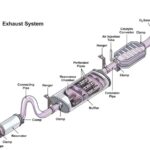
OBDII: On-Board Diagnostics for Emissions Control
The Clean Air Act mandates On-Board Diagnostics II (OBDII) systems in all cars, vans, and light trucks manufactured since 1996. OBDII utilizes a standardized digital communication protocol allowing external devices to access vehicle diagnostic information. This system continuously monitors engine performance and emissions control components, detecting malfunctions before drivers are aware of any issues. OBDII testing involves connecting a scan tool to the vehicle’s Data Link Connector (DLC), typically located under the dashboard. The scan tool retrieves diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and other data from the vehicle’s computer, providing insights into the health of the emissions system. This data helps technicians diagnose and repair emission-related problems efficiently, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Two-Speed Idle Test: Basic Emissions Measurement
The two-speed idle test, part of basic emissions inspection programs, assesses tailpipe emissions at idle and under moderate acceleration. The process involves a four-gas analyzer and a probe inserted into the tailpipe. The vehicle idles for 30 seconds, accelerates to 2500 RPM for another 30 seconds, and returns to idle for a final 30 seconds. During this process, the analyzer measures concentrations of hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) in the exhaust, indicating combustion efficiency and potential emissions issues. This test is primarily used in areas with moderate ozone non-attainment levels.
Acceleration Simulation Mode (ASM) Testing: Simulating Real-World Driving
Acceleration Simulation Mode (ASM) testing, also known as loaded-mode testing, provides a more comprehensive evaluation of vehicle emissions under simulated real-world driving conditions. This test employs a five-gas analyzer, a dynamometer (a treadmill-like device for the vehicle’s wheels), and a tailpipe probe. The dynamometer simulates driving speeds from 0 to 30 mph, including acceleration and deceleration, while the analyzer measures HC, CO, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions. ASM testing is mandatory in areas with high urban populations and significant ozone pollution. This more rigorous testing method ensures accurate assessment of emissions under load, reflecting actual driving scenarios more closely than the idle test.
Gas Cap Pressure Testing: Preventing Evaporative Emissions
Gas cap pressure testing detects leaks in the vehicle’s fuel system that can lead to evaporative emissions. A specialized adapter is attached to the gas cap and pressurized. The test measures the leak flow rate, determining if the gas cap seal effectively prevents gasoline vapors from escaping the fuel tank. A computerized system controls the target pressure and selects the appropriate test procedure for each vehicle. This simple yet crucial test helps minimize the release of harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere.