For automotive professionals and fleet managers, understanding vehicle health is paramount. In today’s vehicles, On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) systems are crucial for pinpointing issues and ensuring optimal performance. If you’re navigating the complexities of vehicle maintenance, especially within a fleet setting, grasping “Can Obdii Car Scanner Tool Codes” is essential. This guide will delve into OBD-II codes, explain how car scanner tools decipher them, and outline why this knowledge is indispensable for efficient vehicle management.
Understanding OBD-II Codes: The Language of Your Vehicle
Onboard Diagnostics (OBD-II) codes are essentially your vehicle’s way of communicating. They are alphanumeric codes generated by your car’s computer system when it detects a problem. Think of them as error messages from various parts of your vehicle, from the engine and transmission to the emissions system. These codes are designed to alert you to irregularities, ranging from minor glitches to more serious malfunctions that could impact vehicle performance and safety.
When a component, like an engine sensor or part of the exhaust system, operates outside of its expected parameters, the vehicle’s computer logs an OBD-II code. The appearance of a “Check Engine” light on your dashboard is often the first sign that an OBD-II code has been triggered, indicating that something within the engine or related systems isn’t working as it should.
To access these codes, you need an OBD-II car scanner tool. This device connects to your vehicle’s OBD-II port, typically found under the dashboard. Once connected, the scanner tool reads and displays the numerical trouble codes, providing you with a starting point for diagnosing the issue. These codes are not just random numbers and letters; they are a structured system designed to guide you or a technician towards the root of the problem, making troubleshooting and repair decisions more efficient. For fleet operations, understanding and utilizing OBD-II codes is a vital aspect of proactive vehicle maintenance and management.
Types of OBD-II Codes: Categorizing Vehicle Issues with Your Car Scanner Tool
When your OBD-II car scanner tool reveals a code from one of your fleet vehicles, the first step in effective diagnosis is to identify the code type. OBD-II codes are categorized into four main types, each relating to a different area of the vehicle. Knowing these categories helps narrow down the potential problem and streamline the diagnostic process using your scanner tool.
Powertrain Codes (P-Codes): Engine and Transmission Diagnostics with Scanner Tools
Powertrain codes, often starting with the letter “P”, are the most common type and relate to issues within the engine, transmission, and associated drivetrain components. These codes are crucial for maintaining vehicle performance and efficiency. For instance, a common powertrain code is P0101, which signals a problem with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. Using an OBDII car scanner tool to identify this P-code is the first step in diagnosing issues like reduced fuel economy or engine performance problems. The MAF sensor is critical for measuring the air intake, allowing the engine’s computer to calculate the optimal fuel-air mixture. A faulty MAF sensor, indicated by a P-code read by your scanner tool, can lead to a cascade of performance issues.
Body Codes (B-Codes): Scanner Tools for Body System Issues
Body codes, starting with “B”, indicate problems within the vehicle’s body systems. These systems include components like airbags, lighting, power windows, and climate control. For example, a B0020 code, detectable with an OBDII car scanner tool, points to a malfunction in the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. This is a safety-critical issue, as a malfunctioning airbag system could fail to deploy in an accident. Body codes highlight issues that, while not always directly affecting driving performance, are vital for safety and occupant comfort, and are easily identified using a scan tool.
Chassis Codes (C-Codes): Suspension, Steering, and Braking Diagnostics with Scanner Tools
Chassis codes, beginning with “C”, relate to the vehicle’s chassis systems, which include suspension, steering, and braking. These codes are particularly important for vehicle handling and safety. A C1234 code, for example, which a car scanner tool can identify, indicates a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor. A faulty wheel speed sensor can impact the vehicle’s stability control, anti-lock braking system (ABS), and traction control, making driving hazardous, especially in adverse conditions. Chassis codes diagnosed with scanner tools often point to issues that directly affect the vehicle’s safe operation.
Network Communication Codes (U-Codes): Diagnosing Communication Issues with Scanner Tools
Network communication codes, starting with “U”, indicate problems within the vehicle’s communication network. Modern vehicles rely on complex networks to allow various modules and sensors to communicate with each other. A U0100 code, detectable by a car scanner tool, often signifies a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM). This type of issue can stem from various sources, including wiring problems or module failures, and can lead to a range of symptoms, such as reduced engine power, poor acceleration, or even engine stalling. U-codes, identified using scanner tools, are crucial for diagnosing complex electronic issues in modern vehicles.
Decoding OBD-II Codes: How to Read Codes with a Car Scanner Tool
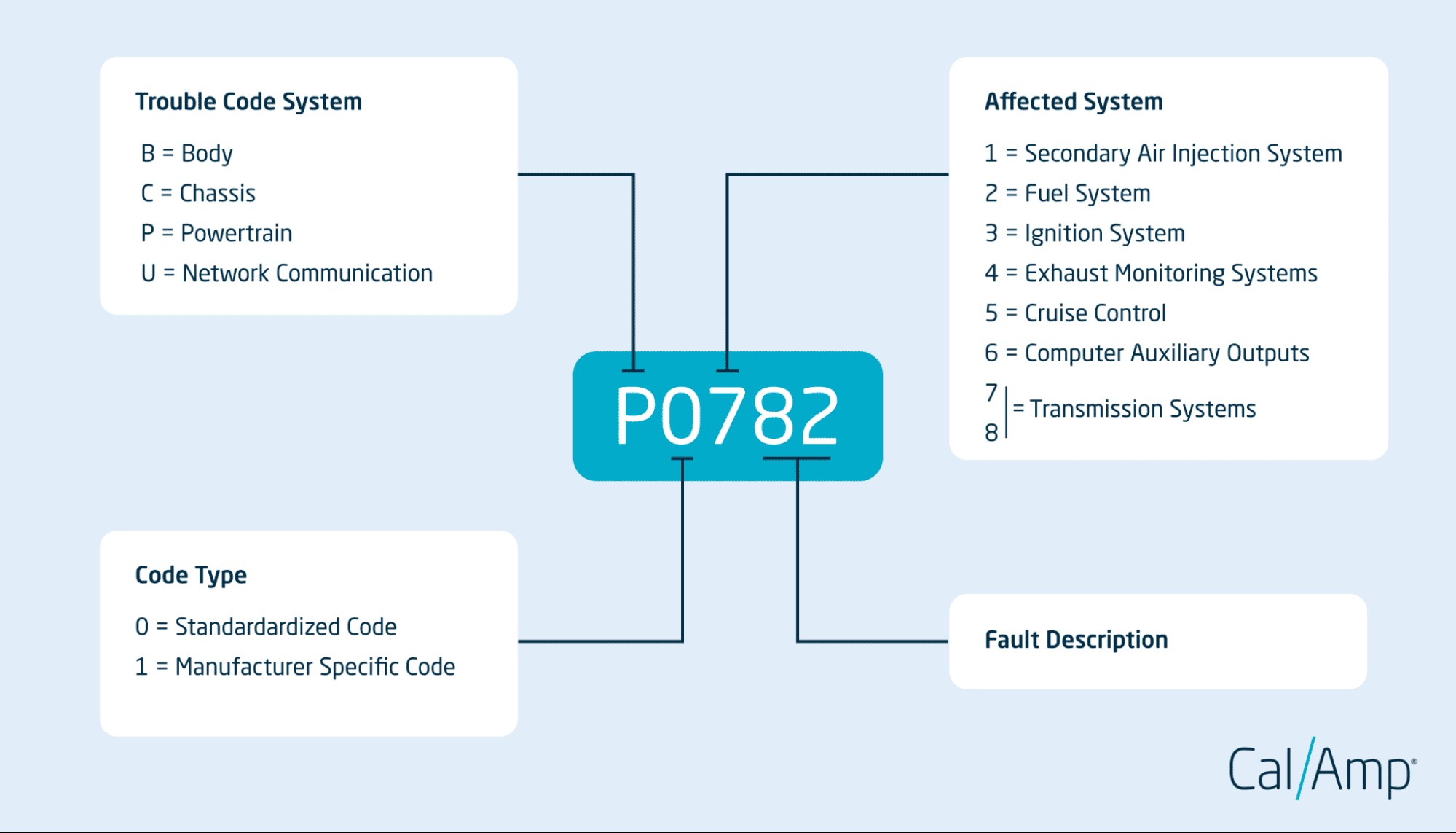
OBD-II codes are structured to provide detailed information about the problem. Each code is five characters long, consisting of a letter followed by four digits. Understanding this structure is key to effectively using a car scanner tool and interpreting the results.
 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Each character position within the code reveals specific details, including the system affected, the type of code, and the specific fault. Using a car scanner tool effectively involves not just reading the code but also understanding what each component of the code signifies.
Trouble Code System: The First Letter – Identifying the Area of Concern with Your Scanner Tool
The first letter of an OBD-II code indicates the primary system affected. As mentioned earlier:
- P – Powertrain (Engine, Transmission)
- B – Body (Airbags, Lighting, Comfort Systems)
- C – Chassis (Brakes, Suspension, Steering)
- U – Network Communication (Vehicle Communication Systems)
When your car scanner tool displays a code, the initial letter immediately tells you the general area of the vehicle where the problem lies.
Code Type: The Second Character – Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific Codes Read by Scanner Tools
The second character in the OBD-II code is a digit that indicates whether the code is standardized or manufacturer-specific:
- 0 – Standardized (Generic) Code: These codes are universal across all makes and models. For example, P0420 (Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold) is a standardized code that any OBDII car scanner tool will recognize across different vehicle brands.
- 1 – Manufacturer-Specific Code: These codes are defined by the vehicle manufacturer and provide more detailed information specific to that brand. For instance, P1101 might be a manufacturer-specific code for a particular issue within the intake air system of a specific vehicle make, as read by a compatible scanner tool.
Affected System: The Third Character – Pinpointing Sub-Systems with Scanner Tools
The third character, a digit, specifies the sub-system within the broader system identified by the first letter. While the exact meaning can vary slightly, common categories include:
- 1 – Fuel and Air Metering
- 2 – Fuel and Air Metering (Injector Circuit)
- 3 – Ignition System or Misfire
- 4 – Auxiliary Emission Controls
- 5 – Idle Control System and Auxiliary Inputs
- 6 – Computer and Output Circuit
- 7, 8 – Transmission
This digit, when viewed on your car scanner tool, helps to further narrow down the problem area within the system identified by the first letter.
Specific Code: The Last Two Characters – Detailed Problem Description from Scanner Tools
The last two characters of the OBD-II code are digits that provide a highly specific description of the fault. For example, in the code P0420, “20” specifies the “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1).” These last two digits are crucial for pinpointing the exact component or circuit that is malfunctioning, giving you precise guidance after using your OBDII car scanner tool.
Clearing OBD-II Codes: Using Your Car Scanner Tool Responsibly
While OBD-II car scanner tools can clear codes, it’s generally not recommended to clear codes without first addressing the underlying issue. However, there are situations where clearing codes might be necessary, such as after completing a repair or for diagnostic purposes. Here are methods for clearing codes, emphasizing responsible use of your scanner tool.
Using an OBD-II Scanner Tool to Clear Codes
OBD-II scanners are designed not only to read codes but also to clear them. After diagnosing and repairing the issue indicated by a code, you can use your scanner tool to clear the code and turn off the “Check Engine” light. This is beneficial for verifying that the repair was successful and for resetting the system. However, simply clearing the code without fixing the problem is not a solution. If the underlying issue persists, the code and the “Check Engine” light will likely reappear. Therefore, using a scanner tool to clear codes should always follow proper diagnosis and repair.
Drive Cycle: Allowing Codes to Clear Naturally (Sometimes)
In some cases, after a repair, certain less severe OBD-II codes might clear on their own after one or more successful “drive cycles.” A drive cycle is a specific set of driving conditions that allows the vehicle’s computer to re-evaluate the system. If the problem is resolved, the computer may automatically clear the code. However, this method is not reliable for all codes and should not be relied upon as a primary method for clearing codes, especially for more serious issues. Using a car scanner tool for clearing provides a more immediate and reliable method.
Seeking Professional Mechanic Assistance for Code Clearing and Diagnosis
If you are unsure about the meaning of an OBD-II code, how to properly diagnose the issue, or how to clear codes effectively, it’s always best to consult a professional mechanic. Mechanics have advanced diagnostic tools and expertise to accurately pinpoint the root cause of OBD-II codes and perform necessary repairs. They can also correctly clear codes after repairs and ensure that the vehicle is functioning correctly. While car scanner tools are valuable for initial diagnostics, professional expertise is crucial for complex issues and ensuring long-term vehicle health.
Preventing OBD-II Codes: Proactive Vehicle Maintenance
Preventing OBD-II codes is far more cost-effective than dealing with repairs after codes appear. Proactive vehicle maintenance is the key to minimizing OBD-II code occurrences and keeping your fleet vehicles running smoothly.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance: The First Line of Defense Against OBD-II Codes
Regular maintenance is crucial for preventing OBD-II codes. Routine inspections, fluid changes, filter replacements, and timely repairs of minor issues can significantly reduce the likelihood of triggering OBD-II codes. Addressing small problems before they escalate prevents strain on vehicle systems and ensures efficient operation.
- Essential Maintenance Tasks: Oil changes, air filter and fuel filter replacements, spark plug inspections and replacements, brake system checks, tire rotations, and regular inspections of hoses and belts are all vital.
- Maintenance Schedule Adherence: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, typically outlined in the vehicle’s owner’s manual. This schedule considers mileage and time intervals for specific maintenance tasks.
- Professional Servicing: Regular servicing by qualified mechanics ensures thorough inspections and early detection of potential issues, preventing problems that could trigger OBD-II codes.
Using Quality Fuel and Fluids: Protecting Vehicle Systems and Preventing Codes
Using high-quality fuel and fluids is another critical preventive measure. Low-quality fluids can lead to inadequate lubrication, increased wear and tear, and subsequent engine or transmission problems, often triggering OBD-II codes. Inferior fuel can cause incomplete combustion, leading to reduced engine efficiency and emissions-related codes.
- Fuel Quality: Use fuel from reputable gas stations and adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended octane rating.
- Fluid Quality: Use manufacturer-recommended fluids, including engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and brake fluid. These are formulated to meet the specific needs of your vehicle’s systems.
- Regular Fluid Checks: Periodically check fluid levels, especially engine oil and coolant, and top them up as needed. Regular checks help ensure systems are properly lubricated and cooled, minimizing the risk of component stress and failure that could lead to OBD-II codes.
Managing OBD-II Codes for Your Fleet: Efficiency and Centralization
For fleet managers, efficiently handling OBD-II codes across multiple vehicles is crucial. Centralizing code tracking and implementing proactive monitoring can save time, reduce downtime, and streamline maintenance operations.
Centralized OBD-II Code Tracking for Fleets
Centralizing OBD-II code tracking involves aggregating diagnostic data from all fleet vehicles into a single management system. This approach simplifies data access and analysis. Advanced fleet management systems, like CalAmp iOn, enhance this by providing real-time alerts for OBD-II code occurrences, tracking vehicle performance metrics, and scheduling maintenance proactively.
A centralized system offers real-time visibility, enabling fleet managers to stay informed about ongoing issues without manual checks. It also facilitates historical data analysis, helping identify trends, recurring issues with specific vehicles or systems, and optimize preventative maintenance schedules.
Ongoing Fleet Monitoring with Telematics Systems
Implementing ongoing fleet monitoring through telematics systems provides real-time data collection from vehicles, including location, performance data, and OBD-II code alerts. Telematics systems enable immediate detection of OBD-II codes as they occur, facilitating rapid response and minimizing vehicle downtime.
Proactive monitoring helps reduce costs by preventing major breakdowns, lowering repair expenses, and optimizing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency through early issue detection and resolution.
Prioritizing Repairs Based on OBD-II Code Severity
Fleet managers should prioritize repairs based on the severity of the OBD-II codes. Categorizing codes by their potential impact on vehicle operation and safety ensures efficient allocation of maintenance resources.
High-severity codes, indicating critical issues that could lead to breakdowns or safety risks, should be addressed immediately to maintain fleet operational continuity. Lower severity codes can be scheduled for repair during routine maintenance windows, optimizing workflow and minimizing disruptions.
In Summary: Leveraging OBDII Car Scanner Tool Codes for Vehicle Health
OBD-II codes are invaluable messages from your vehicles, signaling a range of potential issues. Understanding “can OBDII car scanner tool codes” and how to interpret them using a car scanner tool is essential for effective vehicle maintenance, whether you manage a personal vehicle or a large fleet. From identifying minor sensor glitches to diagnosing major engine problems, OBD-II codes provide the diagnostic starting point.
While basic OBD-II car scanner tools are effective for reading codes and performing initial diagnoses, comprehensive fleet management solutions like CalAmp iOn offer enhanced capabilities. These systems not only read codes but also provide real-time vehicle performance insights, location tracking, and proactive maintenance alerts, offering a holistic approach to fleet vehicle health management.
Request a demo today to learn how the CalAmp iOn can elevate your fleet management strategy, ensuring peak performance and minimizing downtime.