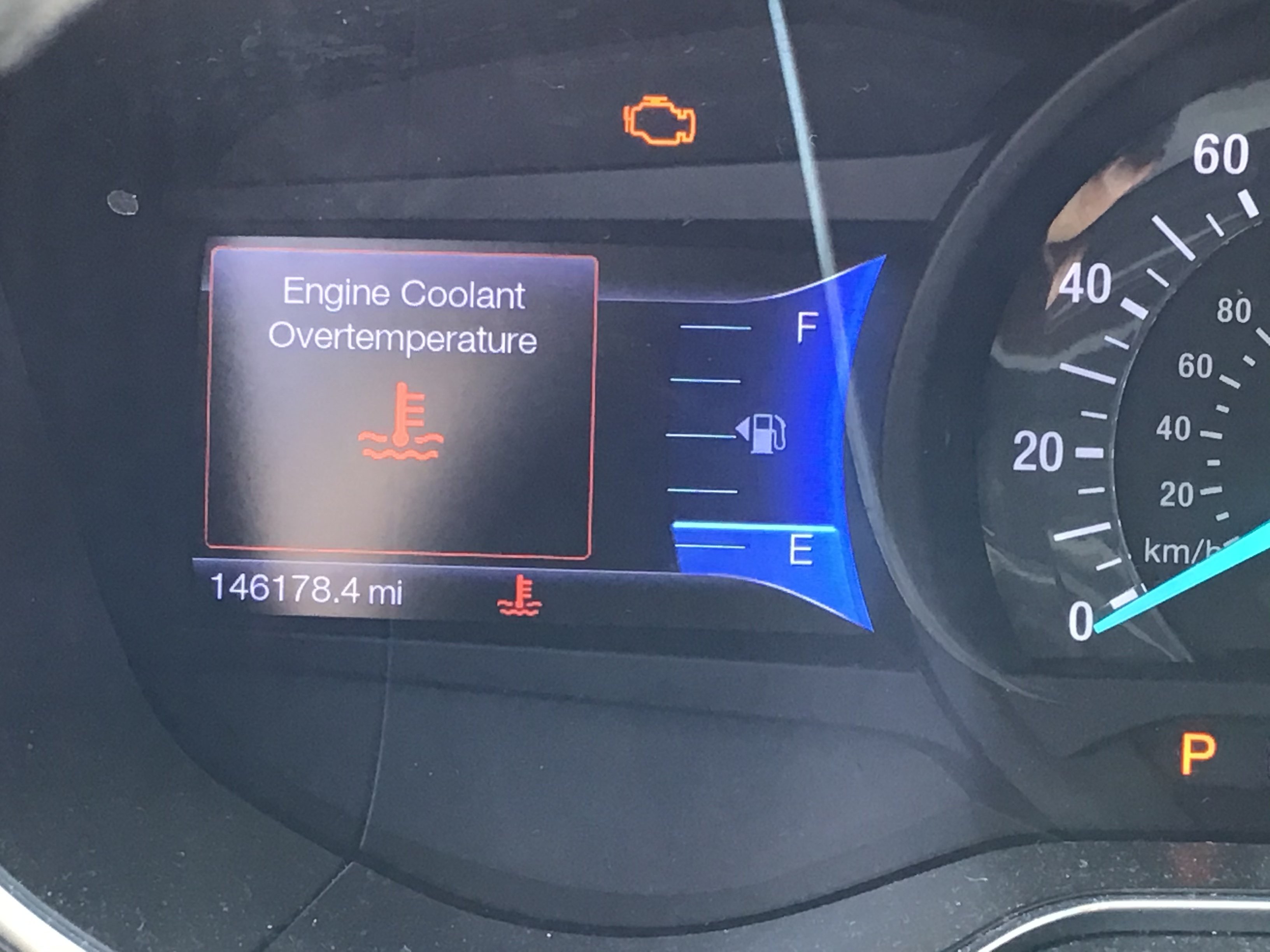
The dreaded “Engine Coolant Overtemp” (ECO) warning light can be a source of anxiety for any driver. This article dives into the specifics of the OBDII error code P1299, often associated with this warning, to help you understand its causes and potential solutions. This code specifically indicates “Cylinder head overtemperature protection active,” signaling a potential overheating issue within your engine.
While a faulty Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) is a common culprit for overheating problems, it’s not always the root cause of a P1299 code. This article will explore a real-world scenario of a 2013 Ford Fusion 1.6L experiencing this issue, highlighting the diagnostic process and emphasizing that even with a functioning CTS, other factors can trigger the P1299 code.
 OBDII Scanner showing error codes
OBDII Scanner showing error codes
Beyond the Coolant Temperature Sensor: Diagnosing P1299
In the case of the 2013 Fusion, the owner experienced an ECO warning and a low coolant level. Despite replacing the CTS and confirming its proper function with a scan tool, the P1299 code persisted alongside other codes: P018C (Fuel Pressure Sensor “B” Circuit Low), P2560 (Engine Coolant Level Low), and U0159 (Lost Communication with Parking Assist Control Module “A”). The owner performed several troubleshooting steps, including checking for 5vDC at the CTS, shorting across pins 1 and 2 on the CTS connector, and testing continuity from the CTS to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
This scenario highlights that a P1299 error can be triggered by components beyond the CTS. Potential causes include:
- Low Coolant Level: Insufficient coolant prevents proper heat dissipation, leading to overheating. The P2560 code in the Fusion confirms this possibility. Addressing any leaks and refilling the coolant to the appropriate level is crucial.
- Faulty Thermostat: A stuck-closed thermostat restricts coolant flow, causing the engine to overheat.
- Cooling Fan Malfunction: A malfunctioning cooling fan reduces airflow across the radiator, hindering heat dissipation.
- Clogged Radiator: A radiator clogged with debris restricts coolant flow and reduces cooling efficiency.
- Water Pump Failure: A failing water pump hinders coolant circulation, leading to localized overheating, especially in the cylinder head.
Addressing the P1299 Error Code: A Holistic Approach
When encountering a P1299 code, it’s crucial to adopt a comprehensive diagnostic approach:
- Check Coolant Level: Ensure the coolant reservoir is filled to the proper level. Address any leaks before proceeding.
- Inspect Thermostat: Test the thermostat’s operation to ensure it opens and closes at the correct temperatures.
- Verify Cooling Fan Operation: Ensure the cooling fan(s) are functioning correctly and engaging when necessary.
- Examine Radiator: Inspect the radiator for any signs of clogging or damage.
- Test Water Pump: Check the water pump for proper operation and coolant circulation.
Diagnosing a P1299 error requires a systematic approach, moving beyond the CTS to investigate other potential culprits within the cooling system. While the CTS plays a critical role, addressing other components is essential to resolve the underlying issue and prevent further engine damage.
Conclusion
The P1299 error code signifies a serious overheating issue that requires immediate attention. While the CTS is a common suspect, a comprehensive diagnostic approach is crucial to identify the root cause. By systematically checking the coolant level, thermostat, cooling fan, radiator, and water pump, you can pinpoint the problem and take the necessary steps to prevent further engine damage. Remember to consult your vehicle’s specific repair manual for detailed diagnostic procedures and wiring diagrams.