Modern vehicles rely heavily on a complex network of sensors to function optimally. One crucial component is the oxygen sensor, and when it malfunctions, it can trigger the P0154 error code. This comprehensive guide delves into the Eobd/obdii Error P0154, explaining its meaning, symptoms, common causes, diagnostic steps, and potential solutions.
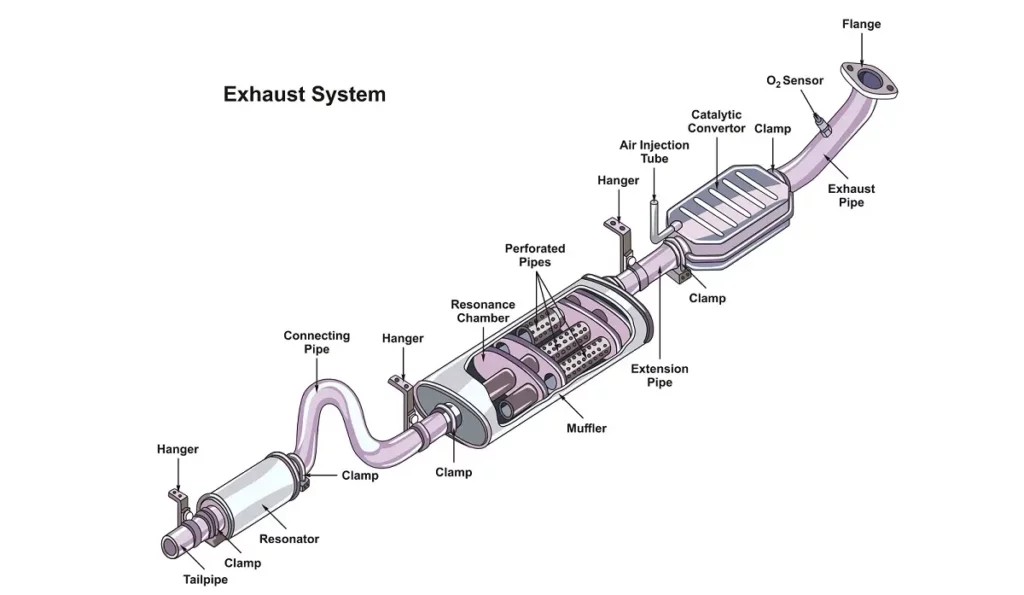 Exhaust System Diagram highlighting the upstream O2 sensor
Exhaust System Diagram highlighting the upstream O2 sensor
What Does the P0154 Code Mean?
The P0154 diagnostic trouble code (DTC) signifies “O2 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 1).” This indicates that the engine control unit (ECU) isn’t receiving a signal from the upstream oxygen sensor on Bank 2 of the engine. “Bank 2” refers to the side of the engine opposite the cylinder designated as number one. “Sensor 1” denotes the upstream oxygen sensor, positioned before the catalytic converter. This sensor plays a vital role in monitoring the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, enabling the ECU to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and emissions control.
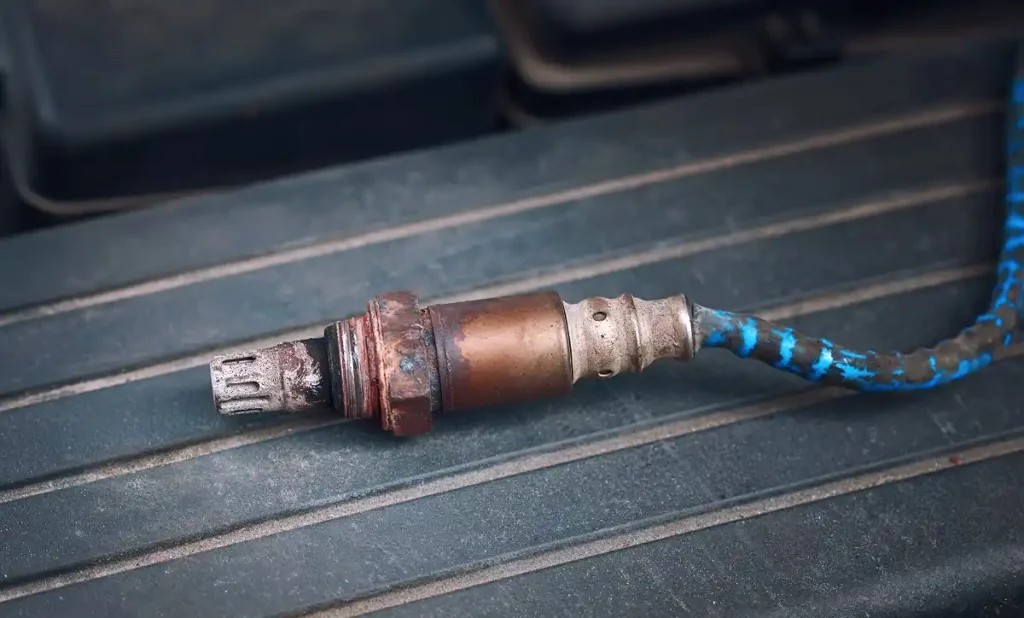 Failed O2 sensor causing P0154
Failed O2 sensor causing P0154
Recognizing the Symptoms of a P0154 Code
A P0154 error often manifests through several noticeable symptoms:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The most obvious sign is the activation of the check engine light on your dashboard.
- Rough Engine Idle: The engine might run unevenly or roughly at idle speeds due to the ECU’s inability to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to a richer air-fuel mixture, resulting in higher fuel consumption and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Black Exhaust Smoke: Excessive fuel in the exhaust can cause black smoke to emanate from the tailpipe, indicating incomplete combustion. This unburnt fuel can also damage the catalytic converter.
Common Causes of the P0154 Error Code
Several factors can contribute to a P0154 code:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: The most frequent cause is a defective oxygen sensor due to age, wear, or contamination from engine oil or coolant.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring in the oxygen sensor circuit can disrupt signal transmission. Heat from the exhaust system can degrade wiring insulation over time.
- Blown Fuse: A blown fuse in the oxygen sensor circuit can interrupt power supply to the sensor.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system, particularly upstream of the oxygen sensor, can introduce outside air and skew the sensor readings. This is less common but possible.
Diagnosing and Fixing the P0154 Code
Diagnosing the P0154 code involves a systematic approach:
- Retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): Use an OBDII scanner to confirm the P0154 code and check for any other related codes.
- Inspect the Fuse: Check the fuse associated with the oxygen sensor circuit for any signs of damage or a blown fuse. Replace if necessary.
- Examine Wiring and Connector: Visually inspect the wiring harness and connector for damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Use a multimeter to test for continuity and voltage.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Listen for unusual noises from the exhaust system and inspect for leaks, especially around joints and connections.
- Test the Oxygen Sensor: If the wiring and fuse are intact, test the oxygen sensor itself using a multimeter following manufacturer specifications.
Can I Drive with a P0154 Code?
While driving short distances with a P0154 code might be possible, it’s not recommended. Prolonged driving with this error can lead to reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and potential damage to the catalytic converter.
Will the P0154 Code Clear Itself?
The P0154 code usually won’t clear itself. After addressing the underlying issue, you’ll need to clear the code using an OBDII scanner. The check engine light will remain off if the problem is resolved.
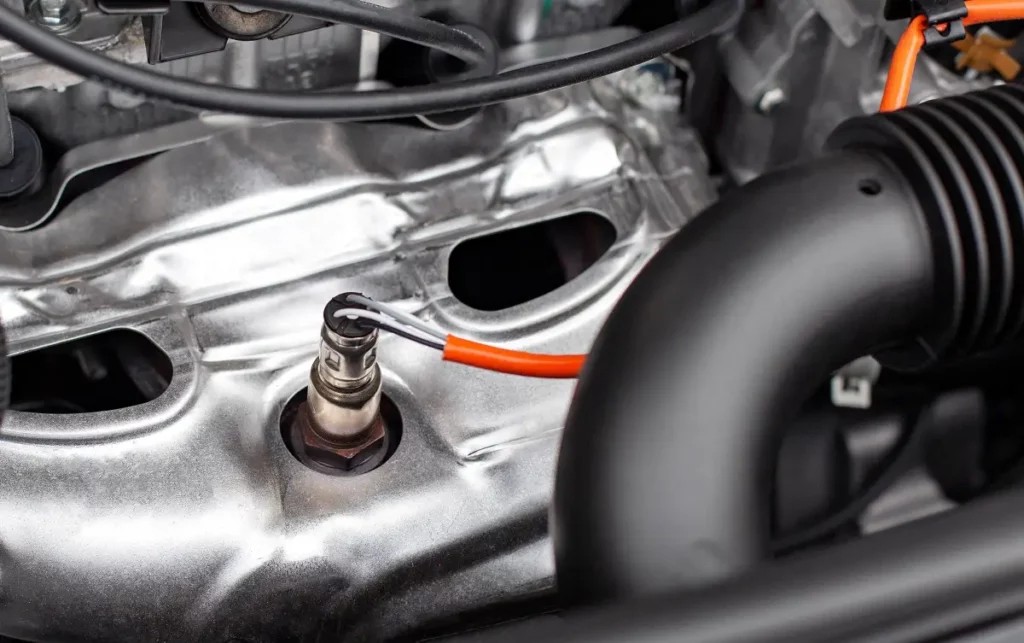 P0154 caused by O2 sensor
P0154 caused by O2 sensor
Addressing the P0154 error promptly ensures optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. If you’re unsure about any diagnostic or repair procedures, consult a qualified automotive technician.
