before starting the adaptation process, gather the following vehicle information:
- Vehicle Identification Number (VIN): The VIN is essential for identifying your vehicle model and accessing specific service information.
- Engine Code: The engine code helps in identifying the correct adaptation procedures and parameters.
- ECU Part Number: Knowing the ECU part number can be useful for verifying compatibility with VCDS and accessing relevant technical data.
3.4 Understanding Adaptation Channels
Adaptation channels in VCDS allow you to adjust specific parameters within the ECU. Understanding these channels is essential for performing the turbo actuator adaptation correctly:
- Identify Relevant Channels: Consult the vehicle service manual or Ross-Tech Wiki to identify the adaptation channels related to the turbo actuator.
- Record Original Values: Before making any changes, record the original values of the adaptation channels. This allows you to revert to the original settings if needed.
- Understand Channel Functionality: Familiarize yourself with the function of each adaptation channel and the impact of changing its value.
3.5 Safety Precautions
Before starting any diagnostic or adaptation procedure, follow these safety precautions:
- Work in a Safe Environment: Ensure you are working in a well-lit and ventilated area.
- Disconnect Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shorts.
- Use Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job to avoid damaging components.
- Follow Instructions: Carefully follow the instructions in the vehicle service manual and VCDS documentation.
- Wear Safety Gear: Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection.
By following these preparation steps, you can ensure a smooth and successful turbo actuator adaptation process. CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing you with the tools and knowledge you need to perform these procedures safely and effectively.
4. Step-by-Step VCDS Adaptation Process
With the necessary preparations completed, you can now proceed with the VCDS adaptation process. Follow these steps carefully, ensuring each step is performed accurately.
4.1 Connecting VCDS to the Vehicle
- Locate the OBD-II Port: Find the OBD-II port in your Audi 3.0 TDI, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Connect the VCDS Interface: Plug the VCDS interface into the OBD-II port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition on, but do not start the engine.
- Launch VCDS Software: Open the VCDS software on your laptop.
- Select Interface: In VCDS, select the correct interface from the options menu.
- Test Connection: Click on the “Test” button to verify that VCDS can communicate with the vehicle’s ECU. A successful test will confirm that the interface is properly connected.
4.2 Accessing the Engine Control Module (ECU)
- Select Control Module: In VCDS, click on the “Select” button to access the control module menu.
- Choose Engine: Select the “01-Engine” control module from the list. This is the ECU that controls the engine and turbocharger.
- Wait for Initialization: Allow VCDS to initialize and establish communication with the ECU. This may take a few seconds.
4.3 Navigating to Adaptation Settings
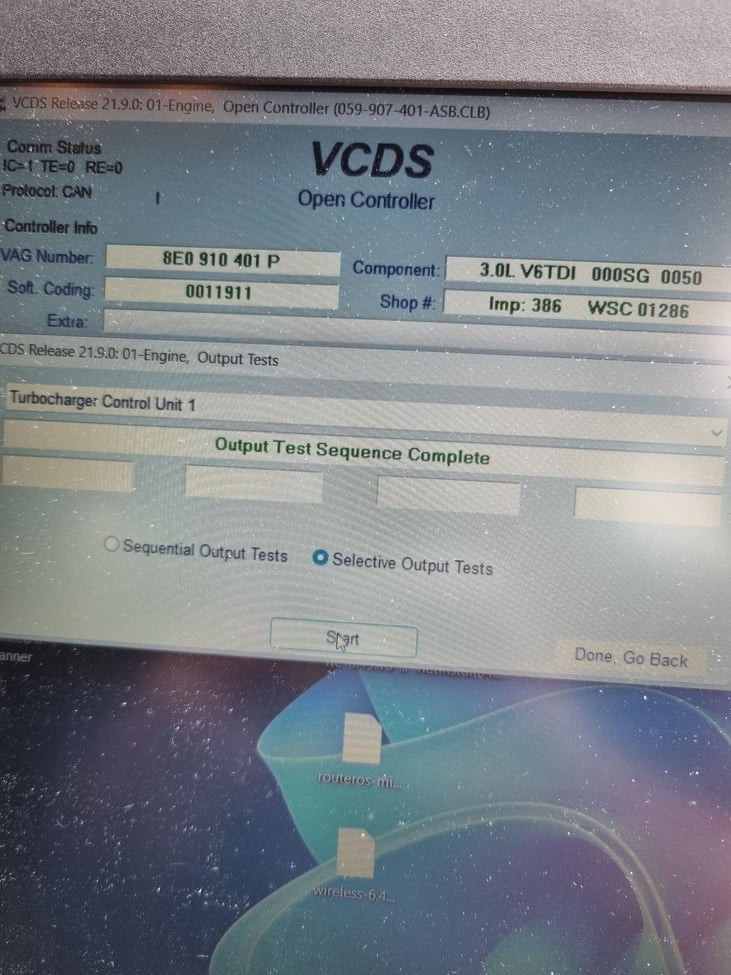
- Access Adaptation: Once you are in the Engine control module, click on the “Adaptation – 10” button. This will take you to the adaptation settings.
- Identify Adaptation Channels: Use the up and down arrow keys to scroll through the available adaptation channels. Refer to the vehicle service manual or Ross-Tech Wiki to identify the specific channels related to the turbo actuator.
4.4 Performing Basic Settings
- Access Basic Settings: In VCDS, navigate to the “Basic Settings – 04” function.
- Select Group: Enter the appropriate group number for the turbo actuator adaptation. Common group numbers include 011, 030, or 046, but refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the correct group.
- Start Adaptation: Click the “Go!” button to start the basic settings procedure. VCDS will display the status of the adaptation process.
- Monitor Progress: Observe the progress of the adaptation. VCDS will typically cycle through different stages, such as “Adjusting,” “Learning,” and “Finished.”
- Wait for Completion: Allow the adaptation process to complete fully. Do not interrupt the process, as this can cause errors or damage to the ECU.
4.5 Adjusting Adaptation Channels
- Select Channel: In the Adaptation – 10 function, select the specific channel you want to adjust.
- Read Current Value: VCDS will display the current value of the selected channel.
- Enter New Value: Enter the new value that you want to set for the channel. Refer to the vehicle service manual or Ross-Tech Wiki for the recommended value.
- Save Changes: Click the “Do It!” button to save the changes. VCDS will prompt you to confirm the changes before applying them.
- Test and Verify: After saving the changes, test the turbo actuator to verify that it is functioning correctly. Monitor boost pressure and engine performance to ensure the adaptation was successful.
4.6 Saving and Testing New Settings
- Save Adaptation: After adjusting the adaptation channels, click on the “Save” button to store the new settings in the ECU.
- Test Drive: Perform a test drive to evaluate the performance of the turbocharger. Monitor boost pressure, engine response, and overall vehicle performance.
- Scan for Errors: Use VCDS to scan for any new error codes that may have appeared after the adaptation. Address any errors promptly.
- Verify Functionality: Ensure that the turbo actuator is functioning correctly under different driving conditions. Check for smooth acceleration, consistent boost pressure, and absence of unusual noises.
4.7 Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
Adaptation Not Accepted: If VCDS displays an error message indicating that the adaptation was not accepted, check the following:
- Ensure that the engine is at the correct temperature.
- Verify that there are no other fault codes present in the ECU.
- Double-check the adaptation values against the recommended specifications.
-
Error Codes Persist: If error codes related to the turbo actuator persist after the adaptation, the actuator may have an underlying mechanical or electrical issue. Further diagnosis and repair may be necessary.
-
Poor Performance: If the vehicle exhibits poor performance after the adaptation, review the adaptation values and ensure they are correctly set. Consider performing a throttle body adaptation or other related procedures.
-
Communication Errors: If VCDS is unable to communicate with the ECU, check the VCDS interface, OBD-II port, and vehicle wiring. Ensure that the ignition is turned on and the battery has sufficient charge.
-
Incorrect Adaptation Channels: Using the wrong adaptation channels can lead to improper turbocharger function. Always refer to the vehicle service manual or Ross-Tech Wiki for the correct channel information.
By following these step-by-step instructions and troubleshooting tips, you can successfully perform the Audi 3.0 TDI turbo actuator adaptation using VCDS. CARDIAGTECH.NET is here to support you with high-quality diagnostic tools and resources to ensure your vehicle runs smoothly. If you encounter any challenges during the adaptation process, our team of experts is available to provide guidance and assistance.
 QqXWuw9.jpeg
QqXWuw9.jpeg
5. Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Sometimes, standard adaptation procedures may not resolve the issue. In such cases, advanced troubleshooting techniques can help identify and address underlying problems.
5.1 Interpreting VCDS Data Logs
VCDS allows you to log data from various sensors and modules in real-time. Interpreting these data logs can provide valuable insights into the performance of the turbocharger and related components.
- Select Data Blocks: In VCDS, click on the “Measuring Blocks – 08” button. Choose the data blocks related to the turbocharger, such as boost pressure, MAF sensor readings, and actuator position.
- Start Logging: Click the “Log” button to start recording data. Drive the vehicle under different conditions to capture a range of data points.
- Analyze Data: After logging, analyze the data using a spreadsheet program or VCDS’s built-in graphing tool. Look for anomalies, such as sudden spikes, drops, or deviations from expected values.
- Identify Issues: Use the data to identify potential issues. For example, a sudden drop in boost pressure may indicate a vacuum leak or a faulty boost pressure sensor. Irregular MAF sensor readings could point to a problem with the MAF sensor itself.
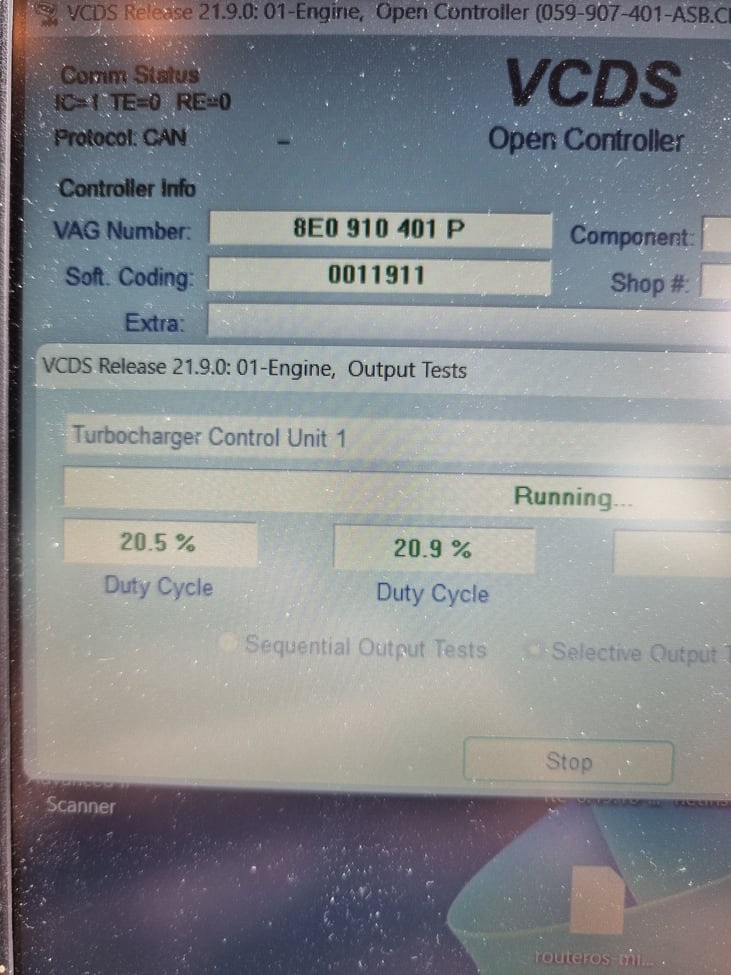
5.2 Checking Actuator Movement with VCDS
VCDS can be used to test the movement of the turbo actuator. This can help determine if the actuator is functioning correctly and responding to commands from the ECU.
- Access Output Tests: In VCDS, navigate to the “Output Tests – 03” function.
- Select Actuator Test: Choose the output test related to the turbo actuator. This test will command the actuator to move between different positions.
- Observe Movement: Watch the actuator arm to see if it moves smoothly and without any binding. Use a mirror or camera if necessary to get a clear view of the actuator.
- Evaluate Response: Evaluate the actuator’s response to the test commands. If the actuator does not move or moves erratically, it may have a mechanical or electrical problem.
5.3 Using a Vacuum Gauge to Test Actuator Function
A vacuum gauge can be used to test the vacuum pressure at the turbo actuator. This can help determine if the actuator is receiving adequate vacuum and if there are any leaks in the vacuum system.
- Connect Vacuum Gauge: Connect a vacuum gauge to the vacuum line that supplies vacuum to the turbo actuator.
- Start Engine: Start the engine and allow it to idle.
- Read Vacuum Pressure: Read the vacuum pressure on the gauge. Compare the reading to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Evaluate Results: If the vacuum pressure is too low, there may be a leak in the vacuum system. Inspect the vacuum lines, connections, and vacuum pump for any issues.
5.4 Inspecting the Turbocharger Vanes
Carbon buildup on the turbocharger vanes can restrict their movement and affect turbocharger performance. Inspecting the vanes can help identify this issue.
- Access Turbocharger: Access the turbocharger by removing the necessary components, such as the intake and exhaust pipes.
- Inspect Vanes: Use a flashlight and mirror to inspect the vanes for carbon buildup. Look for any signs of restriction or damage.
- Clean Vanes: If carbon buildup is present, clean the vanes using a specialized turbocharger cleaner or a mild solvent. Be careful not to damage the vanes during the cleaning process.
- Reassemble Turbocharger: After cleaning the vanes, reassemble the turbocharger and test its performance.
5.5 Checking for Boost Leaks
Boost leaks can reduce turbocharger performance and cause error codes. Checking for boost leaks can help identify and address this issue.
- Pressurize System: Use a boost leak tester to pressurize the intake system. This will force air out of any leaks.
- Listen for Leaks: Listen for hissing sounds that indicate air escaping from the system.
- Inspect Connections: Inspect all connections, hoses, and clamps for leaks. Tighten or replace any faulty components.
- Smoke Test: Perform a smoke test to identify any small leaks that may be difficult to detect by ear.
5.6 Verifying Wiring and Connectors
Faulty wiring and connectors can cause intermittent issues with the turbo actuator. Verifying the wiring and connectors can help identify and address these problems.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, such as fraying, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the wiring between the actuator and the ECU.
- Voltage Test: Verify that the actuator is receiving the correct voltage from the ECU. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for the specified voltage range.
- Clean Connectors: Clean the connectors with a specialized electrical contact cleaner to remove any corrosion or dirt.
- Secure Connections: Ensure that all connections are secure and properly seated.
By employing these advanced troubleshooting techniques, you can effectively diagnose and resolve complex issues with the Audi 3.0 TDI turbo actuator. CARDIAGTECH.NET is dedicated to providing you with the tools and knowledge you need to keep your vehicle running at its best. If you require further assistance, our team of experts is always available to offer guidance and support.
6. Preventive Maintenance Tips
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding turbo actuator problems and ensuring the longevity of your Audi 3.0 TDI engine. Regular inspections, timely servicing, and proper driving habits can significantly reduce the risk of turbocharger issues.
6.1 Regular Inspections of Vacuum Lines
Vacuum lines are essential for the proper functioning of the turbo actuator. Regular inspections can help identify and address potential issues before they lead to major problems.
- Frequency: Inspect the vacuum lines at least every 6 months or during routine maintenance.
- Visual Check: Look for any signs of cracks, splits, or wear on the vacuum lines. Pay close attention to areas near heat sources or moving parts.
- Connection Integrity: Ensure that all connections are secure and properly seated.
- Replacement: Replace any damaged or worn vacuum lines immediately. Use high-quality replacement lines that are designed to withstand the operating conditions of the engine.
6.2 Keeping the Engine Clean
A clean engine runs more efficiently and is less prone to problems. Regular cleaning can help prevent the buildup of dirt, oil, and debris that can damage engine components.
- Engine Bay Cleaning: Clean the engine bay regularly using a mild degreaser and a soft brush. Avoid spraying water directly onto electrical components.
- Air Filter Replacement: Replace the air filter according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. A clean air filter ensures that the engine receives an adequate supply of clean air.
- Oil Changes: Perform regular oil changes using high-quality synthetic oil. Clean oil helps lubricate engine components and prevent the buildup of sludge and deposits.
6.3 Monitoring Engine Performance
Monitoring engine performance can help detect potential issues early on. Pay attention to any changes in engine behavior, such as reduced power, unusual noises, or error codes.
- Boost Pressure Monitoring: Use a boost gauge or VCDS to monitor boost pressure. Ensure that the boost pressure is within the specified range.
- Error Code Scanning: Regularly scan the ECU for error codes using VCDS. Address any codes promptly to prevent further damage.
- Performance Evaluation: Evaluate engine performance during regular driving. Note any changes in acceleration, fuel economy, or overall engine behavior.
6.4 Using Quality Fuel and Additives
Using high-quality fuel and additives can help keep the engine clean and prevent the buildup of deposits.
- Fuel Quality: Use high-quality fuel from reputable sources. Avoid using fuel that may be contaminated or of low quality.
- Fuel Additives: Consider using fuel additives that are designed to clean fuel injectors and prevent the buildup of deposits. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when using fuel additives.
- Oil Additives: Use high-quality oil additives to improve engine lubrication and reduce wear.
6.5 Avoiding Harsh Driving Habits
Harsh driving habits, such as frequent hard acceleration and high-speed driving, can put extra stress on the turbocharger and engine components.
- Smooth Acceleration: Accelerate smoothly and avoid sudden bursts of speed.
- Moderate Speed: Drive at moderate speeds and avoid prolonged high-speed driving.
- Cool-Down Period: Allow the engine to cool down after driving by idling for a few minutes before turning it off. This helps prevent heat buildup in the turbocharger.
6.6 Regular Professional Servicing
Regular professional servicing is essential for maintaining the health of your Audi 3.0 TDI engine. A qualified technician can perform thorough inspections, diagnose potential issues, and perform necessary repairs and maintenance.
- Service Intervals: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended service intervals.
- Qualified Technician: Choose a qualified technician with experience working on Audi vehicles.
- Comprehensive Inspection: Request a comprehensive inspection of the engine, turbocharger, and related components during each service visit.
- Preventive Maintenance: Perform preventive maintenance tasks, such as vacuum line replacement, air filter replacement, and oil changes, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
By following these preventive maintenance tips, you can help avoid turbo actuator problems and ensure the longevity and performance of your Audi 3.0 TDI engine. CARDIAGTECH.NET is committed to providing you with the tools and knowledge you need to keep your vehicle running at its best. Our range of diagnostic tools and expert advice can help you maintain your vehicle and address any issues that may arise.
7. Benefits of Using CARDIAGTECH.NET Tools
Investing in high-quality diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET offers numerous benefits for Audi 3.0 TDI owners and automotive technicians. These tools provide accurate diagnostics, efficient repairs, and enhanced vehicle performance.
7.1 High-Quality VCDS Interfaces
CARDIAGTECH.NET offers genuine VCDS interfaces that provide reliable communication with your vehicle’s ECU. These interfaces are essential for performing accurate diagnostics, adaptations, and coding.
- Reliable Communication: Genuine VCDS interfaces ensure stable and reliable communication with the ECU. This is crucial for performing accurate diagnostics and adaptations.
- Full Functionality: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s VCDS interfaces provide access to all VCDS functions, including diagnostics, adaptations, coding, and data logging.
- Software Updates: Genuine VCDS interfaces receive regular software updates, ensuring compatibility with the latest vehicle models and features.
- Technical Support: CARDIAGTECH.NET provides technical support for its VCDS interfaces, helping you troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
7.2 Accurate Diagnostics
CARDIAGTECH.NET’s diagnostic tools provide accurate and detailed information about your vehicle’s performance. This allows you to identify potential issues early on and address them before they lead to major problems.
- Error Code Reading: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can read error codes from all vehicle modules, providing a comprehensive overview of potential issues.
- Data Logging: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can log data from various sensors and modules in real-time, allowing you to monitor engine performance and identify anomalies.
- Component Testing: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can perform component tests, such as actuator tests and sensor tests, to verify the functionality of individual components.
- Detailed Information: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools provide detailed information about error codes and sensor readings, helping you understand the root cause of the problem.
7.3 Efficient Repairs
CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools help you perform repairs efficiently and effectively. By providing accurate diagnostics and detailed information, these tools can help you identify the problem quickly and perform the necessary repairs.
- Guided Diagnostics: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools provide guided diagnostics, walking you through the troubleshooting process step-by-step.
- Adaptation and Coding: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools allow you to perform adaptations and coding, ensuring that components are properly configured after replacement or repair.
- Component Location: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools provide information about component location, helping you find the components you need to access quickly.
- Wiring Diagrams: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools provide wiring diagrams, helping you troubleshoot electrical issues.
7.4 Cost Savings
Investing in CARDIAGTECH.NET’s diagnostic tools can save you money in the long run. By performing your own diagnostics and repairs, you can avoid costly trips to the mechanic.
- DIY Diagnostics: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools allow you to perform your own diagnostics, saving you money on diagnostic fees.
- Preventive Maintenance: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools help you perform preventive maintenance, preventing costly repairs in the future.
- Informed Decisions: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance and repair.
- Avoid Unnecessary Repairs: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools help you avoid unnecessary repairs by providing accurate diagnostics and detailed information.
7.5 Enhanced Vehicle Performance
CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can help you enhance your vehicle’s performance by ensuring that all components are functioning correctly.
- Optimal Engine Performance: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can help you optimize engine performance by ensuring that the turbocharger, fuel system, and other components are functioning correctly.
- Improved Fuel Economy: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can help you improve fuel economy by ensuring that the engine is running efficiently.
- Reduced Emissions: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can help you reduce emissions by ensuring that the engine is burning fuel cleanly.
- Smooth Operation: CARDIAGTECH.NET’s tools can help you ensure smooth operation by identifying and addressing potential issues before they lead to problems.
Investing in CARDIAGTECH.NET’s diagnostic tools is a smart decision for Audi 3.0 TDI owners and automotive technicians. These tools provide accurate diagnostics, efficient repairs, cost savings, and enhanced vehicle performance. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more about our range of diagnostic tools and how they can benefit you. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
8. Case Studies and Examples
Real-world examples can illustrate the importance of proper turbo actuator adaptation and the benefits of using VCDS.
8.1 Case Study 1: Resolving P3348 Error Code
A customer was experiencing a P3348 error code on their Audi 3.0 TDI, indicating an electrical malfunction in the turbocharger control circuit. The dealership had replaced the turbo actuator, but the issue persisted.
- Diagnosis: Using VCDS, the customer performed a thorough scan of the ECU and identified the P3348 error code. They also logged data from the turbocharger sensors, which revealed inconsistent boost pressure and actuator position.
- Troubleshooting: The customer checked the wiring and connectors for any signs of damage, but found none. They then used VCDS to perform an actuator test, which revealed that the actuator was not moving smoothly.
- Solution: The customer discovered that the new turbo actuator had not been properly adapted to the ECU. They used VCDS to perform the turbo actuator adaptation, following the steps outlined in this article.
- Outcome: After performing the adaptation, the P3348 error code disappeared, and the customer’s Audi 3.0 TDI returned to its normal performance.
8.2 Case Study 2: Improving Turbocharger Performance
Another customer was experiencing sluggish turbocharger performance on their Audi 3.0 TDI. The turbocharger was spooling up slowly, and the engine lacked power during acceleration.
- Diagnosis: Using VCDS, the customer logged data from the turbocharger sensors, which revealed that the turbocharger was not reaching its maximum boost pressure.
- Troubleshooting: The customer checked the vacuum lines and intercooler for any leaks, but found none. They then used VCDS to perform an actuator test, which revealed that the actuator was moving correctly.
- Solution: The customer suspected that the turbocharger vanes were dirty. They used a specialized turbocharger cleaner to clean the vanes, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Outcome: After cleaning the turbocharger vanes, the customer’s Audi 3.0 TDI experienced a significant improvement in turbocharger performance. The turbocharger was spooling up quickly, and the engine had more power during acceleration.
8.3 Case Study 3: Preventing Turbocharger Failure
A customer was proactive about maintaining their Audi 3.0 TDI and wanted to prevent turbocharger failure.
- Preventive Maintenance: The customer regularly inspected the vacuum lines, cleaned the engine bay, and monitored engine performance using VCDS.
- Early Detection: During one of their inspections, the customer noticed that the vacuum lines were starting to crack. They replaced the vacuum lines before they caused any problems.
- Proactive Measures: The customer also used a fuel additive to clean the fuel injectors and prevent the buildup of deposits.
- Outcome: By taking these preventive measures, the customer was able to avoid turbocharger failure and keep their Audi 3.0 TDI running smoothly.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of proper turbo actuator adaptation and the benefits of using VCDS for diagnosing and resolving turbocharger issues. By following the steps outlined in this article and investing in high-quality diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET, you can keep your Audi 3.0 TDI running at its best. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more about our range of diagnostic tools and how they can benefit you. Our address is 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions about Audi 3.0 TDI turbo actuator adaptation using VCDS:
-
What is a turbo actuator and why is it important?
A turbo actuator controls the vanes inside the turbocharger, regulating boost pressure. It’s crucial for engine performance and efficiency.
-
What are the symptoms of a faulty turbo actuator?
Symptoms include reduced engine power, error codes, limp mode, and inconsistent boost pressure.
-
What is VCDS and why is it needed for adaptation?
VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System) is a software used for diagnosing and adapting VW, Audi, Skoda, and SEAT vehicles. It allows you to communicate with the ECU and adjust specific parameters.
-
How do I connect VCDS to my Audi 3.0 TDI?
Connect the VCDS interface to the OBD-II port, turn on the ignition, launch the VCDS software, and test the connection.
-
What are adaptation channels and how do I use them?
Adaptation channels allow you to adjust specific parameters within the ECU. Identify relevant channels, record original values, and understand channel functionality before making changes.
-
How do I perform basic settings using VCDS?
Navigate to the “Basic Settings – 04” function in VCDS, enter the appropriate group number, and start the adaptation process.
-
What should I do if the adaptation is not accepted by VCDS?
Ensure the engine is at the correct temperature, verify there are no other fault codes, and double-check the adaptation values.
-
Can I use a generic OBD-II scanner instead of VCDS?
While a generic OBD-II scanner can read basic error codes, it cannot perform the advanced functions needed for turbo actuator adaptation.
-
How often should I perform turbo actuator adaptation?
Perform turbo actuator adaptation after replacing the turbo actuator or if you experience performance issues related to the turbocharger.
-
Where can I get reliable VCDS interfaces and diagnostic tools?
CARDIAGTECH.NET provides high-quality VCDS interfaces and diagnostic tools. Contact us at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET.
9. Conclusion
The Audi 3.0 TDI turbo actuator adaptation using VCDS is a critical procedure for maintaining optimal engine performance. By understanding the function of the turbo actuator, identifying potential issues, and following the step-by-step adaptation process, you can ensure your Audi 3.0 TDI operates efficiently and delivers the power and responsiveness you expect. Investing in high-quality diagnostic tools from CARDIAGTECH.NET can further enhance your ability to diagnose and resolve turbocharger issues, saving you time and money in the long run. Contact CARDIAGTECH.NET today at +1 (641) 206-8880 or visit our website at CARDIAGTECH.NET to learn more about our range of diagnostic tools and how they can benefit you. Our address is 276 Reock St, City
