Since 1996, if you’ve owned a car, it almost certainly came equipped with an OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) port. This standardized port is a legal requirement for all cars and trucks manufactured since then. But what exactly is it, and how can a Car Obdii Port Diagnostics Scanner help you? Let’s dive into the world of automotive diagnostics and explore the power of this little port.
Understanding the OBD-II Port
The OBD-II system is essentially an onboard computer that diligently monitors various aspects of your vehicle’s performance. It keeps tabs on emissions, fuel efficiency, speed, and a host of other crucial data points. This system is directly linked to your car’s check engine light and other warning lights on your dashboard. When the OBD-II system detects an issue, it illuminates these lights to alert you to a potential problem.
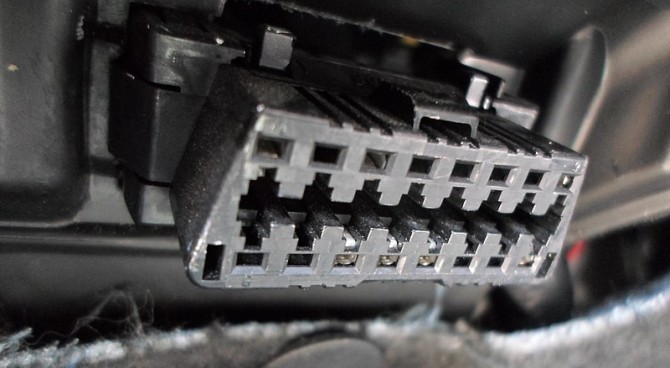
This sophisticated computer communicates through a standardized 16-pin port, typically found beneath the driver’s side dashboard. This port is designed to allow mechanics, and even car owners with the right tools, to access and interpret error codes using a specialized car OBDII port diagnostics scanner.
Image: Close-up view of a standard OBD-II port connector, highlighting its 16-pin configuration, used for automotive diagnostics.
From OBD-I to OBD-II: A Leap in Standardization
Before OBD-I, the landscape of onboard diagnostics was fragmented. Each car manufacturer had its own unique set of standards for OBD systems. This meant mechanics were burdened with the need to purchase expensive, manufacturer-specific scan tools for each different plug type they encountered. OBD-I, introduced in 1987, marked the beginning of standardization in onboard diagnostics. It incorporated sensors to detect and mitigate emissions, but it was plagued with inconsistencies and limitations.
In 1996, the automotive industry took a significant step forward by agreeing on a new, universal standard: OBD-II. Car manufacturers began integrating this more advanced port into all cars and trucks. While the fundamental system remains consistent across vehicles, subtle variations exist in communication protocols, tailored to specific vehicle manufacturers.
These communication variations are categorized into five primary signal protocols:
- SAE J1850 PWM (Pulse Width Modulation): Predominantly used in Ford vehicles.
- SAE J1850 VPW (Variable Pulse Width): Primarily found in General Motors vehicles.
- ISO9141-2: Implemented in all Chrysler vehicles and a range of European and Asian makes.
- ISO14230-4 (KWP2000 – Keyword Protocol 2000): Utilized across various American, European, and Japanese brands, including Honda, Jeep, Land Rover, Subaru, Mazda, and Nissan.
- ISO 15765 CAN (Controller Area Network): Standard on all vehicles manufactured from 2008 onwards.
Regardless of the protocol, pins 4 and 5 are universally designated for ground connections, and pin 16 consistently provides power from the car’s battery.
When the onboard computer detects an anomaly in the engine or any other vehicle system, it triggers the check engine light or other relevant warnings on the instrument panel, prompting the driver to investigate the issue.
How Car OBDII Port Diagnostics Scanners Work
At the heart of OBD-II diagnostics are Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes are generated and stored within the vehicle’s computer system whenever a fault is detected. While the specifics of DTCs can vary between manufacturers, the fundamental structure and interpretation are standardized. The beauty of the OBD-II system lies in its accessibility. Anyone equipped with a car OBDII port diagnostics scanner can connect to the OBD-II port and retrieve these diagnostic trouble codes directly from the computer.
These scanners communicate with your vehicle, accessing the standardized pinout which is structured as follows:
- Pin 1: Manufacturer-discretionary use.
- Pin 2: SAE J1850 PWM and VPW communication.
- Pin 3: Manufacturer-defined use.
- Pin 4: Ground connection.
- Pin 5: Ground connection.
- Pin 6: ISO 15765-4 CAN communication.
- Pin 7: K-Line for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 protocols.
- Pin 10: SAE J1850 PWM communication only.
- Pin 14: ISO 15765-4 CAN communication.
- Pin 15: K-Line for ISO 9141-2 and ISO 14230-4 protocols.
- Pin 16: Power supply from the car battery.
Exploring the Versatility of the OBD-II Port
Traditionally, mechanics utilize professional scan tools connected to the OBD-II port to read DTCs and gain a comprehensive understanding of vehicle faults. Basic, more affordable scanners might only display a numeric code, requiring mechanics to consult manufacturer manuals or online service databases for interpretation.
However, the accessibility of car diagnostics has expanded significantly in recent years. Now, a wide range of advanced tools are available for everyday drivers who prefer to understand their car’s health without immediately relying on a mechanic.
Car OBDII port diagnostics scanners are a prime example. These scanners come in various forms, from wired handheld devices to wireless adapters. Many wireless scanners seamlessly connect to smartphones or laptops, while others feature integrated screens for standalone operation. This variety ensures there’s a scanner to suit every preference and need.
Beyond diagnostics, the OBD-II port also serves other functions. GPS trackers, for instance, often utilize the OBD-II port for a convenient power source, although some can be hardwired into the vehicle’s electrical system. These trackers are valuable for vehicle location and monitoring, especially for families concerned about young drivers or vehicle security.
Mobile OBD-II Scanner Apps: Diagnostics in Your Pocket
Your car continuously monitors its systems, generating a wealth of data accessible through the diagnostic port. This data can be harnessed by mobile OBD-II scanner apps. By pairing a compatible OBD-II adapter with your smartphone, you can transform your mobile device into a powerful diagnostic tool. These apps mirror the functionality of dedicated scanners, allowing you to monitor real-time vehicle parameters like fuel consumption, temperatures, and oil pressure, and of course, scan for and interpret error codes.
This capability extends to virtually any modern car when paired with a suitable OBD-II adapter. Several excellent options are available:
1. Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner: Budget-Friendly Android Diagnostics
Image: The Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner, a compact and affordable tool for basic car diagnostics on Android devices.
For Android users seeking an affordable entry into OBD-II diagnostics, the Veepeak Mini WiFi OBD II Scanner is a strong contender. Compatible with popular Android apps like Torque Pro, Torque Lite, and OBD Car Doctor, this scanner connects via WiFi, enabling you to view sensor data and diagnose error codes when your check engine light illuminates. Notably, even at its budget-friendly price point, it allows users to clear minor error codes, such as those triggered by a loose fuel cap.
2. BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader and Scan Tool: iOS Enhanced Diagnostics
Image: The BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader, a wireless scanner designed to work with iOS devices for comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
The BAFX Products OBDII Code Reader leverages Bluetooth to transform your iOS device into a sophisticated OBD-II tool. Beyond reading diagnostic data, it allows real-time monitoring of parameters not typically displayed on your dashboard, including engine temperature, fuel rate, O2 sensor voltages, and battery voltage. While powerful, it’s important to note that compatible third-party apps for this device may require purchase.
3. Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner: Versatile iOS and Android Compatibility
Image: The Veepeak OBDCheck BLE, a Bluetooth 4.0 OBD-II scanner offering improved performance and compatibility with both Android and iOS systems.
The Veepeak OBDCheck BLE Bluetooth OBD II Scanner offers enhanced performance and broader compatibility for both Android and iOS devices. Utilizing Bluetooth 4.0, this scanner provides a reliable connection for accessing OBD-II data. It supports all OBD-II protocols and integrates seamlessly with various software options like Torque, BimmerCode, BimmerLink, DashCommand, and ScanMaster for Bluetooth-enabled laptops.
4. BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool: Professional-Grade Features for DIYers
Image: The BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool, a more advanced option offering professional-level diagnostic features for iOS and Android users.
For users seeking more advanced diagnostic capabilities, the BlueDriver Pro OBD2 Bluetooth Scan Tool delivers professional-grade features in a user-friendly package. While priced higher than basic wireless adapters, it provides functionality comparable to expensive mechanic’s scan tools. It supports both Android and iOS, enabling reading and clearing of both basic and advanced error codes. Furthermore, it offers live data streaming, graphing, and access to a regularly updated online database for repair reports, providing valuable insights and guidance.
5. OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner: The Ultimate Real-Time Data Powerhouse
Image: The OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner, a premium tool focused on providing extensive real-time vehicle data and advanced features.
For enthusiasts and advanced users prioritizing real-time data access, the OBDLink MX+ OBD2 Bluetooth Scanner stands out. While positioned at a higher price point, its feature set justifies the investment for those demanding comprehensive vehicle insights. It excels in real-time data acquisition, even remotely, and offers enhanced support for a wide range of manufacturers, including Ford, GM, Toyota, Honda, and more. It allows users to display, graph, and log hundreds of real-time parameters and even offers features like door lock/unlock control on compatible vehicles.
Unlock Your Car’s Potential with OBD-II Diagnostics
The OBD-II port, once primarily the domain of mechanics, is now readily accessible to car owners. Utilizing car OBDII port diagnostics scanners and compatible apps empowers you with unprecedented insight into your vehicle’s health, often long before major issues arise.
While some scanners incorporate location tracking features, dedicated GPS trackers offer more specialized solutions for vehicle security and monitoring.
Beyond diagnostics, the OBD-II port opens doors to vehicle customization and performance enhancement. Tuning your car’s ECU via the OBD-II port can unlock increased power and improved fuel economy, demonstrating the vast potential of this often-overlooked port. The possibilities are truly expansive, making understanding and utilizing your car’s OBD-II port a valuable asset for any car owner.