OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) codes are a valuable tool for understanding and resolving issues with your 2006 Ford Expedition. When your Expedition encounters a problem, the onboard computer generates a specific code that corresponds to the malfunction. These codes can then be read using an OBDII scanner, providing crucial information for diagnosis and repair. This article will guide you through understanding OBDII codes on your 2006 Ford Expedition and offer troubleshooting steps.
Understanding OBDII Codes on Your 2006 Ford Expedition
OBDII codes are standardized across most vehicles manufactured after 1996, including your 2006 Ford Expedition. Each code consists of a letter and four numbers. The letter indicates the system where the fault originates:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, emissions)
- B: Body (airbags, power seats, etc.)
- C: Chassis (ABS, steering, etc.)
- U: Network communication
The four numbers provide more specific information about the nature of the problem. For instance, a code like P0300 indicates a random misfire, while P0420 suggests a problem with the catalytic converter.
Common 2006 Ford Expedition OBDII Codes
Some common OBDII codes encountered by 2006 Ford Expedition owners include:
- P0171 and P0174: Lean fuel mixture (Bank 1 and Bank 2 respectively)
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
- P0420 and P0430: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1 and Bank 2 respectively)
- P0442: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (small leak)
- P0700: Transmission Control System (TCS) Malfunction
Troubleshooting OBDII Codes
If your OBDII scanner displays “Error” or fails to communicate with your Expedition’s computer, try these troubleshooting steps:
-
Check the Fuse: The OBDII port and cigarette lighter often share a fuse. Even if the lighter works, replace the fuse with a new one of the correct amperage. A visually good fuse can still be faulty.
-
Verify Power to the OBDII Port: Use a test light or multimeter to confirm power at the OBDII port’s pins.
-
Inspect the Wiring: Examine the wiring leading to the OBDII port for damage, loose connections, or corrosion.
-
CAN Bus Compatibility: The 2006 Ford Expedition uses CAN bus communication for OBDII. Ensure your scanner supports CAN bus protocols (ISO 15765-4 and SAE-J2284). Older scanners may only support ISO 9141-2, ISO 14230-4, and SAE J1850 PWM, which are not fully implemented on the 2006 Expedition’s PCM.
-
Disconnect the Battery: Disconnecting the battery for a few minutes can sometimes reset the vehicle’s computer and resolve communication issues.
-
Consult a Professional: If the problem persists, consult a qualified mechanic with a professional-grade scan tool capable of diagnosing CAN bus systems.
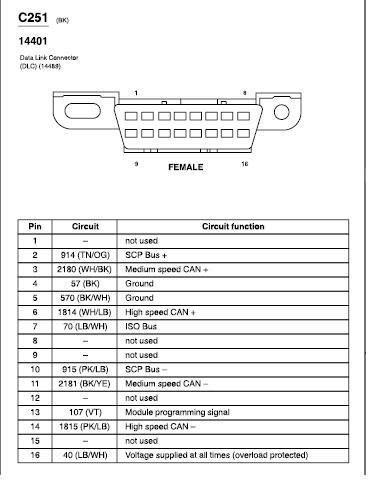 expeditiondlcpinout.jpg
expeditiondlcpinout.jpg
Using an OBDII Scanner
Once communication is established, use the scanner to retrieve the trouble codes. Write down all codes displayed. Look up the code definitions online or in a repair manual specific to the 2006 Ford Expedition. This will give you a starting point for diagnosis. Remember, a code indicates a symptom, not necessarily the root cause. Further diagnosis may be needed.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing OBDII codes is crucial for maintaining your 2006 Ford Expedition. Using a compatible OBDII scanner and following these troubleshooting steps can help you identify and resolve issues, saving you time and money on repairs. If you are unsure about any part of the diagnostic process, consult a qualified mechanic for assistance.